Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength but lacks the durability and oil resistance of HNBR in demanding applications.
Table of Comparison
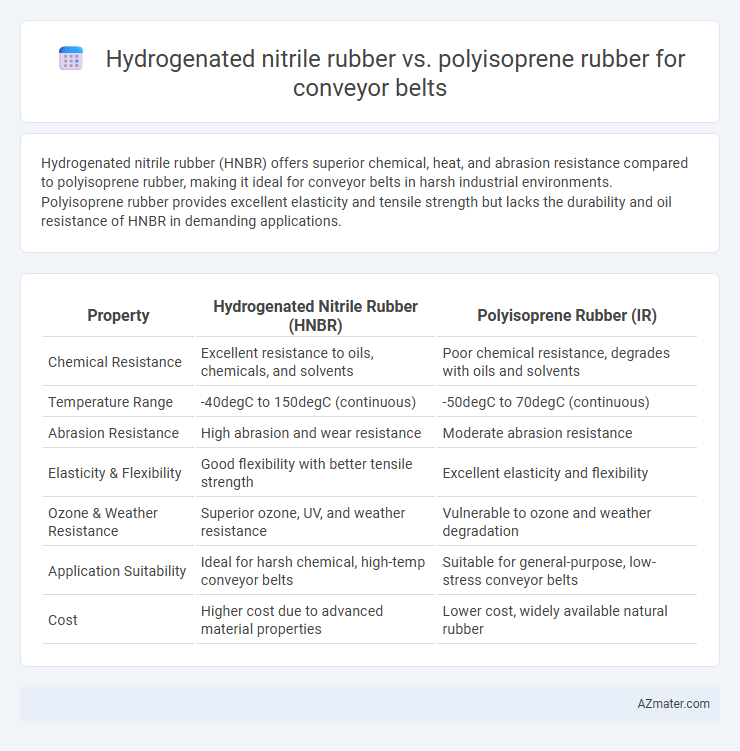
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and solvents | Poor chemical resistance, degrades with oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (continuous) | -50degC to 70degC (continuous) |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion and wear resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Good flexibility with better tensile strength | Excellent elasticity and flexibility |
| Ozone & Weather Resistance | Superior ozone, UV, and weather resistance | Vulnerable to ozone and weather degradation |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for harsh chemical, high-temp conveyor belts | Suitable for general-purpose, low-stress conveyor belts |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced material properties | Lower cost, widely available natural rubber |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) and polyisoprene rubber are prominent materials used in conveyor belt manufacturing, each offering distinct chemical and physical properties suited for industrial applications. HNBR provides exceptional resistance to heat, oils, and abrasion, making it ideal for harsh environments where durability and longevity are critical. Polyisoprene rubber, closely resembling natural rubber, delivers excellent flexibility and tensile strength but is less resistant to chemicals and temperature extremes, positioning it best for lighter-duty conveyor systems.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for conveyor belt applications in harsh industrial environments. Its hydrogenation process enhances thermal stability and ozone resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, extending the conveyor belt's service life and reducing maintenance costs. HNBR's excellent mechanical properties and abrasion resistance contribute to reliable operation in demanding material handling systems.
Key Properties of Polyisoprene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts requiring flexibility and durability under dynamic loads. Its excellent resilience and low compression set ensure long service life and consistent performance in varying temperatures. Unlike hydrogenated nitrile rubber, polyisoprene has superior mechanical properties tailored for applications demanding high elasticity and wear resistance.
Comparative Chemical Resistance: HNBR vs Polyisoprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, particularly against oils, fuels, and certain solvents, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. Polyisoprene rubber, while resilient and flexible, tends to degrade more quickly when in contact with petroleum-based products and oxidative agents, limiting its durability in chemically aggressive settings. The enhanced molecular stability of HNBR ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance in conveyor belt applications subject to chemical exposure.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Stability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior temperature tolerance, with continuous operating temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, making it highly suitable for demanding conveyor belt applications in harsh thermal environments. Polyisoprene rubber, with a narrower temperature range typically between -50degC and 70degC, shows lower thermal stability and is prone to degradation under prolonged heat exposure. HNBR's enhanced thermal resistance and oxidative stability significantly extend conveyor belt lifespan and performance in high-temperature industrial settings.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced abrasion resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. HNBR's improved resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations contributes significantly to its durability and longevity in demanding applications. Polyisoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity and tensile strength, tends to degrade faster under chemical exposure and high-temperature conditions, limiting its durability for heavy-duty conveyor belt use.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for demanding conveyor belt applications. HNBR's enhanced chemical stability and resistance to heat and oil contribute to prolonged belt life under harsh operational conditions. In contrast, polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience but generally falls short in abrasive environments due to its lower wear resistance.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and longer service life compared to polyisoprene rubber, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs in conveyor belt applications. Although HNBR has a higher initial cost, its durability and resistance to oils and heat improve overall cost efficiency and lower total cost of ownership. In contrast, polyisoprene rubber's lower upfront price is offset by faster wear and increased downtime, making it less economical for heavy-duty or chemically aggressive environments.
Application Suitability for Conveyor Belts
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil, heat, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts in harsh industrial environments such as mining, automotive, and chemical processing. Polyisoprene rubber, with excellent elasticity and resilience, suits conveyor belts handling lightweight materials in sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals where flexibility and comfort are prioritized. The choice between HNBR and polyisoprene hinges on conveyor belt exposure to chemicals, temperature extremes, and mechanical wear conditions.
Final Recommendation: Optimal Rubber Choice
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, oil resistance, and durability, making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in harsh industrial environments with exposure to chemicals and high temperatures. Polyisoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, lacks the same level of chemical and thermal stability found in HNBR. For conveyor belts requiring long-lasting performance in demanding conditions, HNBR represents the optimal choice due to its balanced combination of mechanical strength and environmental resilience.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com