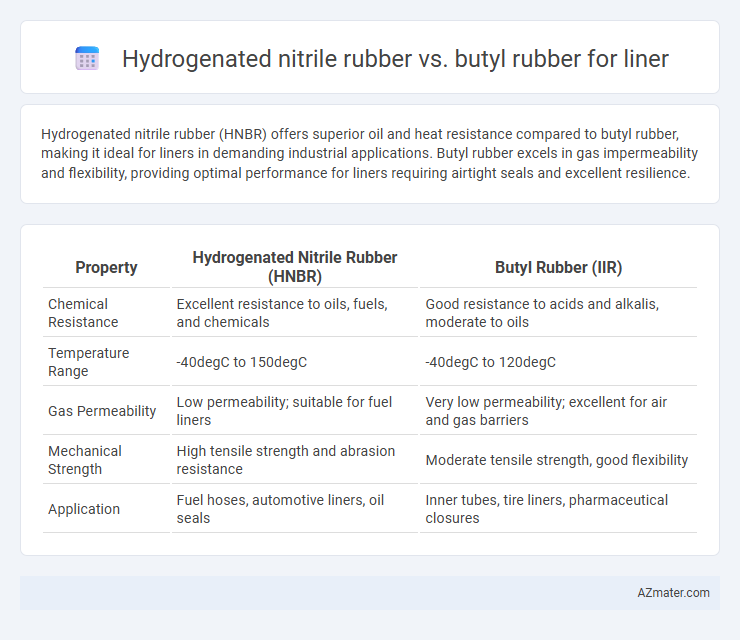
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior oil and heat resistance compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for liners in demanding industrial applications. Butyl rubber excels in gas impermeability and flexibility, providing optimal performance for liners requiring airtight seals and excellent resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to acids and alkalis, moderate to oils |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Gas Permeability | Low permeability; suitable for fuel liners | Very low permeability; excellent for air and gas barriers |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength, good flexibility |
| Application | Fuel hoses, automotive liners, oil seals | Inner tubes, tire liners, pharmaceutical closures |
Introduction to Liner Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, heat stability, and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-performance liner applications in automotive and industrial seals. Butyl rubber provides excellent air impermeability and flexibility, making it suitable for liners requiring low gas permeability and good damping properties. Selection between HNBR and butyl rubber depends on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to the liner's intended environment.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 150degC, and durability compared to traditional nitrile rubber, making it ideal for liner applications exposed to harsh environments. Its saturated polymer backbone enhances resistance to oxidation, ozone, and heat, outperforming standard nitrile and butyl rubber in performance longevity under mechanical stress. HNBR liners provide excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals, presenting a balanced solution where both elasticity and durability are critical.
Overview of Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber (IIR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent impermeability to gases, making it a preferred choice for inner linings in tires and protective gloves. Its superior resistance to heat, ozone, and chemical attack ensures durability and long service life compared to hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR). The unique methyl and isobutylene composition in butyl rubber provides exceptional air retention and flexibility, crucial for maintaining tire pressure and enhancing liner performance.
Key Properties Comparison: HNBR vs Butyl Rubber
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior heat resistance up to 150degC and enhanced resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion compared to butyl rubber, which excels in gas impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures down to -40degC. Butyl rubber demonstrates excellent air retention and ozone resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring airtight seals, whereas HNBR provides higher tensile strength and better mechanical durability under harsh conditions. The choice between HNBR and butyl rubber for liners hinges on operational environment demands, with HNBR favored for high-performance applications requiring chemical stability and butyl rubber preferred for superior impermeability and weather resistance.
Chemical Resistance in Liner Applications
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance compared to butyl rubber, especially against oils, fuels, and solvents commonly encountered in liner applications. Butyl rubber provides excellent resistance to water, steam, and polar chemicals but falls short under exposure to hydrocarbons and aromatic solvents. For liner applications requiring robust performance in aggressive chemical environments, HNBR delivers enhanced durability and longer service life.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior temperature resistance, maintaining stability and flexibility in continuous service temperatures up to 150degC, with intermittent exposure reaching 160degC. Butyl rubber, while excellent in impermeability and chemical resistance, typically operates effectively within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 120degC. The enhanced thermal stability of HNBR makes it a preferred choice for liners in high-temperature environments requiring long-term durability.
Permeability and Gas Barrier Characteristics
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior gas barrier properties and significantly lower permeability to gases like oxygen and nitrogen compared to butyl rubber, making it ideal for high-performance liner applications. Butyl rubber, known for excellent impermeability to air and moisture, exhibits higher permeability rates to gases such as helium and hydrogen than HNBR, limiting its effectiveness in extreme sealing environments. The enhanced chemical resistance and reduced gas diffusion of HNBR liners provide extended service life in automotive and industrial gas containment systems.
Durability and Lifespan in Real-world Conditions
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, and oil exposure, resulting in enhanced durability and a longer lifespan in demanding liner applications compared to butyl rubber. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster under high-temperature and oxidative environments, limiting its real-world durability. For industries requiring extended service life under harsh conditions, HNBR liners provide a more reliable performance, maintaining structural integrity and flexibility over time.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) generally incurs higher costs compared to butyl rubber due to its enhanced performance properties and more complex production process. Butyl rubber remains more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from established manufacturing infrastructure and greater raw material abundance. For liner applications requiring budget-conscious selection with reliable supply, butyl rubber offers significant advantages over HNBR in terms of cost efficiency and availability.
Best Uses and Recommendations for Liner Selection
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) excels in liner applications requiring superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for automotive and industrial seals operating under extreme conditions. Butyl rubber offers outstanding impermeability to gases and excellent resistance to weathering and ozone, which is recommended for liners in inner tubes, pharmaceutical stoppers, and gas containment systems. Choose HNBR liners for high-performance environments demanding durability and chemical stability, while butyl rubber liners are best for applications requiring gas retention and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Butyl rubber for Liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com