Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and resilience for weather seals but degrades faster under UV exposure, while ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance with greater durability in outdoor applications. EPDM's enhanced chemical stability and temperature tolerance make it the preferred choice for long-lasting weather seals.
Table of Comparison
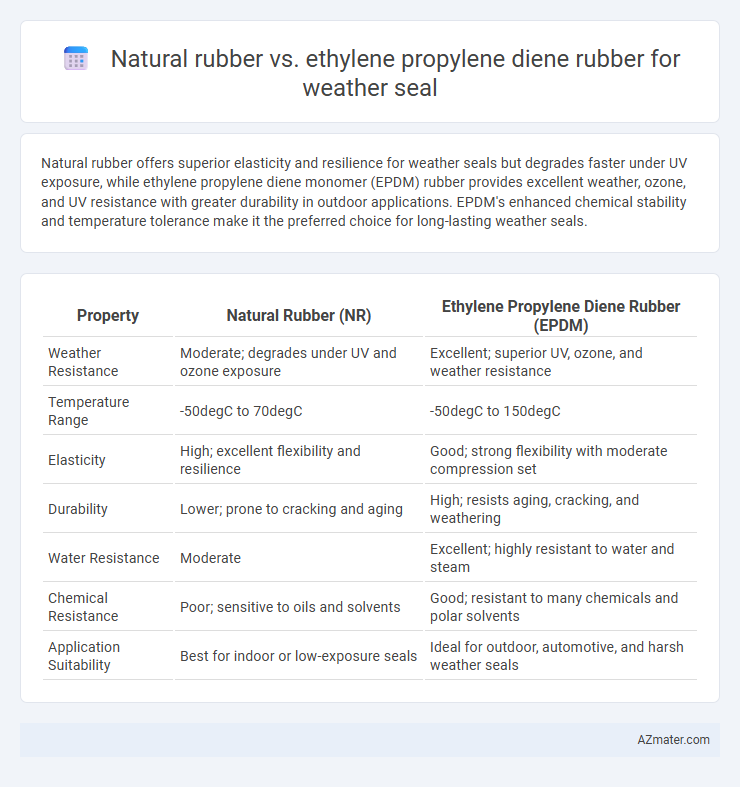
| Property | Natural Rubber (NR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Moderate; degrades under UV and ozone exposure | Excellent; superior UV, ozone, and weather resistance |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 70degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Elasticity | High; excellent flexibility and resilience | Good; strong flexibility with moderate compression set |
| Durability | Lower; prone to cracking and aging | High; resists aging, cracking, and weathering |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | Excellent; highly resistant to water and steam |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor; sensitive to oils and solvents | Good; resistant to many chemicals and polar solvents |
| Application Suitability | Best for indoor or low-exposure seals | Ideal for outdoor, automotive, and harsh weather seals |
Introduction to Weather Seals
Weather seals require materials with excellent elasticity, durability, and resistance to environmental factors like UV radiation and ozone. Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and resilience, making it effective for flexible sealing applications but has limited weather resistance. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides outstanding weather, ozone, and UV resistance, ideal for long-lasting weather seals in outdoor and automotive environments.
Overview of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, exhibits excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for weather seals exposed to mechanical stress. Its natural resilience and ability to maintain flexibility at low temperatures enhance sealing effectiveness against environmental elements such as water, dust, and air. While natural rubber offers superior grip and elasticity, it is less resistant to ozone, UV radiation, and certain chemicals compared to synthetic alternatives like ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM).
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, ultraviolet radiation, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for weather seal applications. EPDM maintains flexibility and durability over prolonged outdoor exposure, outperforming natural rubber which tends to degrade under similar environmental conditions. Its chemical stability and low permeability to gases enhance the longevity and effectiveness of seals in automotive, construction, and industrial uses.
Key Properties Comparison
Natural rubber exhibits exceptional elasticity and tensile strength, providing superior flexibility and resilience for weather seals, especially in dynamic environments. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, making it highly durable and weather-resistant for outdoor sealing applications. EPDM's enhanced chemical stability and aging resistance surpass natural rubber, ensuring longer service life in harsh weather conditions.
Weather Resistance: Natural Rubber vs EPDM
Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and tensile strength but is prone to degradation under prolonged exposure to UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, limiting its effectiveness as a weather seal. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior weather resistance, maintaining flexibility and durability against UV radiation, ozone, heat, and cold, making it ideal for outdoor sealing applications. The molecular structure of EPDM provides resilience in harsh environments, ensuring longer service life compared to natural rubber in weather seal usage.
Durability and Longevity
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and ozone, limiting its durability for weather seals in harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber exhibits superior resistance to weathering, ozone, UV rays, and temperature extremes, significantly enhancing its longevity in outdoor sealing applications. EPDM's chemical stability and low compression set make it a preferred choice for long-lasting weather seals requiring reliable performance over extended periods.
Cost Considerations
Natural rubber offers a lower initial cost compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for weather seals in short-term applications. EPDM, though more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and resistance to UV, ozone, and extreme temperatures, resulting in lower replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing immediate cost savings with long-term performance and lifecycle costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, is biodegradable and renewable, making it a more sustainable choice for weather seals compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. EPDM's production relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to a higher carbon footprint, whereas natural rubber cultivation supports carbon sequestration and reduces environmental pollution. However, natural rubber's sustainability can be affected by land use changes and agrochemical inputs, requiring responsible sourcing to minimize ecological impact.
Typical Applications in Weather Sealing
Natural rubber offers excellent flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for weather seals in automotive door seals, window gaskets, and HVAC systems where tight sealing against water and dust is critical. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in outdoor applications due to its superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, commonly used in roofing membranes, automotive weatherstrips, and sealing systems in construction. EPDM's durability in harsh weather environments often outperforms natural rubber in long-term outdoor sealing applications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber Material
Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tensile strength, making it ideal for flexible weather seals exposed to moderate temperature variations. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, ensuring long-lasting durability in harsh outdoor environments. Selecting the right rubber material depends on specific application requirements, with EPDM preferred for high durability and natural rubber favored for elasticity and moderate weather resilience.
Infographic: Natural rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com