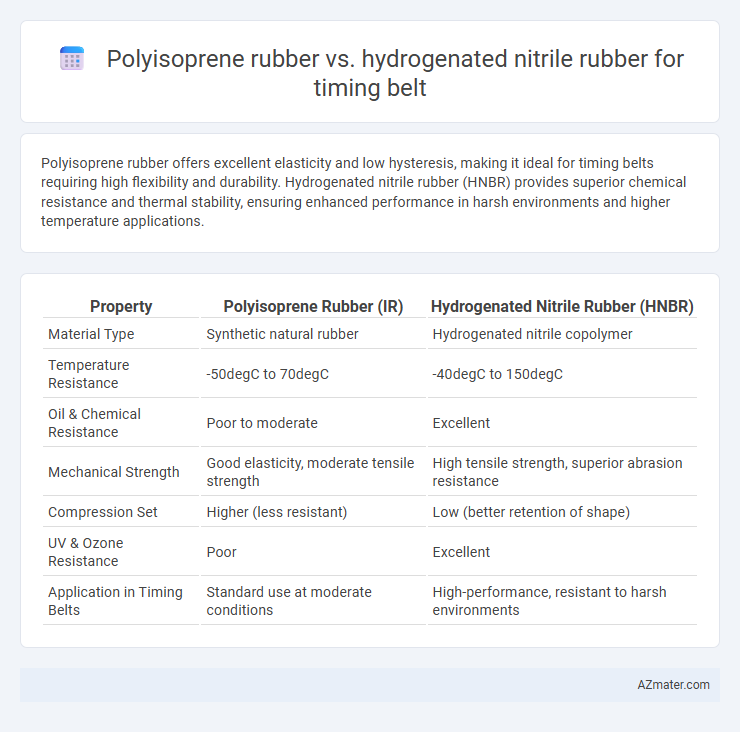
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and low hysteresis, making it ideal for timing belts requiring high flexibility and durability. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, ensuring enhanced performance in harsh environments and higher temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic natural rubber | Hydrogenated nitrile copolymer |
| Temperature Resistance | -50degC to 70degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Poor to moderate | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Good elasticity, moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, superior abrasion resistance |
| Compression Set | Higher (less resistant) | Low (better retention of shape) |
| UV & Ozone Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Application in Timing Belts | Standard use at moderate conditions | High-performance, resistant to harsh environments |
Introduction to Timing Belt Materials
Timing belts require materials with high abrasion resistance, heat resistance, and flexibility to ensure durable and efficient power transmission. Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and fatigue resistance but has limited heat and oil resistance compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). HNBR combines superior thermal stability, oil resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for timing belts exposed to harsh automotive environments.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and resilience, closely mimicking natural rubber properties, making it ideal for timing belts requiring flexibility and tensile strength. Its superior abrasion resistance and low compression set contribute to longer belt life and consistent performance under dynamic loads. Polyisoprene's excellent resistance to fatigue and aging outperforms hydrogenated nitrile rubber in applications focused on flexibility and impact resistance in timing belt systems.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength compared to Polyisoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for timing belt applications in automotive and industrial engines. HNBR maintains elasticity and performance under extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, while resisting oils, fuels, and ozone degradation. Its enhanced durability and resistance to wear significantly extend the timing belt's operational lifespan in demanding environments.
Mechanical Properties: Polyisoprene vs HNBR
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and low hysteresis, providing superior flexibility and resilience in timing belts, while Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and better performance under high temperatures and chemical exposure. HNBR timing belts withstand harsher mechanical stresses and have improved durability compared to polyisoprene, making them ideal for demanding automotive and industrial applications. Polyisoprene is preferred for quieter operation and flexibility, whereas HNBR excels in longevity and resistance to oil, heat, and wear.
Heat and Temperature Resistance
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits moderate heat resistance with an operational temperature range typically up to 80degC, making it less ideal for high-temperature timing belt applications. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior thermal stability, maintaining performance at temperatures up to 150degC and resists thermal degradation, ensuring long-lasting durability in demanding engine environments. The enhanced heat and temperature resistance of HNBR significantly reduces wear and prevents premature failure in timing belts exposed to elevated temperatures.
Chemical and Oil Resistance
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity but has limited chemical and oil resistance, making it less suitable for timing belts exposed to harsh oils and aggressive chemicals. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to a wide range of oils, fuels, and chemicals due to its saturated polymer backbone, enhancing durability and performance in automotive and industrial timing belt applications. HNBR's enhanced thermal stability and resistance to oxidative degradation ensure longer service life under demanding conditions compared to polyisoprene rubber.
Wear and Durability Comparison
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent flexibility and elasticity, providing superior wear resistance in timing belt applications under moderate temperatures but tends to degrade faster when exposed to oils and high heat. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates enhanced durability due to its exceptional resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, significantly extending the timing belt lifespan in harsh automotive environments. Wear analysis reveals HNBR outperforms polyisoprene by maintaining structural integrity and tensile strength over extended periods, making it the preferred choice for high-performance and industrial timing belts.
Cost Implications for Timing Belt Manufacturing
Polyisoprene rubber generally offers a lower raw material cost compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), making it a cost-effective choice for timing belt manufacturing. However, HNBR provides superior heat resistance and durability, potentially reducing warranty claims and maintenance expenses over the product lifecycle. Manufacturers must weigh initial material savings against long-term performance benefits when selecting between polyisoprene and hydrogenated nitrile rubber for timing belt applications.
Common Applications in Automotive Timing Belts
Polyisoprene rubber is frequently used in automotive timing belts due to its excellent flexibility and resistance to wear, making it ideal for smooth engine operation and noise reduction. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance, oil resistance, and mechanical strength, enhancing timing belt durability in high-temperature engine environments. Common applications for polyisoprene include standard passenger vehicles, while HNBR is preferred in performance and heavy-duty engines requiring extended service life and enhanced chemical resistance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Timing Belts
Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and high tensile strength, making it suitable for timing belts requiring precise elasticity and durability under moderate heat conditions. Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) provides superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure, ideal for timing belts operating in harsh automotive or industrial environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific application demands, with polyisoprene preferred for dynamic flexibility and HNBR favored for enhanced chemical and thermal stability in timing belt performance.
Infographic: Polyisoprene rubber vs Hydrogenated nitrile rubber for Timing belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com