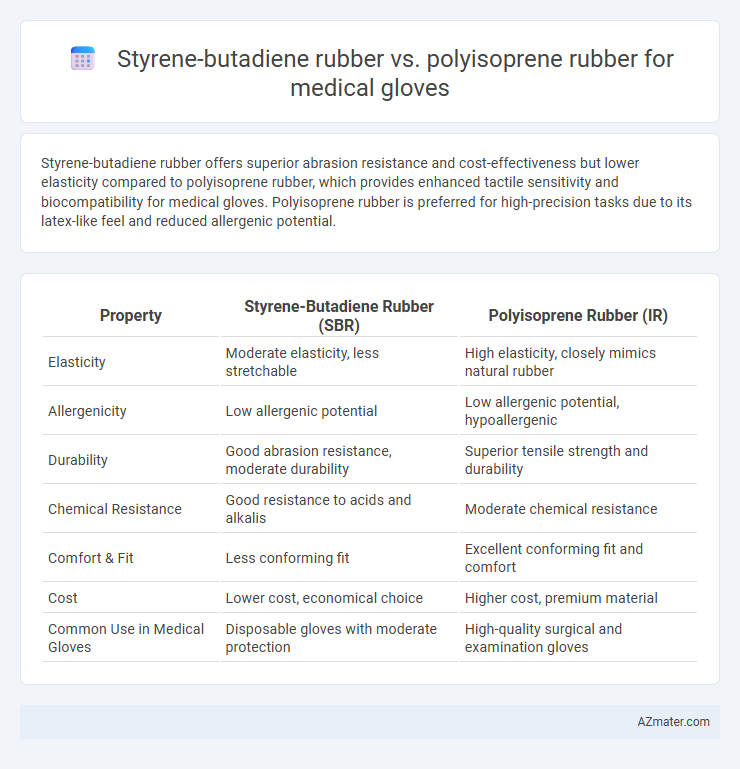
Styrene-butadiene rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lower elasticity compared to polyisoprene rubber, which provides enhanced tactile sensitivity and biocompatibility for medical gloves. Polyisoprene rubber is preferred for high-precision tasks due to its latex-like feel and reduced allergenic potential.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, less stretchable | High elasticity, closely mimics natural rubber |
| Allergenicity | Low allergenic potential | Low allergenic potential, hypoallergenic |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate durability | Superior tensile strength and durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Comfort & Fit | Less conforming fit | Excellent conforming fit and comfort |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical choice | Higher cost, premium material |
| Common Use in Medical Gloves | Disposable gloves with moderate protection | High-quality surgical and examination gloves |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and polyisoprene rubber are prominent materials used in medical glove manufacturing, each offering distinct chemical and physical properties that impact performance and safety. SBR is favored for its cost-effectiveness and abrasion resistance, while polyisoprene closely mimics natural rubber latex in elasticity and tactile sensitivity, making it suitable for users with latex allergies. The choice between SBR and polyisoprene in medical gloves depends on desired durability, biocompatibility, and manufacturing requirements critical for healthcare environments.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for medical gloves requiring durability. Unlike natural rubber polyisoprene, SBR offers enhanced resistance to heat aging and chemical exposure, but typically has lower elasticity and tactile sensitivity. Medical gloves made from SBR provide reliable protection in industrial or non-surgical environments where durability and chemical resistance are prioritized over fine motor control and comfort.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer closely resembling natural rubber in terms of elasticity, strength, and tactile properties, making it an excellent choice for medical gloves requiring high sensitivity and comfort. IR exhibits superior flexibility and low protein content, minimizing allergic reactions compared to natural rubber latex, while offering excellent barrier protection against pathogens and chemicals. Its enhanced durability and resistance to punctures and tears ensure reliable performance in demanding medical environments.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it suitable for durable medical gloves requiring extended wear. Polyisoprene rubber exhibits enhanced elasticity and greater elongation at break, providing better flexibility and tactile sensitivity crucial for precision tasks in medical settings. Both materials demonstrate excellent barrier protection, but polyisoprene's lower modulus improves comfort and reduces hand fatigue during prolonged glove use.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance to oils, solvents, and acids compared to polyisoprene rubber, which is more susceptible to degradation by hydrocarbons and organic solvents. Polyisoprene offers excellent barrier properties against water and biological fluids, while SBR provides enhanced durability in harsh chemical environments commonly encountered in medical settings. The choice between SBR and polyisoprene for medical gloves depends on the specific chemical exposure risks, with SBR favored for resistance to cleaning agents and disinfectants, and polyisoprene preferred for natural latex-like elasticity and biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility and Allergenicity
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits lower biocompatibility compared to polyisoprene rubber, as SBR contains synthetic polymers that may induce skin irritation in sensitive individuals. Polyisoprene rubber closely mimics natural latex in elasticity and comfort but presents significantly reduced allergenicity due to the absence of natural latex proteins responsible for type I latex allergies. Medical gloves made from polyisoprene offer enhanced hypoallergenic properties making them preferable for healthcare environments requiring biocompatible and low-allergen materials.
Durability and Tear Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior durability and tear resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it more suitable for medical gloves requiring extended use and high mechanical stress. SBR features enhanced abrasion resistance and greater tensile strength, which contribute to its ability to withstand repeated stretching and rough handling. Polyisoprene rubber, while softer and more elastic, exhibits lower tear resistance and reduced durability under prolonged stress, limiting its use in high-wear medical applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior cost effectiveness compared to polyisoprene rubber due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it a budget-friendly option for medical glove production. SBR enjoys broader availability as it is a synthetic rubber produced from abundant petrochemical sources, ensuring consistent supply chains globally. In contrast, polyisoprene rubber, closely mimicking natural rubber properties, tends to be more expensive and less readily available, limiting its use in cost-sensitive medical applications.
Applications in Medical Settings
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) gloves offer excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for non-sterile medical procedures, making them suitable for general examination and cleaning tasks. Polyisoprene rubber gloves provide superior elasticity and natural latex-like comfort without allergenic proteins, ideal for surgical and diagnostic applications requiring tactile sensitivity and patient safety. Both materials cater to diverse medical settings, with polyisoprene preferred for high-precision tasks and SBR suited for protective, non-invasive roles.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Medical Gloves
Polyisoprene rubber offers superior elasticity, softness, and biocompatibility compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring high sensitivity and durability. Styrene-butadiene rubber, while cost-effective and resistant to abrasion, lacks the natural feel and comfort crucial for long-term medical use. Therefore, polyisoprene rubber stands out as the best choice for medical gloves due to its enhanced tactile performance and hypoallergenic properties.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com