Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior flexibility, durability, and thermal insulation compared to traditional chloroprene rubber in wetsuits. Its enhanced tensile strength and conductivity improve performance and comfort for prolonged water activities.
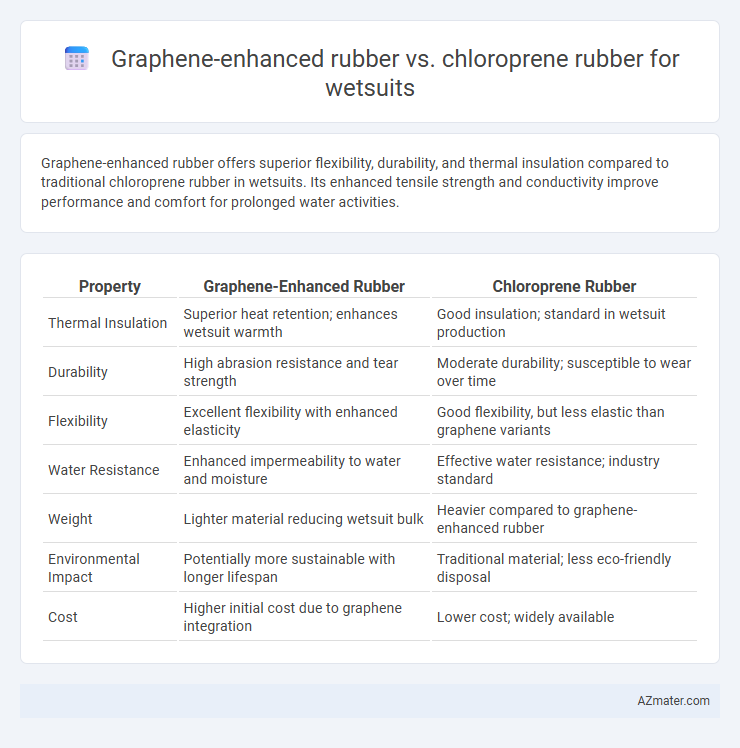
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | Chloroprene Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Superior heat retention; enhances wetsuit warmth | Good insulation; standard in wetsuit production |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance and tear strength | Moderate durability; susceptible to wear over time |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility with enhanced elasticity | Good flexibility, but less elastic than graphene variants |
| Water Resistance | Enhanced impermeability to water and moisture | Effective water resistance; industry standard |
| Weight | Lighter material reducing wetsuit bulk | Heavier compared to graphene-enhanced rubber |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially more sustainable with longer lifespan | Traditional material; less eco-friendly disposal |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to graphene integration | Lower cost; widely available |
Introduction to Modern Wetsuit Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior flexibility, thermal conductivity, and durability compared to traditional chloroprene rubber used in wetsuits. The integration of graphene nanoparticles improves the material's strength while maintaining lightweight comfort, essential for enhanced swimmer performance and insulation in cold water. Chloroprene rubber, known for its elasticity and water resistance, remains a popular choice but lacks the advanced mechanical and thermal properties provided by graphene-infused alternatives.
What is Graphene-Enhanced Rubber?
Graphene-enhanced rubber integrates graphene nanoparticles into traditional rubber matrices, significantly improving thermal conductivity, tensile strength, and flexibility compared to standard chloroprene rubber used in wetsuits. This advanced composite material offers superior insulation, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making wetsuits warmer and longer-lasting. The incorporation of graphene also enhances the material's lightweight properties and quick-drying capabilities, optimizing underwater performance and comfort for divers and surfers.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, is a synthetic elastomer widely used in wetsuits for its excellent insulation, flexibility, and resistance to water, oils, and weathering. Its closed-cell foam structure provides thermal protection by trapping nitrogen gas, which reduces heat transfer and maintains body warmth in cold water. Despite being durable and versatile, chloroprene rubber may exhibit lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to graphene-enhanced rubber alternatives.
Thermal Insulation: Graphene vs Chloroprene
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior thermal insulation in wetsuits due to its exceptional thermal conductivity and ability to retain body heat more effectively than traditional chloroprene rubber. Chloroprene rubber, while providing good insulation through its closed-cell foam structure, lacks the advanced heat retention properties present in graphene composites. The integration of graphene significantly improves overall warmth retention and reduces heat loss, enhancing wetsuit performance in cold water conditions.
Flexibility and Comfort Comparison
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior flexibility and enhanced thermal conductivity compared to traditional chloroprene rubber, resulting in increased comfort and better mobility in wetsuits. The incorporation of graphene improves the material's elasticity and reduces stiffness, allowing for a more adaptive fit and prolonged wear without compromising thermal insulation. Chloroprene rubber, while durable and water-resistant, lacks the advanced flexibility and lightweight properties provided by graphene composites, which can limit overall comfort during extended aquatic activities.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior durability for wetsuits by significantly improving tensile strength and resistance to abrasion compared to chloroprene rubber. The nanomaterial properties of graphene enhance elasticity and reduce micro-tear formation, extending the wetsuit's lifespan even under constant exposure to saltwater and UV radiation. Chloroprene rubber provides good flexibility but tends to degrade faster over time, making graphene composites a more reliable choice for long-term performance.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Graphene-enhanced rubber wetsuits offer significantly lower weight compared to chloroprene rubber, improving wearability and reducing fatigue during extended water activities. The incorporation of graphene enhances the material's density and thermal conductivity, resulting in improved buoyancy control without the bulk typically associated with thicker chloroprene suits. Chloroprene rubber, while offering strong insulation and buoyancy, tends to be heavier and less flexible, which can affect swimmer agility and comfort in aquatic environments.
Environmental Impact of Both Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber in wetsuits offers improved durability and elasticity, reducing the frequency of replacement and thereby lowering landfill waste compared to chloroprene rubber, which often involves more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and releases higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Graphene additives can be sourced sustainably, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint during production, while traditional chloroprene production relies heavily on petrochemicals with significant greenhouse gas emissions. The biodegradability of graphene-enhanced rubber remains under research but shows potential for eco-friendlier disposal options compared to chloroprene, which is less biodegradable and poses greater environmental persistence.
Price and Market Availability
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior durability and flexibility for wetsuits but comes at a higher price due to advanced material costs and limited production scale. Chloroprene rubber, commonly known as neoprene, remains the market standard with widespread availability and more affordable pricing, supported by established manufacturing processes. Demand for graphene-enhanced wetsuits is growing, yet chloroprene dominates due to cost-effectiveness and broad supplier networks.
Which Rubber is Best for Your Wetsuit?
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior thermal conductivity and increased flexibility compared to traditional chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for wetsuits requiring both warmth and freedom of movement. Chloroprene rubber, widely used in wetsuits, provides excellent insulation, durability, and moisture resistance but lacks the enhanced performance benefits of graphene integration. Choosing graphene-enhanced rubber is best for advanced wetsuits aimed at improved heat retention and enhanced stretchability, while chloroprene remains a reliable choice for standard wetsuit applications.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Wetsuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com