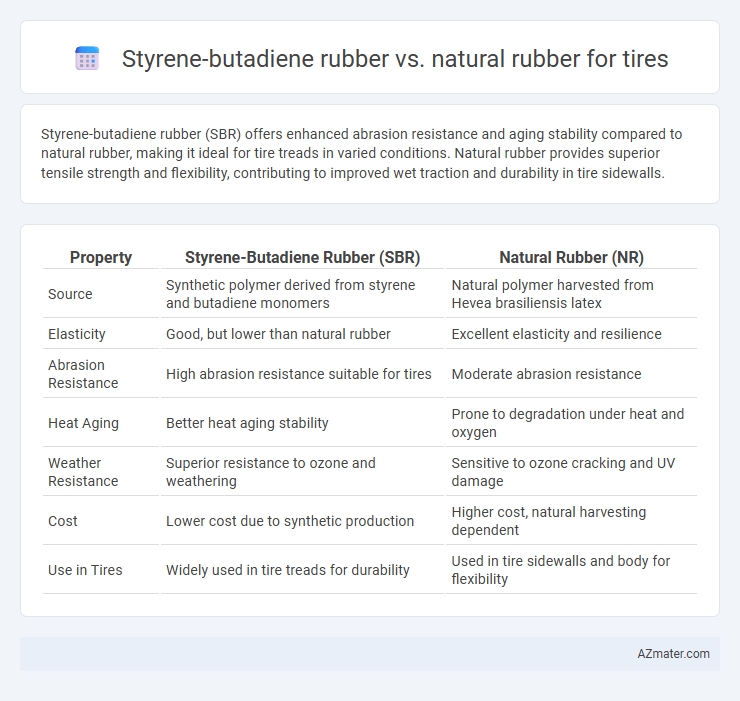
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire treads in varied conditions. Natural rubber provides superior tensile strength and flexibility, contributing to improved wet traction and durability in tire sidewalls.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic polymer derived from styrene and butadiene monomers | Natural polymer harvested from Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Elasticity | Good, but lower than natural rubber | Excellent elasticity and resilience |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance suitable for tires | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Heat Aging | Better heat aging stability | Prone to degradation under heat and oxygen |
| Weather Resistance | Superior resistance to ozone and weathering | Sensitive to ozone cracking and UV damage |
| Cost | Lower cost due to synthetic production | Higher cost, natural harvesting dependent |
| Use in Tires | Widely used in tire treads for durability | Used in tire sidewalls and body for flexibility |
Introduction to Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Natural Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer composed of styrene and butadiene, widely used in tire manufacturing for its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. Natural rubber, derived from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, offers superior tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for providing durability and flexibility in tires. The combination of SBR and natural rubber optimizes performance by balancing wear resistance with elasticity in tire applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic polymer composed of styrene and butadiene monomers, produced through emulsion or solution polymerization, offering enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability. Natural rubber (NR) consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene derived from rubber tree latex, processed via coagulation and drying, giving it superior elasticity and tensile strength. In tire manufacturing, SBR's synthetic composition allows for controlled physical properties and improved wear, while NR's natural composition contributes to excellent resilience and low heat buildup, often blending both to optimize performance and durability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and better aging stability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire treads exposed to harsh road conditions. Natural rubber exhibits higher tensile strength and elasticity, providing enhanced grip and comfort but lower resistance to heat and ozone degradation. The choice between SBR and natural rubber in tire manufacturing depends on balancing durability with performance characteristics like traction and wear resistance.
Performance in Various Weather Conditions
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and better aging stability than natural rubber, making it more durable in diverse weather conditions, especially in wet and cold climates. Natural rubber excels in flexibility and resilience, providing excellent grip and traction in warm and dry environments due to its higher tensile strength and elasticity. Tires combining SBR and natural rubber optimize performance by balancing wear resistance with superior wet traction and low-temperature adaptability.
Tread Wear and Longevity Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior tread wear resistance compared to natural rubber, making it a preferred choice for tire treads in terms of durability and longevity. SBR's abrasion resistance and heat aging properties contribute to extended tire life under a wide range of driving conditions, whereas natural rubber provides excellent grip and elasticity but tends to wear faster. The longevity of tires using SBR compounds is enhanced by their balanced mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors like ozone and UV exposure.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers lower rolling resistance compared to natural rubber, enhancing tire fuel efficiency by reducing energy loss during rolling. Tires with higher SBR content typically improve fuel economy by minimizing friction between the tire and the road surface. Although natural rubber provides superior elasticity and grip, its higher rolling resistance results in decreased fuel efficiency relative to SBR-based tires.
Wet and Dry Traction Capabilities
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior wear resistance and better wet traction compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for tire treads used in rainy or slippery conditions. Natural rubber excels in dry traction due to its elasticity and resilience, providing enhanced grip and handling on dry roads. Combining SBR for wet traction and natural rubber for dry performance optimizes tire safety and durability across varying driving environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) derives from petrochemical sources, leading to higher carbon emissions and non-renewable resource depletion compared to natural rubber, which is harvested from rubber trees with a renewable lifecycle and carbon sequestration benefits. Natural rubber production supports biodiversity and soil health when managed sustainably, whereas SBR's synthetic manufacturing involves energy-intensive processes and generates more environmental pollutants. Biodegradability of natural rubber offers reduced long-term ecological impact, contrasting with synthetic rubber's persistence and challenges in recycling or disposal.
Cost Analysis: SBR vs Natural Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a cost advantage over natural rubber due to its synthetic production and stable pricing unaffected by agricultural fluctuations. Natural rubber prices are subject to volatility influenced by weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and geopolitical factors in major producing countries like Thailand and Indonesia. The consistent supply and lower raw material costs make SBR a more economical choice for tire manufacturing in large-scale production.
Industry Applications and Market Trends
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely favored in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for passenger car and truck tires. Natural rubber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity, enhancing wet traction and durability in heavy-duty and off-road tires. The market trend shows increasing demand for SBR in eco-friendly, fuel-efficient tire formulations, while natural rubber maintains steady growth driven by high-performance and specialty tire segments.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Natural rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com