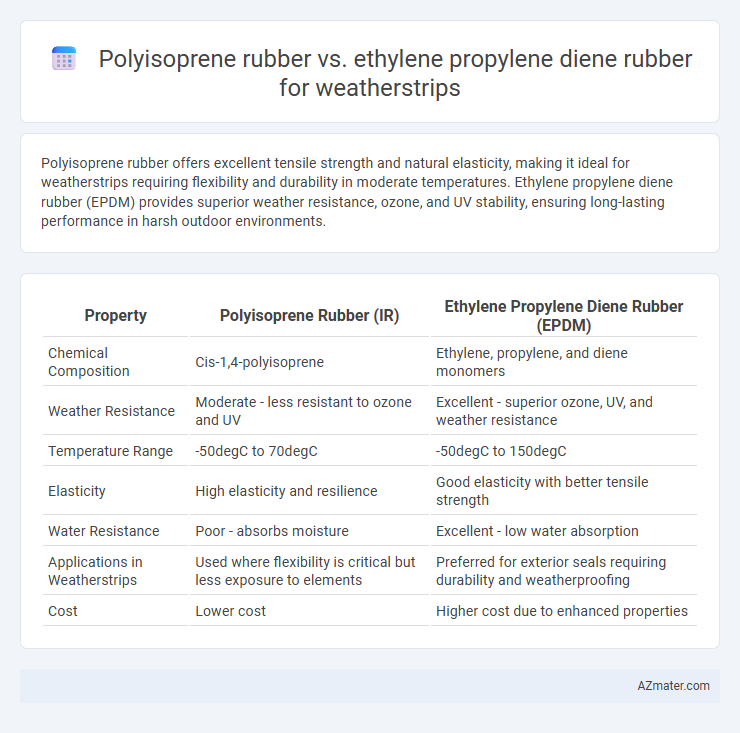
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent tensile strength and natural elasticity, making it ideal for weatherstrips requiring flexibility and durability in moderate temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior weather resistance, ozone, and UV stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Cis-1,4-polyisoprene | Ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate - less resistant to ozone and UV | Excellent - superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Good elasticity with better tensile strength |
| Water Resistance | Poor - absorbs moisture | Excellent - low water absorption |
| Applications in Weatherstrips | Used where flexibility is critical but less exposure to elements | Preferred for exterior seals requiring durability and weatherproofing |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Polyisoprene and EPDM Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber, a synthetic variant of natural rubber, offers excellent elasticity, resilience, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications requiring flexibility and durability. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in weatherstrip use due to its superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, heat, and aging, providing long-term performance in outdoor environments. EPDM's chemical structure ensures exceptional water and steam resistance, while polyisoprene's natural-like properties favor compression set resistance and tensile strength for dynamic sealing needs.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyisoprene rubber features a natural cis-1,4-polyisoprene structure with repeating isoprene units, resulting in high elasticity and tensile strength ideal for weatherstrip flexibility. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) possesses a saturated ethylene-propylene backbone with a small amount of diene comonomer, enhancing its resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering. The chemical saturation in EPDM's backbone provides superior chemical and environmental stability compared to the unsaturated polyisoprene structure, making EPDM more durable for extended outdoor exposure.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent elasticity, making it suitable for weatherstrips requiring flexibility and durability under dynamic stress. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures while maintaining moderate tensile strength and elongation properties. The mechanical advantage of EPDM in weatherstrips lies in its long-term weatherability and aging resistance, whereas polyisoprene provides better resilience and tear resistance in less harsh environmental conditions.
Weather Resistance Capabilities
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits moderate weather resistance, primarily suited for applications with limited exposure to harsh environmental elements, but it tends to degrade under prolonged UV radiation and ozone exposure. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior weather resistance, demonstrating excellent durability against UV rays, ozone, oxidation, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for weatherstrip applications in outdoor and automotive contexts. The enhanced chemical stability and elasticity of EPDM ensure prolonged service life and reliable sealing performance in diverse weather conditions.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent resilience and flexibility at low temperatures, maintaining performance down to -50degC, but degrades faster above 100degC. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in withstanding both extreme cold (-60degC) and high heat up to 150degC, making it ideal for weatherstripping applications requiring durability under varied thermal conditions. EPDM's superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance further enhances its effectiveness in outdoor environments compared to polyisoprene.
Ozone and UV Stability
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits moderate ozone resistance but degrades more rapidly under UV exposure, making it less suitable for prolonged outdoor weatherstrip applications. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers superior ozone and UV stability due to its saturated polymer backbone and protective diene monomer, enhancing durability in harsh weather conditions. EPDM's chemical structure allows it to maintain elasticity and prevent cracking, providing longer-lasting weatherstrip performance in UV-intensive environments.
Cost and Production Considerations
Polyisoprene rubber generally offers lower raw material costs compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it cost-effective for large-scale Weatherstrip production. EPDM rubber, while more expensive, provides superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Production-wise, polyisoprene requires precise control during vulcanization due to its natural polymer structure, whereas EPDM allows more flexible processing parameters, enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
Application Suitability for Weatherstripping
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for weatherstripping applications requiring good tactile softness and compression set resistance. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, making it the preferred choice for outdoor and automotive weatherstripping. For applications demanding long-term durability in harsh environments, EPDM outperforms polyisoprene in maintaining sealing integrity and elasticity.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyisoprene rubber, a natural polymer, offers better biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is synthetic and derived from petrochemicals. EPDM, widely used in weatherstripping for its excellent weather resistance, poses challenges in recycling due to its cross-linked structure and lengthy degradation process. Sustainable weatherstrip solutions prioritize natural polymers like polyisoprene for reduced ecological footprint and enhanced recyclability.
Final Recommendations for Weatherstrip Selection
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for weatherstrips requiring flexibility and comfort. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) excels in weatherability, UV resistance, and ozone durability, ideal for outdoor and automotive weatherstripping exposed to harsh environments. For weatherstrip selection, EPDM is generally recommended for long-term exposure to sunlight and extreme weather, while polyisoprene is preferred for applications prioritizing softness and resilience.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weatherstrip
 azmater.com
azmater.com