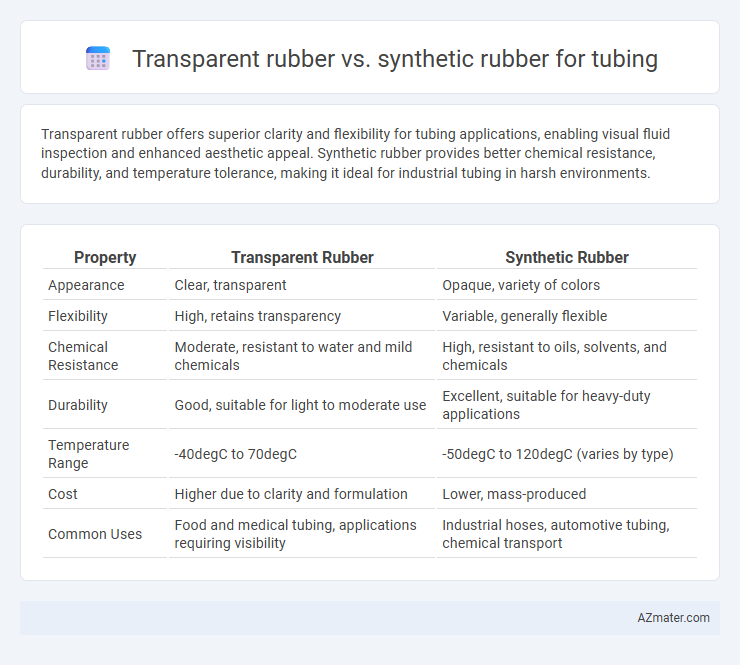
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity and flexibility for tubing applications, enabling visual fluid inspection and enhanced aesthetic appeal. Synthetic rubber provides better chemical resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance, making it ideal for industrial tubing in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, transparent | Opaque, variety of colors |
| Flexibility | High, retains transparency | Variable, generally flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resistant to water and mild chemicals | High, resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Durability | Good, suitable for light to moderate use | Excellent, suitable for heavy-duty applications |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 70degC | -50degC to 120degC (varies by type) |
| Cost | Higher due to clarity and formulation | Lower, mass-produced |
| Common Uses | Food and medical tubing, applications requiring visibility | Industrial hoses, automotive tubing, chemical transport |
Introduction: The Role of Rubber Tubing in Industry
Rubber tubing serves as a critical component across various industries, enabling the safe and efficient transfer of liquids and gases. Transparent rubber tubing allows for visual monitoring of fluid flow, making it essential in medical, laboratory, and food processing applications. Synthetic rubber tubing, characterized by enhanced chemical resistance and durability, is favored in automotive, chemical, and industrial manufacturing sectors where performance under harsh conditions is paramount.
What is Transparent Rubber?
Transparent rubber is a type of elastomer characterized by its clear, see-through appearance, commonly used in tubing applications where visibility of fluid flow is crucial. Unlike synthetic rubber, which can vary in opacity and is typically engineered for strength and chemical resistance, transparent rubber offers the advantage of easy inspection and leak detection. Materials such as silicone and polyurethane are popular transparent rubbers, providing flexibility, durability, and biocompatibility essential for medical, pharmaceutical, and food industry tubing.
Understanding Synthetic Rubber: Types and Properties
Synthetic rubber used in tubing primarily includes types like EPDM, nitrile, and silicone, each offering distinct chemical and temperature resistance suited to various industrial applications. EPDM excels in weather and ozone resistance, nitrile is preferred for oil and fuel handling, while silicone provides exceptional flexibility and thermal stability from -60degC to 230degC. Transparent rubber tubing, often made from silicon or polyurethane, offers clarity for visual monitoring but may have different mechanical and chemical resistance properties compared to opaque synthetic rubbers.
Key Differences Between Transparent Rubber and Synthetic Rubber
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity and visual inspection capabilities, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility of fluid flow within tubing. Synthetic rubber, including nitrile and EPDM variants, provides enhanced chemical resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance, suitable for harsh environments and industrial uses. Key differences lie in transparency versus performance properties such as flexibility, chemical resistance, and environmental stability.
Clarity and Aesthetics: Impact on Tubing Applications
Transparent rubber offers superior clarity compared to synthetic rubber, making it ideal for applications where visibility of fluid flow or internal components is critical. The high transparency enhances aesthetic appeal in medical devices, food processing, and cosmetic industries, ensuring clean and professional presentation. Synthetic rubber, while durable, often exhibits a cloudy or opaque appearance, limiting its use in applications demanding clear visual monitoring.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Transparent rubber tubing offers excellent flexibility and clarity but generally has lower durability and chemical resistance compared to synthetic rubber options like EPDM or Viton. Synthetic rubber tubing excels in withstanding harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and mechanical wear, making it more suitable for industrial applications requiring robust performance. Choosing between transparent and synthetic rubber tubing depends on balancing the need for visibility with the demands for enhanced durability and chemical resistance.
Flexibility and Performance Under Pressure
Transparent rubber tubing offers excellent flexibility, allowing for easy bending and maneuverability in various applications, while synthetic rubber tubing provides superior performance under high pressure due to its enhanced tensile strength and resistance to deformation. The molecular structure of synthetic rubber materials like nitrile or EPDM enhances durability and prevents cracking when subjected to intense stress, outperforming transparent rubbers such as silicone in demanding pressure environments. Selecting synthetic rubber tubing ensures reliable long-term performance in high-pressure systems, whereas transparent rubber tubing is preferred when visual fluid monitoring and moderate flexibility are required.
Cost Analysis: Transparent vs Synthetic Rubber Tubing
Transparent rubber tubing generally incurs higher material and manufacturing costs compared to synthetic rubber due to the specialized polymers and processing techniques required for clarity. Synthetic rubber tubing offers a cost-effective alternative with broad availability and easier production, often resulting in lower overall expenses for large-scale applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including durability and chemical resistance, is essential when deciding between transparent and synthetic rubber tubing for specific industrial uses.
Typical Applications: Choosing the Right Tubing Material
Transparent rubber tubing excels in medical and pharmaceutical applications due to its clarity, allowing for easy visual inspection of fluid flow and contamination detection. Synthetic rubber tubing, such as nitrile or silicone, is preferred in industrial and automotive settings for its superior chemical resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance. Selecting the right tubing material depends on application-specific requirements like transparency for monitoring or resistance to chemicals and environmental factors for longevity.
Conclusion: Making the Best Choice for Your Needs
Choosing between transparent rubber and synthetic rubber for tubing depends on factors such as chemical resistance, flexibility, and clarity requirements. Transparent rubber offers excellent visibility for fluid monitoring and moderate chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications needing visual inspection. Synthetic rubber provides superior durability and resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals, better suited for heavy-duty or industrial tubing needs.
Infographic: Transparent rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Tubing
 azmater.com
azmater.com