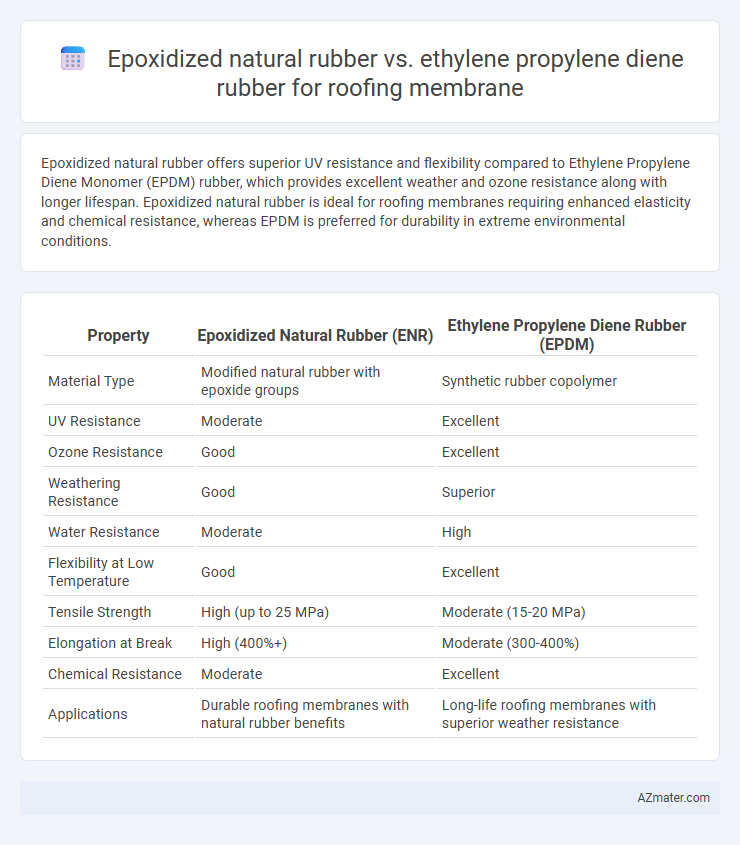
Epoxidized natural rubber offers superior UV resistance and flexibility compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which provides excellent weather and ozone resistance along with longer lifespan. Epoxidized natural rubber is ideal for roofing membranes requiring enhanced elasticity and chemical resistance, whereas EPDM is preferred for durability in extreme environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Modified natural rubber with epoxide groups | Synthetic rubber copolymer |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Ozone Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Weathering Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility at Low Temperature | Good | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 25 MPa) | Moderate (15-20 MPa) |
| Elongation at Break | High (400%+) | Moderate (300-400%) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Applications | Durable roofing membranes with natural rubber benefits | Long-life roofing membranes with superior weather resistance |
Introduction to EPDM and ENR for Roofing Membranes
Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) offers enhanced oil resistance and weatherability compared to standard natural rubber, making it suitable for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is widely used in roofing due to its exceptional resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and temperature extremes, providing long-lasting durability. Both ENR and EPDM deliver elastomeric properties essential for flexible, waterproof roofing membranes, but EPDM remains the industry standard for superior weather resistance and mechanical performance.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) features a modified polyisoprene backbone with epoxy groups introduced through oxidation, enhancing polarity and crosslinking potential for improved oil resistance and adhesion in roofing membranes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber consists of a saturated ethylene-propylene backbone with diene monomers providing sites for vulcanization, yielding superior weathering, ozone resistance, and thermal stability. The chemical structure of ENR allows better compatibility with polar additives, while EPDM's fully saturated backbone offers exceptional durability against UV radiation and oxidation in roofing applications.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), making it highly suitable for roofing membranes requiring enhanced mechanical durability. ENR's improved elasticity and chemical resistance contribute to its long-term performance under varying weather conditions, while EPDM is known for excellent UV and ozone resistance but may show lower tensile strength and tear resistance. The combination of excellent mechanical properties and durability enables ENR to maintain structural integrity and extend roofing membrane lifespan in demanding environmental conditions.
Weathering and UV Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior weathering and UV resistance compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, due to its enhanced polarity and crosslinked structure that minimizes degradation from sunlight and ozone exposure. EPDM exhibits excellent UV resistance and durability under prolonged outdoor conditions but tends to undergo surface cracking and stiffness over extended periods when exposed to harsh weather. ENR's molecular modification improves its retention of mechanical properties and flexibility, making it a more resilient choice for roofing membranes subjected to intense UV radiation and fluctuating weather patterns.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior water resistance due to its enhanced polarity, which improves impermeability and reduces water absorption in roofing membranes. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, especially against acids, alkalis, and ozone, making it highly durable in harsh environmental conditions. While ENR provides improved hydrophobic properties, EPDM remains the preferred choice for roofing membranes requiring long-term chemical stability and resistance to weathering.
Flexibility and Elasticity Under Temperature Variations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity under temperature variations due to its enhanced polarity and strain-induced crystallization, allowing it to maintain performance in both low and high temperatures. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) demonstrates excellent thermal stability and resistance to ozone and UV exposure but may experience reduced elasticity at extremely low temperatures compared to ENR. ENR's unique molecular structure provides better adaptability to thermal expansion and contraction cycles, making it more suitable for roofing membranes in fluctuating climates.
Installation and Processing Methods
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced compatibility with bituminous materials, improving adhesion and ease of application during roofing membrane installation compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM). ENR membranes typically require lower processing temperatures and can be vulcanized using conventional sulfur-based systems, facilitating efficient on-site curing and reduced installation time. EPDM membranes rely on specialized primers and adhesives, often necessitating more complex surface preparations and curing methods, which can extend installation duration and increase labor costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) used in roofing membranes, making it a more sustainable choice. ENR's renewable origin from natural latex reduces dependency on fossil fuels, while EPDM production involves petrochemical processes that contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions. The improved environmental profile of ENR supports eco-friendly roofing applications by enhancing recyclability and minimizing long-term ecological impact.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) roofing membranes offer enhanced elasticity and environmental resistance but typically come at a higher initial cost compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, which is known for its affordability and proven durability. While EPDM provides excellent UV and ozone resistance, ENR exhibits superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating long-term value, ENR may deliver cost savings through extended membrane lifespan and fewer repairs despite higher upfront investment, whereas EPDM remains a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive projects with reliable weather resistance.
Application Suitability and Industry Recommendations
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers superior flexibility, enhanced resistance to oils and ozone, and excellent adhesion properties, making it suitable for roofing membranes requiring high durability and weather resistance. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in UV, heat, and chemical resistance, providing long service life and low maintenance, which is why it is commonly recommended by roofing industry professionals for commercial and residential applications. Industry standards often favor EPDM for large-scale, exposed roofing systems due to its proven performance, while ENR is preferred in applications demanding enhanced elasticity and environmental resilience.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com