Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding seal applications. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but lacks the chemical and thermal stability of HNBR seals.
Table of Comparison
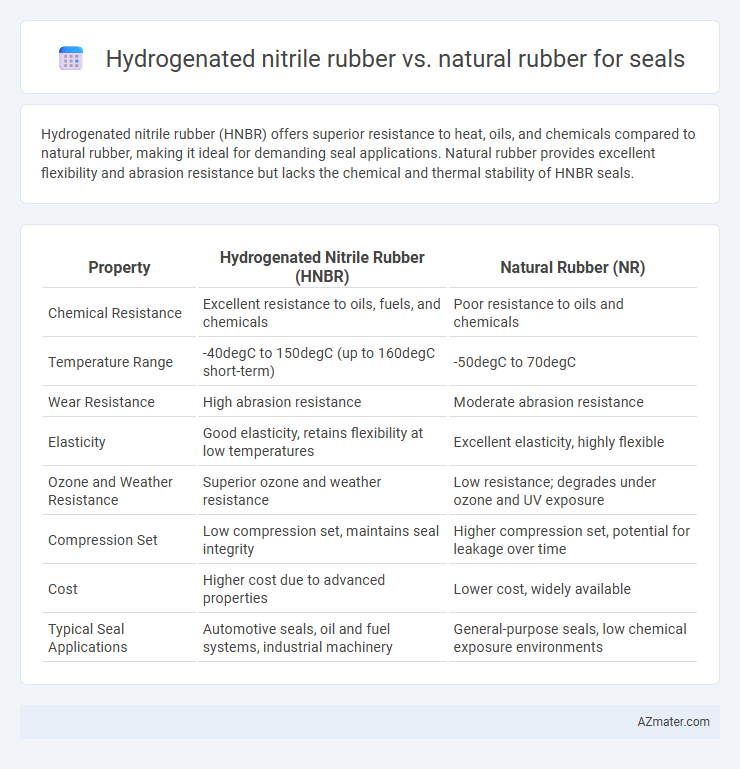
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor resistance to oils and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (up to 160degC short-term) | -50degC to 70degC |
| Wear Resistance | High abrasion resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity, retains flexibility at low temperatures | Excellent elasticity, highly flexible |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Superior ozone and weather resistance | Low resistance; degrades under ozone and UV exposure |
| Compression Set | Low compression set, maintains seal integrity | Higher compression set, potential for leakage over time |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Seal Applications | Automotive seals, oil and fuel systems, industrial machinery | General-purpose seals, low chemical exposure environments |
Introduction to Seal Materials: HNBR vs. Natural Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for demanding sealing applications in automotive and industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent flexibility and resilience but lacks the chemical and thermal stability required for high-performance seals. Seal materials selection depends on operating conditions, with HNBR preferred for durability under harsh conditions and natural rubber favored for general-purpose sealing where elasticity is critical.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) is a saturated polymer derived from the hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), characterized by enhanced resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals due to its reduced double bonds. Natural rubber (NR) consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a hydrocarbon polymer with unsaturated double bonds that provide excellent elasticity but lower chemical and thermal stability. The hydrogenation in HNBR improves chemical resistance and durability in seals compared to NR, making HNBR more suitable for harsh environments requiring resilience to oil, solvents, and high temperatures.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior performance in extreme temperatures compared to natural rubber, maintaining elasticity and tensile strength from -40degC to 150degC. Natural rubber tends to harden and lose flexibility below -20degC and degrades above 80degC, limiting its effectiveness in harsh thermal environments. HNBR's enhanced chemical structure provides better resistance to thermal aging, oxidation, and ozone, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial applications exposed to wide temperature ranges.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) demonstrates superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and oils compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for sealing applications in harsh environments. HNBR maintains its mechanical properties and elasticity when exposed to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and many aggressive chemicals, whereas natural rubber tends to degrade, swell, and lose strength under similar conditions. This enhanced chemical and oil resistance of HNBR ensures longer seal life and improved performance in automotive, industrial, and oilfield applications.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior mechanical properties and enhanced durability compared to natural rubber, exhibiting higher tensile strength, improved abrasion resistance, and better resilience to heat and chemical exposure. HNBR's molecular structure provides excellent resistance to ozone, oils, and oxidative degradation, significantly extending seal lifespan in demanding environments. Natural rubber, while flexible and cost-effective, has lower resistance to aging, heat, and chemicals, making it less suitable for high-performance sealing applications requiring long-term durability.
Aging and Weathering Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior aging and weathering resistance compared to natural rubber, maintaining elasticity and tensile strength under prolonged exposure to ozone, heat, and oxygen. Its molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to oxidation and thermal degradation, making HNBR ideal for seals in harsh environments. Natural rubber tends to degrade faster with exposure to UV light, ozone, and elevated temperatures, leading to cracking and loss of sealing performance over time.
Application Suitability in Various Industries
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, making it ideal for seals in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Natural rubber excels in applications requiring excellent flexibility, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, commonly used in consumer goods, footwear, and general industrial seals. Choosing between HNBR and natural rubber depends on the specific environmental exposure and mechanical demands within industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and transportation.
Cost and Availability Factors
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) typically costs more than natural rubber due to its enhanced chemical resistance and durability, which justifies the higher price in demanding sealing applications. Natural rubber is generally more affordable and widely available, benefiting from large-scale production and renewable sourcing. Availability of HNBR can be limited by specialized manufacturing processes, while natural rubber enjoys steady supply from tropical regions, influencing overall cost and procurement ease.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, resulting in longer seal life and reduced material waste. Natural rubber, derived from renewable latex sourced from rubber trees, boasts a lower carbon footprint and is biodegradable, promoting eco-friendly disposal. Choosing between HNBR and natural rubber seals requires balancing the longevity and performance benefits of HNBR against the renewable, sustainable attributes of natural rubber.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Seal Material
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and chemicals compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for seals in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, suitable for applications requiring high resilience and dynamic performance. Selecting the right seal material depends on specific operational conditions such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Natural rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com