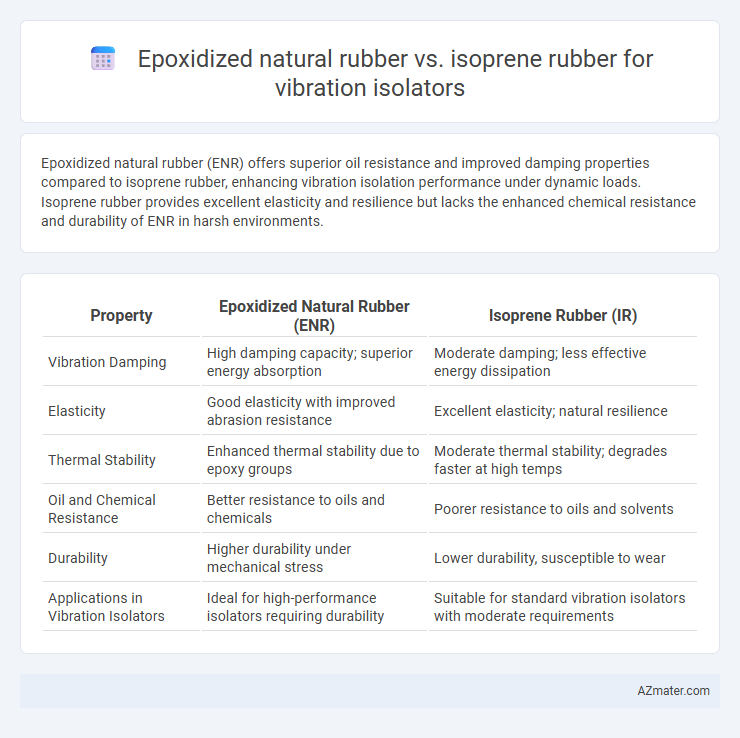
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior oil resistance and improved damping properties compared to isoprene rubber, enhancing vibration isolation performance under dynamic loads. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but lacks the enhanced chemical resistance and durability of ENR in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Isoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Damping | High damping capacity; superior energy absorption | Moderate damping; less effective energy dissipation |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity with improved abrasion resistance | Excellent elasticity; natural resilience |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced thermal stability due to epoxy groups | Moderate thermal stability; degrades faster at high temps |
| Oil and Chemical Resistance | Better resistance to oils and chemicals | Poorer resistance to oils and solvents |
| Durability | Higher durability under mechanical stress | Lower durability, susceptible to wear |
| Applications in Vibration Isolators | Ideal for high-performance isolators requiring durability | Suitable for standard vibration isolators with moderate requirements |
Introduction to Vibration Isolators: Importance and Applications
Vibration isolators are crucial components used to reduce or eliminate unwanted vibrations in machinery and structures, enhancing performance and longevity. Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior damping properties and chemical resistance compared to isoprene rubber, making it effective in absorbing vibrations in automotive and industrial applications. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but lacks the enhanced damping capabilities of ENR, limiting its use in high-performance vibration isolation systems.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR)
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance, improved gas barrier properties, and superior mechanical strength compared to conventional natural rubber, making it highly suitable for vibration isolator applications. Its epoxide groups introduce polarity, which increases adhesion to fillers and enhances dynamic performance under cyclic loading. These features enable ENR-based vibration isolators to effectively reduce noise and vibration while maintaining durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of Isoprene Rubber (IR)
Isoprene Rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent tensile strength, high resilience, and outstanding resistance to wear and fatigue, making it highly suitable for vibration isolators. Compared to Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR), IR offers superior elasticity, better low-temperature flexibility, and enhanced durability under repeated dynamic stress. Its molecular structure closely resembles natural rubber, ensuring excellent damping properties and energy absorption in vibration isolation applications.
Mechanical Properties: ENR vs. IR
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) exhibits enhanced mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and improved abrasion resistance compared to Isoprene Rubber (IR), making it suitable for vibration isolators requiring durability and resilience. ENR's increased polarity from epoxidation also contributes to better oil and chemical resistance, which enhances the lifespan of vibration isolators under harsh conditions. Conversely, IR offers excellent elasticity and low hysteresis, providing superior vibration damping performance but with less mechanical robustness than ENR.
Damping Performance Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior damping performance compared to isoprene rubber due to its enhanced viscoelastic properties and improved energy dissipation capabilities. The introduction of epoxy groups in ENR increases intermolecular interactions, resulting in higher internal friction and better vibration attenuation. Isoprene rubber, while flexible, generally shows lower damping capacity, making ENR more effective for vibration isolator applications requiring efficient noise and shock absorption.
Environmental Resistance: Durability in Harsh Conditions
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced environmental resistance compared to isoprene rubber due to its improved chemical stability and oxidation resistance, making it ideal for vibration isolators used in harsh conditions. ENR's epoxide groups increase its polarity, which enhances resistance to ozone, heat, and oils, thereby extending durability under aggressive environmental stressors. Isoprene rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone and oxidative environments, limiting its effectiveness in long-term vibration isolation applications in demanding settings.
Cost and Processing Considerations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and improved mechanical properties compared to isoprene rubber, but it generally comes at a higher material cost due to specialized processing requirements. Isoprene rubber, while more cost-effective and easier to process with conventional rubber manufacturing techniques, may require additional additives to meet durability demands in vibration isolators. Processing ENR involves careful control of epoxidation levels to balance stiffness and elasticity, impacting curing cycles and equipment compatibility, whereas isoprene rubber benefits from established, streamlined processing protocols that reduce overall production expenses.
Aging and Fatigue Characteristics
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior aging resistance compared to isoprene rubber (IR) due to its enhanced oxidative stability and reduced susceptibility to ozone cracking, which contributes to longer service life in vibration isolators. ENR's molecular structure, incorporating epoxide groups, provides improved fatigue resistance by maintaining elasticity and damping properties under cyclic loading conditions. Conversely, isoprene rubber tends to degrade faster under thermal and environmental stress, leading to a decline in mechanical integrity and vibration isolation performance over time.
Suitability for Specific Vibration Isolation Applications
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior damping properties and enhanced resistance to heat and oils, making it highly suitable for vibration isolators in automotive and industrial machinery where durability and oil resistance are critical. Isoprene rubber (IR) provides excellent elasticity, resilience, and low hysteresis, ideal for precise vibration isolation in instruments and sensitive equipment requiring minimal energy loss. Selection between ENR and IR depends on application-specific demands such as temperature exposure, chemical resistance, and elastic recovery requirements.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for Vibration Isolators
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior damping properties and enhanced mechanical strength compared to isoprene rubber, making it more effective for vibration isolators requiring higher energy absorption. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but may not perform as well under prolonged dynamic stress or high-frequency vibration. Choosing ENR ensures improved isolation efficiency and durability in demanding vibration control applications.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Vibration isolator
 azmater.com
azmater.com