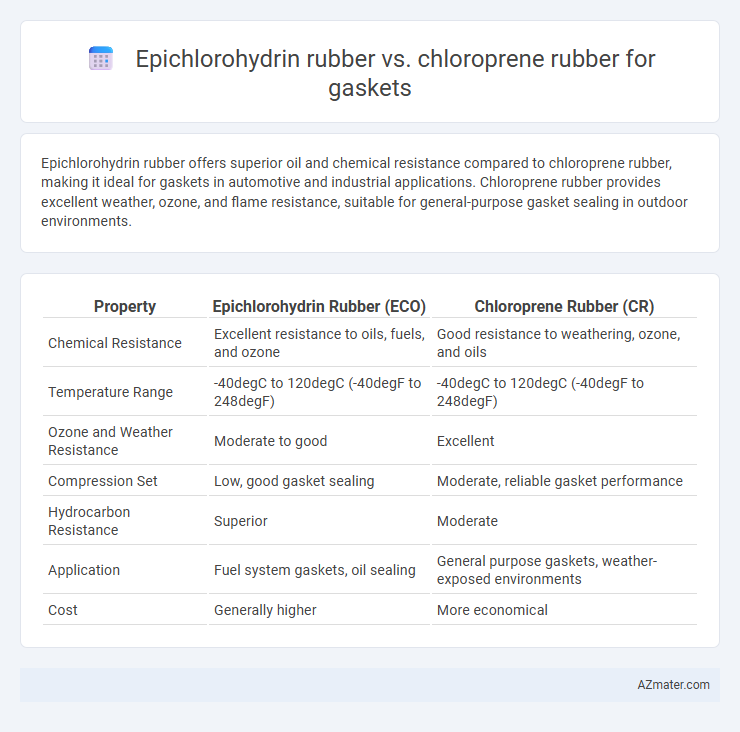
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and flame resistance, suitable for general-purpose gasket sealing in outdoor environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone | Good resistance to weathering, ozone, and oils |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Ozone and Weather Resistance | Moderate to good | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low, good gasket sealing | Moderate, reliable gasket performance |
| Hydrocarbon Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Application | Fuel system gaskets, oil sealing | General purpose gaskets, weather-exposed environments |
| Cost | Generally higher | More economical |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin and Chloroprene Rubbers
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits outstanding resistance to oil, fuel, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications requiring durability under chemical exposure. Chloroprene rubber (CR), commonly known as Neoprene, offers excellent flexibility, resistance to heat, and moderate chemical resistance, favored in general-purpose gasket manufacturing where elastic recovery and weather resistance are essential. Both rubbers differ significantly in chemical structure, with ECO characterized by epichlorohydrin units imparting high chemical stability, while CR's polychloroprene backbone provides balanced mechanical properties and aging resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a copolymer of epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide, characterized by its polar ether groups that provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, while chloroprene rubber (CR), composed of polychloroprene units with chlorine atoms attached to the polymer backbone, offers superior weather, flame, and chemical resistance. The molecular structure of ECO imparts flexibility and low gas permeability, making it suitable for fuel-resistant gaskets, whereas CR's chlorinated diene structure delivers enhanced mechanical strength and abrasion resistance for demanding sealing applications. The difference in chemical composition influences their performance: ECO excels in hydrocarbon resistance and low compression set, while CR withstands harsh environmental conditions and maintains elasticity over a wide temperature range.
Key Physical Properties of Both Rubber Types
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering with a tensile strength ranging from 10 to 20 MPa and elongation at break up to 350%, making it suitable for gasketing in automotive and industrial applications requiring resilience to chemicals and heat up to 150degC. Chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) offers superior flame resistance, good chemical stability, and tensile strength between 7 to 17 MPa with elongation around 300%, providing durable sealing performance under moderate temperature conditions up to 120degC. Both materials deliver effective gasketing solutions, but epichlorohydrin rubber is preferred for enhanced oil resistance, whereas chloroprene excels in environments requiring resistance to weathering and flames.
Temperature Resistance: Epichlorohydrin vs Chloroprene
Epichlorohydrin rubber demonstrates superior temperature resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, maintaining stability in continuous use up to 120degC and short-term peaks reaching 150degC. Chloroprene rubber typically withstands temperatures up to 100degC continuously and short-term exposure to approximately 120degC, making it less suitable for higher thermal conditions. These temperature resistance characteristics position epichlorohydrin as the preferred choice for gaskets subjected to elevated heat environments.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Capabilities
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance, particularly against aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, and greases, making it highly suitable for gasketing applications exposed to fuels and lubricants. Chloroprene rubber, while exhibiting moderate chemical resistance, excels in durability against weathering, ozone, and flame, but has lower resistance to petroleum-based oils than epichlorohydrin. The enhanced oil resistance of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures longer gasket performance in environments with aggressive oils and chemicals, whereas chloroprene is often preferred for general-purpose sealing with balanced chemical and environmental resilience.
Mechanical Performance in Gasket Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance with excellent abrasion resistance, making it highly durable in gasket applications exposed to fuel and lubricants. Chloroprene rubber offers balanced mechanical performance with good flexibility, weather resistance, and moderate chemical stability, suitable for general-purpose gaskets in automotive and industrial use. For high-stress environments requiring enhanced mechanical strength and oil resistance, epichlorohydrin rubber provides a notable advantage over chloroprene rubber in maintaining gasket integrity.
Aging and Ozone Resistance Differences
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone and aging compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The molecular structure of epichlorohydrin resists oxidative degradation and ozone cracking, extending gasket lifespan in outdoor and industrial applications. In contrast, chloroprene rubber, while providing moderate ozone resistance, tends to harden and crack faster under prolonged exposure, reducing its effectiveness in long-term sealing solutions.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers cost advantages over chloroprene rubber due to lower raw material expenses and simpler synthesis processes, making it a budget-friendly choice for gasket manufacturing. Chloroprene rubber, while generally more expensive, benefits from widespread availability and established supply chains that ensure consistent procurement for industrial applications. Cost-sensitive projects with moderate demand favor epichlorohydrin, whereas high-volume or specialized gaskets often rely on the dependable availability of chloroprene rubber.
Typical Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Epichlorohydrin rubber is extensively used for gaskets requiring excellent resistance to oil, fuels, and weathering, making it suitable for automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications. Chloroprene rubber, known for its balanced chemical, ozone, and aging resistance, is preferred in gasket manufacturing for HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and water sealing solutions. Both elastomers offer durable sealing properties, but epichlorohydrin excels in hydrocarbon environments while chloroprene is favored for general-purpose, weather-resistant gasket applications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber provides excellent flexibility, moderate chemical resistance, and strong sealing properties, suitable for general-purpose gaskets requiring durability and resilience. Choosing between Epichlorohydrin and Chloroprene rubber ultimately depends on specific application demands such as exposure conditions, temperature range, and chemical compatibility to ensure optimal gasket performance and longevity.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com