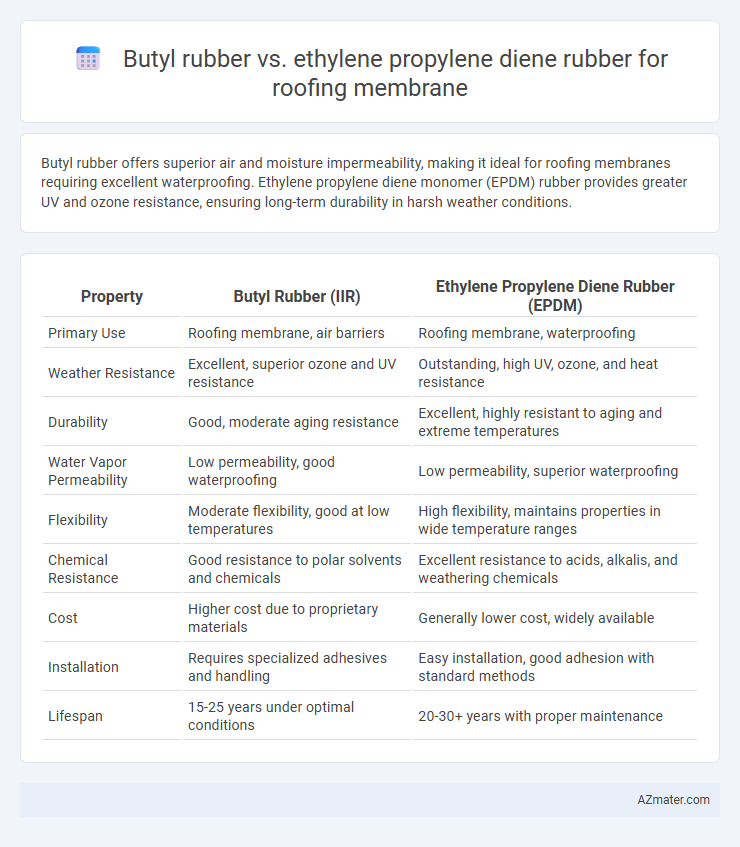
Butyl rubber offers superior air and moisture impermeability, making it ideal for roofing membranes requiring excellent waterproofing. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber provides greater UV and ozone resistance, ensuring long-term durability in harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Roofing membrane, air barriers | Roofing membrane, waterproofing |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent, superior ozone and UV resistance | Outstanding, high UV, ozone, and heat resistance |
| Durability | Good, moderate aging resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to aging and extreme temperatures |
| Water Vapor Permeability | Low permeability, good waterproofing | Low permeability, superior waterproofing |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, good at low temperatures | High flexibility, maintains properties in wide temperature ranges |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to polar solvents and chemicals | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and weathering chemicals |
| Cost | Higher cost due to proprietary materials | Generally lower cost, widely available |
| Installation | Requires specialized adhesives and handling | Easy installation, good adhesion with standard methods |
| Lifespan | 15-25 years under optimal conditions | 20-30+ years with proper maintenance |
Introduction to Roofing Membranes
Butyl rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) are two prominent materials used in roofing membranes, each offering unique properties for weather resistance and durability. Butyl rubber provides excellent impermeability to air and moisture, making it ideal for waterproofing applications in roofing systems. EPDM excels in flexibility and UV resistance, allowing it to withstand extreme temperatures and prolonged sun exposure, which are critical factors for long-lasting roofing membranes.
What is Butyl Rubber?
Butyl rubber, a synthetic elastomer composed primarily of isobutylene with small amounts of isoprene, offers exceptional impermeability to gases and superior weather resistance, making it ideal for roofing membranes. It provides excellent resistance to UV rays, ozone, and moisture, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environmental conditions. Compared to ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), butyl rubber exhibits lower permeability and enhanced chemical resistance, contributing to stronger waterproofing performance in roofing applications.
What is Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM)?
Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber (EPDM) is a synthetic rubber known for its exceptional resistance to weathering, UV rays, and ozone, making it a preferred material for roofing membranes. EPDM exhibits excellent elasticity and durability in extreme temperatures, providing long-lasting protection against water infiltration and environmental damage. Unlike Butyl rubber, EPDM offers superior flexibility and is easier to install, often resulting in lower maintenance costs for commercial and residential roofing applications.
Key Material Properties Compared
Butyl rubber offers exceptional impermeability and excellent resistance to gases and chemicals, making it ideal for roofing membranes exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) provides superior UV and ozone resistance, along with excellent flexibility at low temperatures, ensuring durability in diverse climates. Both materials exhibit strong tensile strength and weathering resistance, but Butyl rubber's superior gas barrier contrasts with EPDM's enhanced resilience to solar radiation and temperature fluctuations.
Weather Resistance: Butyl vs EPDM
Butyl rubber roofing membranes exhibit excellent resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperature fluctuations, maintaining flexibility in both hot and cold climates. EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) roofing membranes are highly weather-resistant, particularly effective against UV rays, ozone, and moisture, thus preventing cracking and degradation over time. While both materials provide superior durability, EPDM generally offers better long-term resistance to weathering, making it a preferred choice for extreme exposure conditions.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Butyl rubber roofing membranes offer exceptional flexibility and are renowned for their ease of installation due to their excellent elongation and self-adhesive properties, allowing seamless application even on complex roof shapes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) roofing membranes also provide high flexibility but require more meticulous installation techniques, such as the use of adhesives or mechanical fastening, to ensure proper sealing and durability. Both materials accommodate temperature fluctuations well, but butyl rubber's superior tackiness often results in faster, more efficient installation processes.
Longevity and Durability
Butyl rubber roofing membranes exhibit exceptional longevity due to their superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, and weathering, typically lasting 20-30 years with minimal degradation. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) membranes also provide high durability and can last 25-30 years, with excellent flexibility and resistance to thermal cycling and chemical exposure. However, Butyl rubber generally offers better impermeability and resistance to air and gas infiltration, enhancing long-term performance in extreme environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison
Butyl rubber roofing membranes generally involve higher initial material costs compared to ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) due to their superior impermeability and UV resistance. EPDM membranes offer a more cost-effective solution for large-scale roofing projects, as their production and installation expenses are typically lower while maintaining adequate durability. Long-term maintenance and repair costs for butyl rubber can be more economical because of its enhanced weathering properties, balancing out the upfront price differences over the roof's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Butyl rubber roofing membranes exhibit superior impermeability and resistance to weathering, contributing to longer roof lifespan and reduced material waste. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) membranes are highly recyclable and often produced from sustainable raw materials, enhancing their environmental profile. Both materials offer low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, but EPDM's recyclability typically results in lower overall environmental impact compared to butyl rubber.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Roof
Butyl rubber excels in roofing membranes requiring superior impermeability and resistance to gas and moisture, making it ideal for flat roofs and low-slope applications prone to water pooling. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers exceptional UV and ozone resistance, flexibility in extreme temperatures, and durability, which suits it best for exposed roofs in varying climates. Selecting Butyl rubber benefits roofing systems prioritizing airtight seals, while EPDM is optimal for long-lasting, weather-resilient roof membranes.
Infographic: Butyl rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene rubber for Roofing membrane
 azmater.com
azmater.com