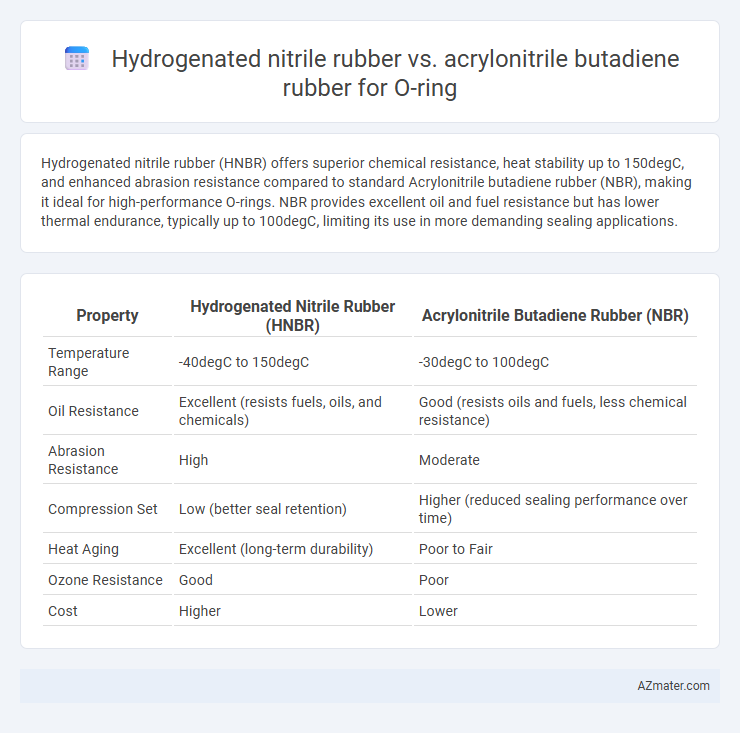
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, heat stability up to 150degC, and enhanced abrasion resistance compared to standard Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-performance O-rings. NBR provides excellent oil and fuel resistance but has lower thermal endurance, typically up to 100degC, limiting its use in more demanding sealing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -30degC to 100degC |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent (resists fuels, oils, and chemicals) | Good (resists oils and fuels, less chemical resistance) |
| Abrasion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Compression Set | Low (better seal retention) | Higher (reduced sealing performance over time) |
| Heat Aging | Excellent (long-term durability) | Poor to Fair |
| Ozone Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to O-Ring Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) are common materials used in O-ring manufacturing, each offering distinct chemical and mechanical properties. HNBR is valued for its superior resistance to heat, oils, and abrasion, making it ideal for demanding automotive and industrial sealing applications. NBR provides excellent resistance to petroleum-based fluids and good elasticity, often chosen for general-purpose seals in fuel systems and hydraulic components.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a high-performance elastomer known for its superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical degradation compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR). Its saturated polymer backbone enhances thermal stability, allowing HNBR O-rings to maintain elasticity and mechanical properties in temperatures up to 150degC or higher. This makes HNBR an ideal choice for demanding applications such as automotive seals, industrial machinery, and oilfield equipment where durability and resistance to harsh environments are critical.
Understanding Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it a preferred choice for O-rings in automotive and industrial applications. NBR's nitrile content typically ranges from 18% to 50%, balancing flexibility with aggressive chemical resistance, especially against petroleum-based fluids. Compared to Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR), NBR provides cost-effective sealing performance but has lower thermal stability and aging resistance, limiting its use in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) features a saturated hydrocarbon backbone achieved through hydrogenation of the nitrile butadiene rubber, significantly enhancing its thermal and chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), which has an unsaturated carbon-carbon backbone. The saturation in HNBR's polymer chain reduces susceptibility to ozone, heat, and oxidation, while NBR's acrylonitrile content provides good oil resistance but lower durability under high temperatures and harsh chemicals. These structural differences make HNBR preferable for extreme environments and NBR suitable for moderate applications requiring oil resistance in O-ring seals.
Temperature Resistance: HNBR vs NBR
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior temperature resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), maintaining performance in continuous service up to 150degC and short-term exposure up to 160degC. In contrast, NBR typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC continuously, with short-term limits near 120degC, limiting its application in high-heat environments. This enhanced thermal stability makes HNBR more suitable for O-rings used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sealing applications requiring extended heat exposure.
Chemical Compatibility and Resistance
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), particularly against oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons, making it ideal for demanding environments where exposure to aggressive chemicals is frequent. NBR displays excellent resistance to many petroleum-based fluids but can degrade faster when exposed to ozone, weathering, and certain solvents, limiting its application in harsh conditions. HNBR's enhanced hydrogenation process improves its thermal stability and resistance to heat, ozone, and oxidative degradation, providing a longer service life for O-rings exposed to challenging chemical environments.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and enhanced thermal stability compared to acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), making it ideal for high-performance O-ring applications. HNBR exhibits excellent aging resistance and resilience under oxidative and chemical exposure, improving long-term durability in harsh environments. In contrast, NBR provides good flexibility and oil resistance but has lower mechanical strength and shorter lifespan when exposed to elevated temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) generally commands a higher price than acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) due to its superior chemical and heat resistance, which warrants its use in demanding O-ring applications. NBR offers greater availability and lower cost, making it the preferred choice for less aggressive environments and budget-sensitive projects. When selecting O-ring materials, balancing the initial investment in HNBR against the extended service life and reduced maintenance can influence overall cost-effectiveness.
Typical Applications in O-Ring Sealing
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) O-rings are ideal for high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments, commonly used in automotive, oil and gas, and industrial hydraulic sealing applications. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) O-rings excel in fuel handling, pneumatic systems, and general-purpose sealing due to their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Both materials offer reliable sealing performance, but HNBR provides superior heat and ozone resistance, while NBR is preferred for cost-effective, fuel-compatible applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Takeaways
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance up to 150degC and enhanced chemical stability, making it ideal for dynamic O-ring applications in harsh environments. Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) provides excellent oil, fuel, and abrasion resistance, suitable for static O-rings in automotive and industrial seals. Selecting between HNBR and NBR depends on temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements to ensure optimal O-ring performance and durability.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for O-ring
 azmater.com
azmater.com