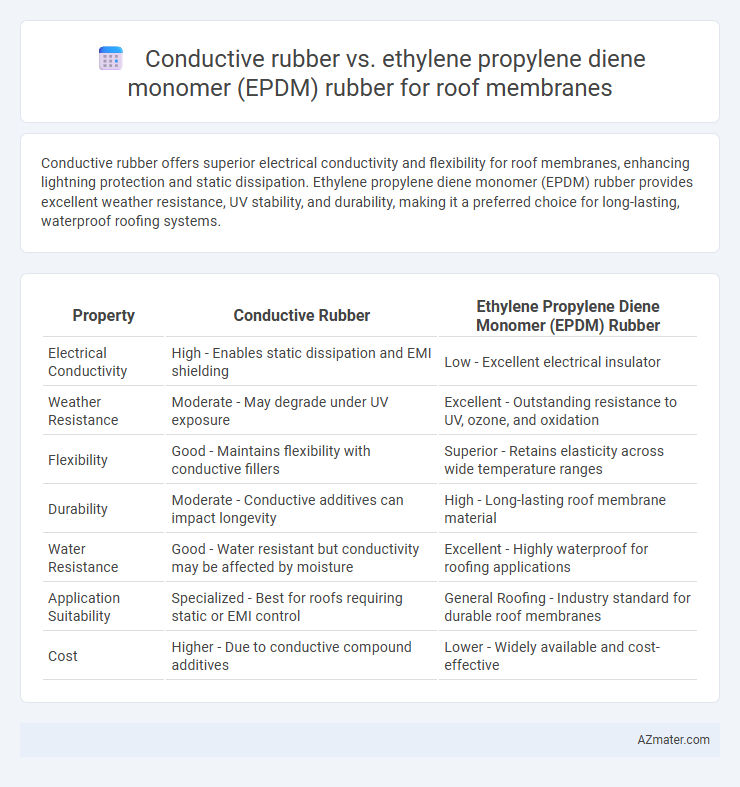
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity and flexibility for roof membranes, enhancing lightning protection and static dissipation. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and durability, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting, waterproof roofing systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High - Enables static dissipation and EMI shielding | Low - Excellent electrical insulator |
| Weather Resistance | Moderate - May degrade under UV exposure | Excellent - Outstanding resistance to UV, ozone, and oxidation |
| Flexibility | Good - Maintains flexibility with conductive fillers | Superior - Retains elasticity across wide temperature ranges |
| Durability | Moderate - Conductive additives can impact longevity | High - Long-lasting roof membrane material |
| Water Resistance | Good - Water resistant but conductivity may be affected by moisture | Excellent - Highly waterproof for roofing applications |
| Application Suitability | Specialized - Best for roofs requiring static or EMI control | General Roofing - Industry standard for durable roof membranes |
| Cost | Higher - Due to conductive compound additives | Lower - Widely available and cost-effective |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Conductive rubber roofing membranes offer enhanced electrical conductivity and durability, making them suitable for applications requiring static dissipation and weather resistance. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber membranes are widely favored for roofing due to their excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and longevity in various climates. Both materials provide effective waterproofing solutions, but EPDM remains a cost-effective choice for standard commercial and residential roofing systems.
Overview of Conductive Rubber
Conductive rubber for roof membranes offers enhanced electrical conductivity due to the incorporation of conductive fillers like carbon black or metal particles, enabling effective dissipation of static electricity and improving lightning strike protection. This material provides excellent flexibility, weather resistance, and durability similar to traditional roofing rubbers, while also supporting electromagnetic shielding and reducing maintenance costs. Compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, conductive rubber focuses on combining insulation properties with conductivity, making it suitable for specialized roofing applications requiring static control and electrical grounding.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is a highly durable synthetic elastomer widely used for roof membranes due to its excellent resistance to UV radiation, ozone, weathering, and extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC. As a non-conductive material, EPDM offers superior electrical insulation compared to conductive rubber, making it ideal for roofing applications where electrical safety and long-term weather resistance are critical. Its outstanding elasticity and resistance to chemical degradation further enhance roof longevity and reduce maintenance costs in commercial and residential buildings.
Physical Properties Comparison
Conductive rubber exhibits higher electrical conductivity but generally lower weather resistance compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is renowned for its excellent tensile strength and superior UV, ozone, and water resistance essential for roof membranes. EPDM also demonstrates superior elasticity and thermal stability across a broad temperature range (-40degC to 150degC), making it highly durable under fluctuating environmental conditions. While conductive rubber may offer unique static discharge properties, EPDM's balanced physical properties such as high elongation at break (typically 300-500%) and robust aging resistance make it the preferred choice for long-lasting roof membrane applications.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Conductive rubber exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity due to the presence of conductive fillers such as carbon black or metal particles, making it suitable for dissipating static electricity on roof membranes. In contrast, Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is an electrical insulator, offering minimal conductivity which prevents current flow for enhanced safety but does not aid in static dissipation. The choice between conductive rubber and EPDM for roof membranes primarily hinges on the need for electrical discharge management versus insulating properties in roofing applications.
Weather Resistance and Durability
Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior weather resistance for roof membranes, with excellent UV, ozone, and heat resistance that ensures long-lasting durability in harsh environmental conditions. Conductive rubber, while beneficial for specific applications requiring electrical conductivity, generally lacks the chemical stability and weathering resilience of EPDM, making it less ideal for roofing exposed to extreme weather. EPDM's proven resistance to temperature fluctuations, moisture, and oxidative degradation results in a more reliable and enduring roof membrane performance over time.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Conductive rubber roof membranes offer enhanced ease of installation due to their electrical grounding capabilities, which can reduce static buildup and improve safety during application. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber membranes provide superior resistance to UV radiation and ozone, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and longer service life. While EPDM requires periodic inspections to maintain seam integrity, conductive rubber membranes may demand additional care to preserve conductivity and prevent wear-related degradation.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Conductive rubber roofing membranes typically present higher initial costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which remains a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. EPDM offers extended durability, UV resistance, and low maintenance expenses, resulting in lower total life-cycle costs despite potential performance trade-offs in electrical conductivity. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors EPDM for budget-conscious projects prioritizing longevity and weather resistance, while conductive rubber suits specialized roofing needs requiring electrical properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Conductive rubber roof membranes, often made with synthetic materials, may pose higher environmental concerns due to non-biodegradability and potential chemical additives, whereas ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber is known for its durability, recyclability, and lower environmental footprint. EPDM membranes contribute to sustainability efforts through energy-efficient thermal insulation and extended service life, reducing roof replacement frequency and landfill waste. Life cycle assessments reveal EPDM's advantages in carbon emissions and resource conservation compared to conductive rubber alternatives, supporting greener roofing choices.
Best Applications for Each Material
Conductive rubber suits applications requiring electrical conductivity and static dissipation, such as grounding pads and EMI shielding in roofing systems exposed to electronic equipment. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in waterproofing and UV resistance, making it ideal for durable roof membranes in commercial and residential buildings exposed to harsh weather conditions. EPDM's superior flexibility and ozone resistance further enhance its use in long-lasting roofing solutions that need excellent thermal stability.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Roof membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com