Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and tear resistance for gasket applications, while Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber provides superior chemical, ozone, and weather resistance. EPDM gaskets are ideal for outdoor and high-temperature environments, whereas natural rubber gaskets perform better in dynamic, low-temperature sealing conditions.
Table of Comparison
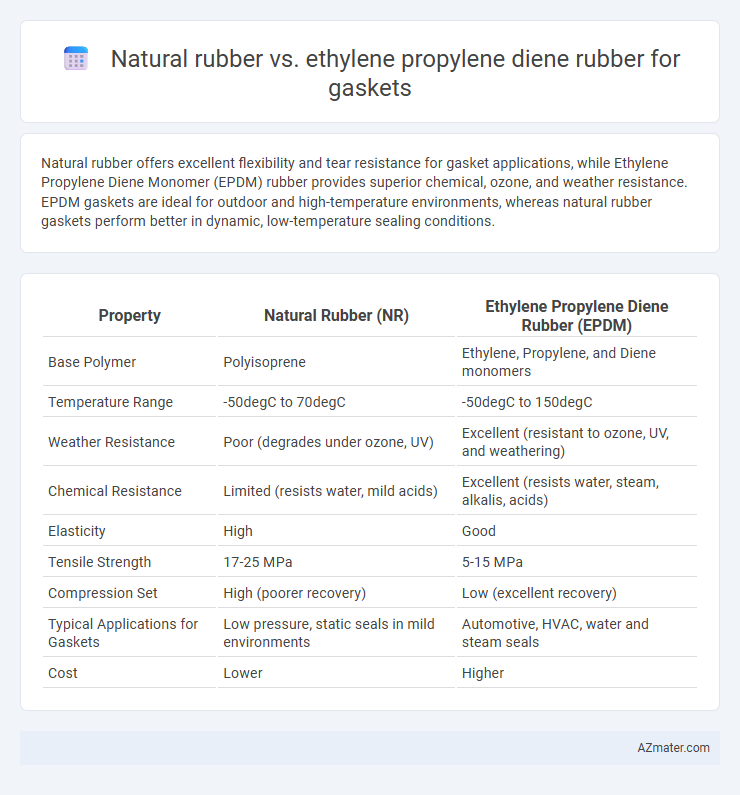
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Base Polymer | Polyisoprene | Ethylene, Propylene, and Diene monomers |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Weather Resistance | Poor (degrades under ozone, UV) | Excellent (resistant to ozone, UV, and weathering) |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (resists water, mild acids) | Excellent (resists water, steam, alkalis, acids) |
| Elasticity | High | Good |
| Tensile Strength | 17-25 MPa | 5-15 MPa |
| Compression Set | High (poorer recovery) | Low (excellent recovery) |
| Typical Applications for Gaskets | Low pressure, static seals in mild environments | Automotive, HVAC, water and steam seals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tear resistance, making it suitable for gasket applications requiring flexibility and a good seal under low to moderate temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) exhibits superior chemical resistance, weathering, and heat endurance, ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh environments and outdoor conditions. Selecting between natural rubber and EPDM for gasket materials depends on the operational temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress involved.
Overview of Natural Rubber Properties
Natural rubber offers exceptional elasticity, high tensile strength, and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it a preferred choice for gaskets requiring flexibility and durability. Its outstanding resilience and excellent impermeability to gases provide reliable sealing performance in dynamic applications. However, natural rubber has limited resistance to oils, solvents, and aging, which can affect long-term gasket functionality in harsh chemical environments.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) Properties
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in gasket applications due to its superior resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and aging compared to natural rubber. EPDM offers excellent elastic recovery, excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and polar solvents, and maintains flexibility in a wide temperature range from approximately -50degC to 150degC. Its non-polar, saturated polymer structure ensures long-term durability and sealing performance in automotive, HVAC, and industrial environments.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Natural rubber exhibits poor chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it less suitable for gaskets exposed to aggressive chemicals. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to water, steam, alkalis, acids, and many polar solvents, enhancing gasket durability in harsh chemical environments. EPDM's superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and oxidation also contributes to its preferred use over natural rubber in chemically demanding gasket applications.
Temperature Tolerance Differences
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but has a limited temperature tolerance, typically ranging from -50degC to 70degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature gasket applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber demonstrates superior temperature resistance, effectively withstanding continuous exposure from -50degC up to 150degC and short-term peaks reaching 180degC. This broader temperature range allows EPDM gaskets to function reliably in automotive, industrial, and HVAC systems where elevated heat exposure is common.
Durability and Longevity
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for dynamic gasket applications; however, it degrades faster under ozone, heat, and chemical exposure compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. EPDM offers superior durability and longevity in harsh environments, including resistance to UV radiation, weathering, and a wide range of chemicals, which significantly extends gasket service life in automotive and industrial seals. Selecting EPDM gaskets ensures enhanced performance in longevity-critical applications, whereas natural rubber remains preferable for flexibility and resilience in less aggressive conditions.
Cost Analysis of Natural Rubber vs EPDM
Natural rubber offers a lower initial cost compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), making it economical for applications with moderate temperature and chemical exposure. EPDM, despite having a higher purchase price, provides superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and a wide temperature range, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance costs in gasket applications. Cost analysis shows that while natural rubber is preferred for budget-sensitive projects, EPDM's durability often results in lower total cost of ownership over the gasket lifecycle.
Environmental and Weather Resistance
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and tensile strength but degrades quickly under prolonged exposure to ozone, UV rays, and harsh weather conditions, limiting its suitability for outdoor gasket applications. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior environmental and weather resistance, with outstanding ozone, UV, heat, and moisture durability, making it the preferred choice for gaskets in extreme climates. EPDM's resistance to oxidation and aging ensures prolonged gasket performance and reduced maintenance costs in industrial and automotive sealing applications.
Common Applications in Gasket Uses
Natural rubber is commonly used for gaskets in automotive, industrial machinery, and plumbing applications due to its excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and low cost. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, known for superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, is preferred for gaskets in outdoor, HVAC, and water system applications. Both materials offer reliable sealing properties, but EPDM is often chosen for harsh environmental conditions where durability against heat and chemicals is critical.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for gaskets requiring superior flexibility and sealing under dynamic conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides outstanding resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and a wide range of chemicals, which is critical for gaskets exposed to harsh environmental or chemical conditions. Selecting the right rubber depends on application-specific factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure gasket durability and performance.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com