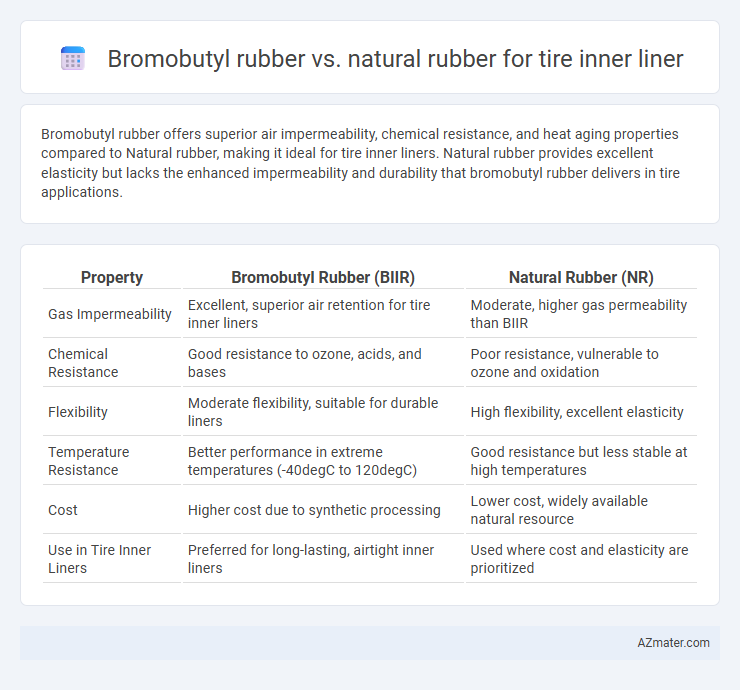
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior air impermeability, chemical resistance, and heat aging properties compared to Natural rubber, making it ideal for tire inner liners. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity but lacks the enhanced impermeability and durability that bromobutyl rubber delivers in tire applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bromobutyl Rubber (BIIR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Impermeability | Excellent, superior air retention for tire inner liners | Moderate, higher gas permeability than BIIR |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to ozone, acids, and bases | Poor resistance, vulnerable to ozone and oxidation |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, suitable for durable liners | High flexibility, excellent elasticity |
| Temperature Resistance | Better performance in extreme temperatures (-40degC to 120degC) | Good resistance but less stable at high temperatures |
| Cost | Higher cost due to synthetic processing | Lower cost, widely available natural resource |
| Use in Tire Inner Liners | Preferred for long-lasting, airtight inner liners | Used where cost and elasticity are prioritized |
Introduction: The Role of Inner Liners in Tire Performance
Bromobutyl rubber excels in tire inner liners due to its superior air retention and resistance to heat, chemicals, and aging compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and mechanical strength but lacks the impermeability and durability needed for prolonged tire performance. The choice between bromobutyl and natural rubber directly impacts tire longevity, safety, and overall efficiency by influencing air pressure retention and resistance to external factors.
Chemical Composition: Bromobutyl Rubber vs Natural Rubber
Bromobutyl rubber consists of a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, modified by bromine atoms to enhance its impermeability and chemical resistance. Natural rubber is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a hydrocarbon polymer that exhibits excellent elasticity but lower resistance to gases and chemicals. The bromine atoms in bromobutyl rubber create reactive sites that improve vulcanization and aging stability, making it superior for tire inner liners in terms of durability and air retention.
Air Retention Capabilities: A Comparative Analysis
Bromobutyl rubber exhibits superior air retention capabilities compared to natural rubber due to its low permeability and excellent resistance to gas diffusion, making it ideal for tire inner liners where maintaining air pressure over time is critical. Natural rubber, while offering high elasticity and tensile strength, is more susceptible to air leakage and oxygen permeation, leading to faster deflation rates. The enhanced impermeability of bromobutyl rubber results from its chemically stable halogenated butyl backbone, which effectively minimizes air loss and improves tire longevity.
Resistance to Permeation and Moisture
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior resistance to gas permeation compared to natural rubber, making it an ideal material for tire inner liners by significantly reducing air loss and maintaining tire pressure over time. Its low moisture permeability enhances the durability and long-term performance of tires in various environmental conditions. Natural rubber, while flexible and cost-effective, exhibits higher permeability to gases and moisture, which can lead to faster degradation and increased maintenance requirements.
Durability and Aging Performance
Bromobutyl rubber outperforms natural rubber in tire inner liner applications due to its superior chemical resistance and low permeability to gases, resulting in enhanced durability and longer-lasting air retention. Its superior resistance to ozone, heat, and oxidative aging ensures minimal degradation over time, maintaining tire integrity better than natural rubber. Natural rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and mechanical strength, is more susceptible to aging and environmental damage, leading to reduced overall lifespan in inner liner usage.
Flexibility and Processing Characteristics
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and excellent chemical resistance, making it a preferred choice for tire inner liners where airtightness is critical. Natural rubber provides greater flexibility and elasticity, enhancing tire comfort and resilience under dynamic loads but may suffer from inferior aging and ozone resistance. Processing bromobutyl rubber requires specialized equipment due to its lower unsaturation, while natural rubber processes more easily, allowing for faster curing and shaping during tire manufacturing.
Impact on Tire Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior air impermeability compared to natural rubber, significantly reducing tire rolling resistance and enhancing fuel efficiency. Its low gas permeability minimizes internal air loss, maintaining optimal tire pressure longer and improving vehicle mileage. In contrast, natural rubber's higher air permeability leads to more frequent inflation, increasing rolling resistance and fuel consumption.
Cost Considerations and Manufacturing Implications
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and chemical resistance, which reduces maintenance costs and extends tire life, but its raw material and production expenses are higher compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber is more cost-effective due to abundant availability and lower processing complexity, yet it requires more frequent replacement because of lower impermeability and aging resistance. Manufacturing with bromobutyl necessitates specialized equipment and longer curing times, impacting production throughput, whereas natural rubber allows faster processing but may compromise tire inner liner performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior chemical resistance and low gas permeability, significantly extending tire lifespan and reducing waste compared to natural rubber, which is less durable and prone to faster degradation. Natural rubber, derived from renewable latex sources, provides a more sustainable base material with a lower carbon footprint but requires extensive land use and can contribute to deforestation. The environmental impact of bromobutyl rubber is higher due to its synthetic production from fossil fuels, whereas natural rubber supports biodiversity and carbon sequestration when managed responsibly.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Inner Liner Material
Bromobutyl rubber offers superior air retention and chemical resistance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for modern tire inner liners that demand long-lasting performance. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and cost-effectiveness but may suffer from higher permeability and reduced durability under harsh conditions. Selecting bromobutyl rubber ensures enhanced tire lifespan and reliability, especially in applications requiring low air permeability and robust resistance to environmental factors.
Infographic: Bromobutyl rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire inner liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com