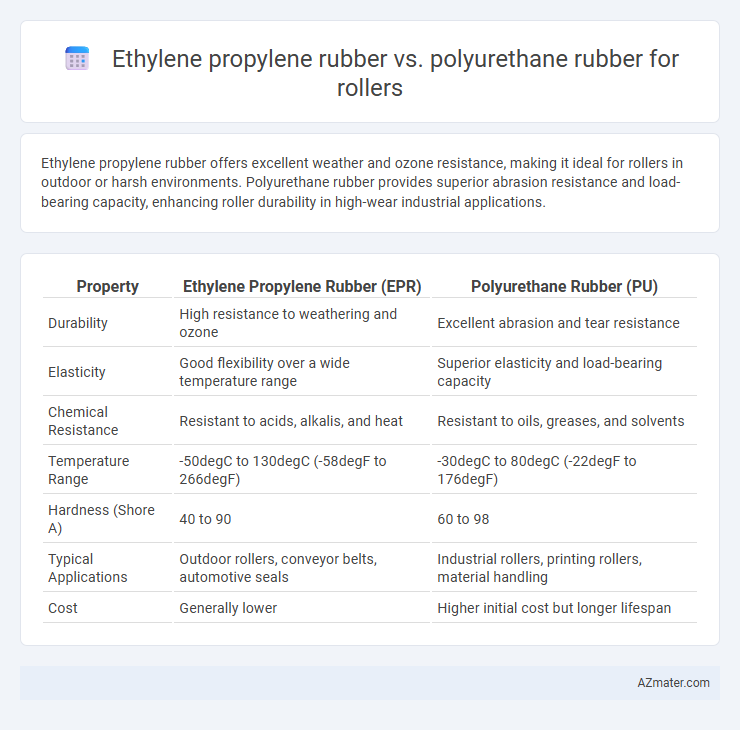
Ethylene propylene rubber offers excellent weather and ozone resistance, making it ideal for rollers in outdoor or harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, enhancing roller durability in high-wear industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to weathering and ozone | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance |
| Elasticity | Good flexibility over a wide temperature range | Superior elasticity and load-bearing capacity |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and heat | Resistant to oils, greases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 130degC (-58degF to 266degF) | -30degC to 80degC (-22degF to 176degF) |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 40 to 90 | 60 to 98 |
| Typical Applications | Outdoor rollers, conveyor belts, automotive seals | Industrial rollers, printing rollers, material handling |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
Introduction to Roller Materials: Ethylene Propylene vs Polyurethane
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent weather resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability, making it ideal for rollers used in outdoor or harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and durability, which enhances roller performance in heavy-duty industrial applications. Choosing between Ethylene propylene and Polyurethane rollers depends on the specific operational demands such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and wear resistance requirements.
Key Material Properties of Ethylene Propylene Rubber
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) offers excellent chemical resistance, superior weatherability, and high elasticity, making it ideal for roller applications exposed to harsh environments and varying temperatures. Its low compression set and outstanding resistance to ozone and UV radiation ensure prolonged durability and consistent performance compared to Polyurethane Rubber. EPR also exhibits good electrical insulating properties and maintains flexibility at low temperatures, enhancing roller lifespan in demanding industrial settings.
Core Characteristics of Polyurethane Rubber for Rollers
Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and superior tear strength, making it ideal for rollers subject to heavy wear and impact. Its high load-bearing capacity and excellent elasticity ensure longer service life and consistent performance in demanding industrial applications. The material also provides outstanding resistance to oils, chemicals, and environmental factors, enhancing durability compared to ethylene propylene rubber.
Durability Comparison: EPDM vs Polyurethane in Industrial Rollers
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemical exposure, making it highly durable in harsh industrial environments for rollers. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, resulting in longer wear life under high-load and dynamic conditions. For industrial rollers, polyurethane outperforms EPDM in durability where mechanical stress and wear are dominant factors, whereas EPDM excels in environments with significant exposure to chemicals and outdoor elements.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers moderate abrasion resistance but excels in weather and chemical resistance, making it suitable for environments with exposure to oils and ozone. Polyurethane rubber, however, demonstrates superior abrasion and wear resistance due to its high tensile strength and elasticity, enabling longer service life in heavy-duty roller applications. For roller surfaces requiring enhanced durability against abrasive materials, polyurethane rubber generally outperforms ethylene propylene rubber.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance: EPDM vs Polyurethane
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and a wide range of chemicals, including acids and alkalis, making it ideal for outdoor and harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane rubber, while less resistant to strong acids and alkalies, excels in resisting oil, grease, and abrasion, providing enhanced durability in mechanical applications. EPDM's high tolerance to heat and oxidation contrasts with polyurethane's vulnerability to hydrolysis and UV degradation, influencing their suitability for specific roller applications based on environmental exposure.
Cost Efficiency and Lifespan Analysis
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior cost efficiency for rollers due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to polyurethane rubber. While EPR provides excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, polyurethane rubber exhibits significantly longer lifespan and enhanced abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear roller applications. Analyzing total cost of ownership, polyurethane's durability offsets its initial higher investment through reduced maintenance and replacement frequency.
Application Suitability: Industry Use Cases
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) demonstrates superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for rollers used in outdoor and automotive industry applications. Polyurethane rubber offers exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, preferred in heavy-duty industrial rollers for conveyor systems, printing presses, and packaging machinery. EPR suits applications requiring flexibility and chemical resistance, while polyurethane excels in high-wear environments demanding durability and resilience.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) rollers exhibit superior resistance to environmental degradation, reducing maintenance frequency compared to polyurethane rollers, which may require more frequent upkeep due to their susceptibility to abrasion and chemical exposure. Polyurethane rollers offer enhanced abrasion resistance, extending their operational lifespan in high-wear applications, but their eventual replacement demands careful inspection for cracks and material fatigue. Maintenance strategies for EPR rollers prioritize monitoring for ozone and heat deterioration, while polyurethane rollers necessitate regular assessment of surface wear to optimize replacement intervals and minimize downtime.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Roller Application
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature roller applications. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and mechanical strength, suited for demanding industrial roller environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on operational conditions, with EPR preferred for environmental durability and polyurethane favored for durability under mechanical stress.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com