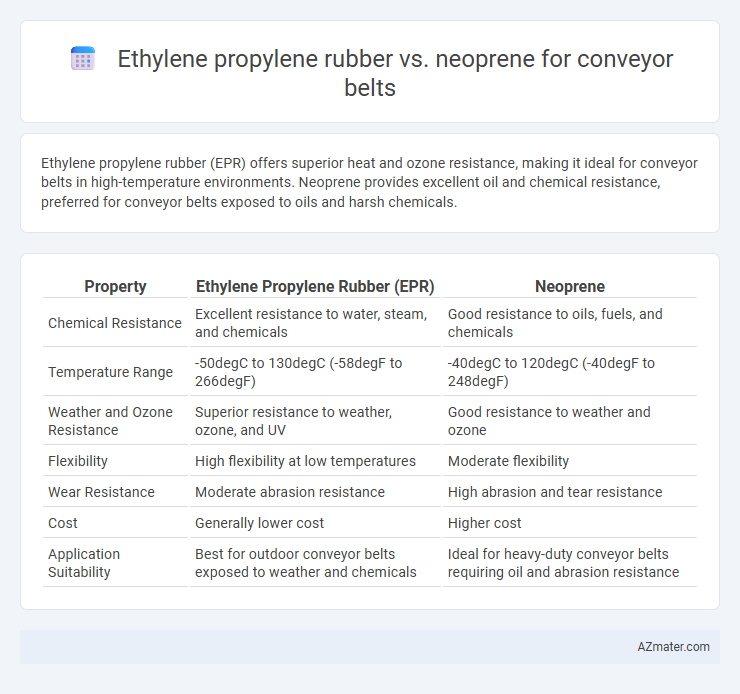
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior heat and ozone resistance, making it ideal for conveyor belts in high-temperature environments. Neoprene provides excellent oil and chemical resistance, preferred for conveyor belts exposed to oils and harsh chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Neoprene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to water, steam, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 130degC (-58degF to 266degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Weather and Ozone Resistance | Superior resistance to weather, ozone, and UV | Good resistance to weather and ozone |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion and tear resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost |
| Application Suitability | Best for outdoor conveyor belts exposed to weather and chemicals | Ideal for heavy-duty conveyor belts requiring oil and abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and neoprene are both widely used materials in conveyor belt applications, offering distinct advantages based on their chemical and physical properties. EPR provides excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature conveying environments, while neoprene is known for its superior resistance to oil, chemicals, and abrasion, enhancing durability in harsh industrial conditions. Selecting the appropriate conveyor belt material depends on factors such as temperature range, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress specific to the operational environment.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for conveyor belt applications in harsh environments. EPR offers superior flexibility and resilience compared to Neoprene, with enhanced resistance to oxidation and UV radiation, which extends the service life of conveyor belts. The material's excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to water and chemicals further position EPR as an optimal choice for conveyor belts in industrial and outdoor settings.
Overview of Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent chemical stability, weather resistance, and moderate heat tolerance, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to oils, greases, and varying environmental conditions. Compared to ethylene propylene rubber, neoprene offers superior resistance to ozone, abrasion, and flame, enhancing durability in heavy-duty conveyor applications. Its balanced flexibility and toughness ensure reliable performance in industrial settings requiring consistent mechanical strength and environmental resilience.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) exhibits superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering compared to neoprene, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Neoprene, while offering good resistance to oils, solvents, and flame, has limited performance in continuous high-temperature applications relative to EPR. Both materials provide elasticity and durability, but EPR's chemical stability against oxidation and UV degradation gives it a distinct advantage in chemically aggressive environments.
Resistance to Heat and Weathering
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat and weathering compared to neoprene, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. EPR maintains flexibility and durability under high temperatures up to 150degC, while neoprene typically withstands temperatures only up to 120degC. In terms of weathering, EPR excels with excellent ozone and UV resistance, significantly reducing degradation and extending conveyor belt lifespan in outdoor applications.
Abrasion and Wear Performance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior abrasion resistance and wear performance compared to neoprene, making it highly suitable for conveyor belt applications subjected to continuous friction and heavy loads. EPR's molecular structure provides excellent flexibility and durability, reducing surface degradation over time, while neoprene tends to exhibit faster wear under similar abrasive conditions due to lower resilience. Selecting EPR for conveyor belts results in extended service life and reduced maintenance costs in environments with high abrasive impact.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to neoprene, making it highly effective for conveyor belts exposed to harsh industrial environments. EPR resists a wide range of acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, ensuring durability and minimal degradation over time. Neoprene provides moderate chemical resistance but is less effective against oils and aggressive chemicals, limiting its suitability for heavy-duty conveyor applications.
Flexibility and Mechanical Strength
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to weathering, making it ideal for conveyor belts requiring frequent bending or movement. Neoprene provides higher mechanical strength and enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion, ensuring durability in demanding industrial environments. Selecting between EPR and Neoprene depends on the specific conveyor application, balancing flexibility needs with mechanical stress tolerance.
Cost Efficiency and Longevity
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior cost efficiency for conveyor belts due to its lower material and maintenance expenses compared to neoprene. EPR exhibits excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, which extends the conveyor belt's operational longevity in harsh industrial environments. Neoprene provides enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength but comes with higher initial costs and potentially shorter service life under certain abrasive conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Conveyor Belt Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for conveyor belts exposed to harsh outdoor environments or extreme temperatures. Neoprene provides excellent oil, chemical, and abrasion resistance, which suits conveyor applications in industrial settings involving exposure to oils and chemicals. Selecting between EPR and neoprene depends on the specific operational conditions, such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress inherent to the conveyor belt application.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Neoprene for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com