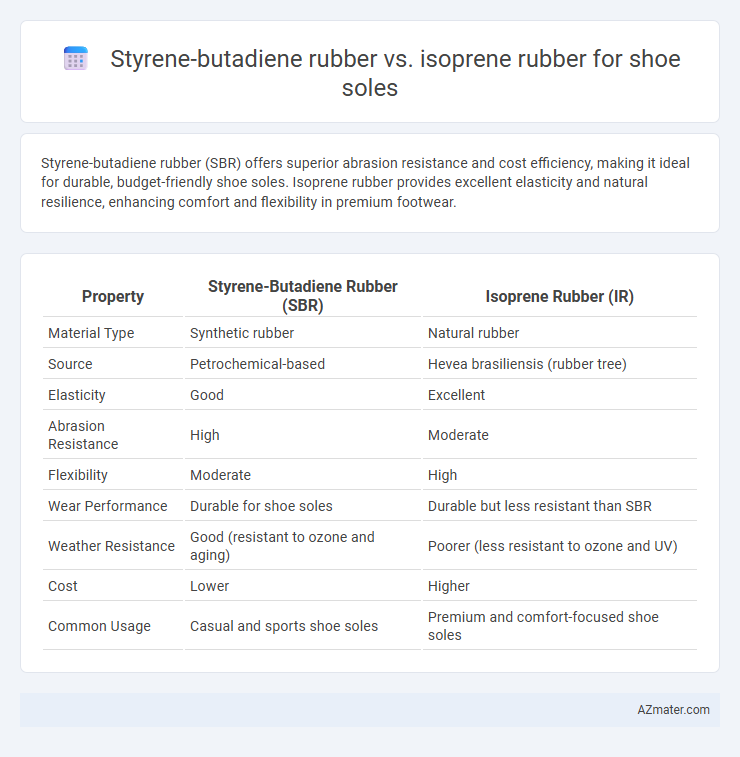
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and cost efficiency, making it ideal for durable, budget-friendly shoe soles. Isoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and natural resilience, enhancing comfort and flexibility in premium footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Isoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber | Natural rubber |
| Source | Petrochemical-based | Hevea brasiliensis (rubber tree) |
| Elasticity | Good | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Wear Performance | Durable for shoe soles | Durable but less resistant than SBR |
| Weather Resistance | Good (resistant to ozone and aging) | Poorer (less resistant to ozone and UV) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Usage | Casual and sports shoe soles | Premium and comfort-focused shoe soles |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Isoprene Rubber
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring durability and cost-effectiveness. Isoprene Rubber, a synthetic equivalent of natural rubber, offers superior elasticity, resilience, and impact resistance, providing enhanced comfort and flexibility in footwear applications. Both rubbers are widely used in the shoe industry, with SBR favored for its toughness and Isoprene valued for its natural rubber-like properties.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer composed of styrene and butadiene monomers, offering a balance of abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it suitable for durable shoe soles. Isoprene rubber (IR), a natural rubber primarily consisting of cis-1,4-polyisoprene units, provides superior elasticity and resilience due to its highly regular polymeric structure. The key chemical difference lies in SBR's synthetic copolymer nature with aromatic styrene rings and diene units, compared to IR's natural polyisoprene chains, influencing their mechanical properties and wear resistance in footwear applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and better aging stability compared to Isoprene rubber, making it ideal for high-wear shoe soles. Isoprene rubber, with its natural elasticity and resilience, provides excellent flexibility and cushioning but tends to have lower tear resistance. SBR's higher tensile strength and resistance to heat and chemicals enhance sole durability in demanding conditions compared to Isoprene rubber.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior wear resistance and excellent abrasion durability, making it highly suitable for shoe soles subjected to frequent friction and harsh surfaces. Isoprene rubber, while providing good elasticity and flexibility, generally exhibits lower wear resistance and may degrade faster under high-stress conditions compared to SBR. The enhanced tensile strength and aging stability of SBR contribute significantly to longer-lasting shoe soles in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Shoe Soles
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and durability but has lower elasticity compared to isoprene rubber, affecting overall flexibility in shoe soles. Isoprene rubber, mimicking natural rubber's molecular structure, provides superior elasticity and cushioning properties, resulting in enhanced comfort and flexibility for prolonged wear. The choice between SBR and isoprene rubber directly impacts the shoe sole's ability to absorb shock and conform to foot movements, crucial for ergonomic footwear design.
Grip and Slip Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and provides strong grip on various surfaces, making it suitable for shoe soles with enhanced slip resistance. Isoprene rubber, known for its superior elasticity and resilience, offers moderate grip but can outperform SBR in dynamic traction due to its natural flexibility. Both materials contribute to slip resistance, but SBR's rugged texture typically delivers better grip on wet and oily surfaces.
Weather and Temperature Performance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and performs well in moderate temperatures but tends to harden and lose flexibility in extreme cold, limiting its use in harsh winter conditions. Isoprene rubber, mimicking natural rubber properties, maintains superior elasticity and resilience across a wider temperature range, especially excelling in low temperatures without significant stiffness. For shoe soles exposed to fluctuating weather, isoprene rubber provides enhanced flexibility and durability in cold climates, while SBR suits warmer environments with less temperature variation.
Cost-Effectiveness and Production Efficiency
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior cost-effectiveness for shoe soles due to its lower raw material price and high availability, making it a commonly preferred choice in mass production. Its enhanced abrasion resistance and heat aging properties contribute to efficient manufacturing processes with reduced material waste compared to isoprene rubber, which generally incurs higher costs due to its natural origin and complex processing requirements. Production efficiency using SBR is further improved by its compatibility with faster vulcanization cycles, leading to increased output rates and consistent sole quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is petroleum-based, leading to higher carbon emissions and reliance on non-renewable resources, whereas isoprene rubber, especially natural isoprene derived from rubber trees, offers better biodegradability and supports sustainable harvesting practices. SBR soles contribute to microplastic pollution due to their synthetic nature and slow degradation, while natural isoprene rubber soles reduce environmental footprint through renewable sourcing and carbon sequestration during rubber tree cultivation. Choosing isoprene rubber for shoe soles aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing goals and reduces long-term ecological damage compared to synthetic SBR alternatives.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Shoe Soles
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for everyday shoe soles that require durability and wear resistance. Isoprene rubber provides superior elasticity and resilience, ideal for high-performance shoe soles demanding flexibility and comfort. Selecting between SBR and isoprene depends on balancing budget, durability needs, and performance requirements for the intended footwear application.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Isoprene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com