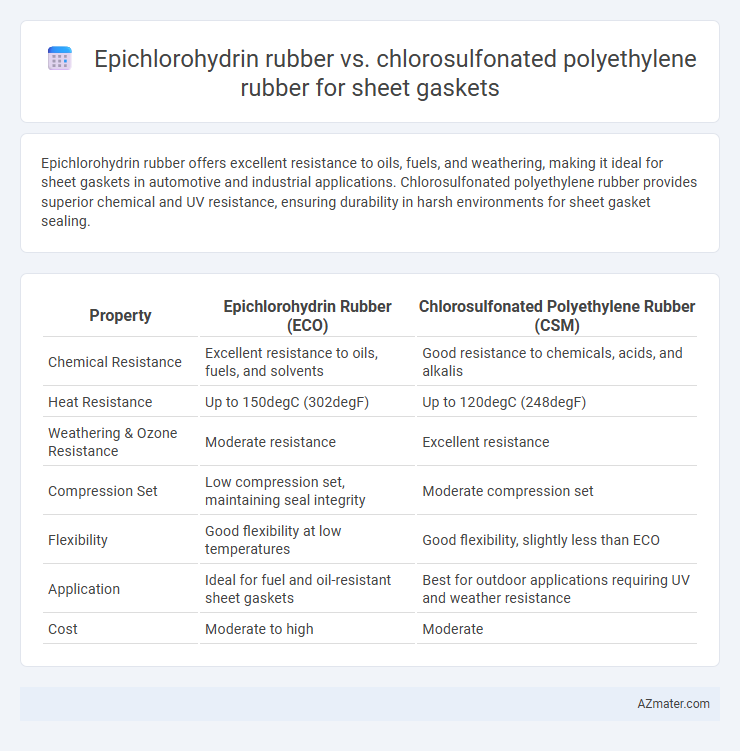
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and weathering, making it ideal for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber provides superior chemical and UV resistance, ensuring durability in harsh environments for sheet gasket sealing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Good resistance to chemicals, acids, and alkalis |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Weathering & Ozone Resistance | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintaining seal integrity | Moderate compression set |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, slightly less than ECO |
| Application | Ideal for fuel and oil-resistant sheet gaskets | Best for outdoor applications requiring UV and weather resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Sheet Gasket Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers exceptional resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering, making it suitable for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial sealing applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM) rubber provides outstanding resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and flame, with excellent mechanical strength and flexibility, ideal for outdoor and chemical exposure environments. Both materials deliver durable, reliable sealing performance, but selection depends on specific application requirements such as chemical compatibility and environmental conditions.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) offers superior resistance to oil, fuels, and various chemicals, making it ideal for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Its excellent low-temperature flexibility and strong ozone resistance enhance durability compared to other elastomers. ECO's balanced performance in heat, weather, and chemical exposure distinguishes it from Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM), which excels more in flame resistance but has lower oil resistance.
Overview of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, making it ideal for sheet gaskets in harsh environments. Its unique molecular structure provides superior tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to oils and solvents compared to epichlorohydrin rubber. CSM's enhanced durability and thermal stability ensure reliable sealing performance in automotive, industrial, and construction applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: ECO vs CSM
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior resistance to oils, greases, and polar solvents compared to chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM), making it ideal for applications exposed to diesel, hydraulic fluids, and oxygenated fuels. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals such as acids and alkalis but has limited resistance to hydrocarbons and polar solvents. For sheet gasket applications requiring enhanced chemical stability in aggressive oil-based environments, ECO outperforms CSM in maintaining integrity and durability.
Temperature Resistance: Performance and Limitations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent temperature resistance, typically performing well in continuous service temperatures up to 135degC, making it suitable for moderate heat environments in sheet gasket applications. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) withstands higher temperatures, functioning effectively up to 150degC and providing superior resistance to ozone and weathering. Limitations of epichlorohydrin include reduced performance in temperatures exceeding 135degC, whereas CSM's temperature resistance is balanced by lower chemical resistance compared to epichlorohydrin in certain aggressive environments.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and low gas permeability, making it highly suitable for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial applications where mechanical resilience is critical. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals, providing enhanced durability for gaskets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break favor epichlorohydrin rubber, while chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber excels in maintaining physical integrity under prolonged UV exposure.
Compatibility with Common Gasket Media
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent compatibility with oils, fuels, and many hydraulic fluids, making it suitable for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to petroleum-based media. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber exhibits superior resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and various chemical agents, ensuring reliable gasket performance in harsher environmental conditions and exposure to acids or alkalis. Both materials provide effective sealing properties, with epichlorohydrin favored for hydrocarbon media and chlorosulfonated polyethylene for chemical and environmental durability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers moderate cost and good chemical resistance but tends to be less readily available compared to Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber, which is more widely produced and distributed globally. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber generally provides a cost advantage due to its extensive manufacturing scales and broader supplier base. For sheet gasket applications requiring reliable availability and budget considerations, Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber is often the preferred choice in terms of economic feasibility and procurement ease.
Industry Applications and Recommendations
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in chemical resistance, oil resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for sheet gaskets in automotive fuel systems, industrial equipment, and refrigeration industries. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM), with superior ozone, weather, and chemical resistance, is preferred for gaskets in harsh outdoor environments, chemical processing plants, and marine applications. For industries requiring resistance to petroleum-based fluids and heat, Epichlorohydrin rubber is recommended, while Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber suits applications exposed to sunlight, oxidation, and aggressive chemicals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Sheet Gaskets
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent oil, chemical, and weather resistance with good flexibility at low temperatures, making it ideal for sheet gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to fuel and hydraulic fluids. Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber (CSM) excels in ozone, UV, and chemical resistance, providing superior durability in harsh outdoor environments and sealing applications involving acids, alkalis, and solvents. Selecting the right material depends on the specific service conditions: choose Epichlorohydrin rubber for fuel and oil resistance, and Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber for broad chemical resistance and long-term outdoor exposure.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Chlorosulfonated polyethylene rubber for Sheet gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com