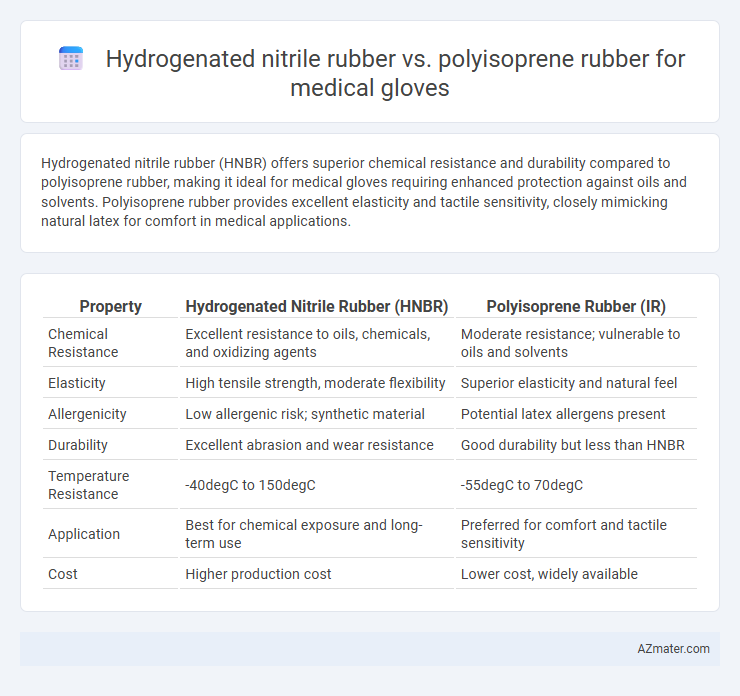
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring enhanced protection against oils and solvents. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex for comfort in medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and oxidizing agents | Moderate resistance; vulnerable to oils and solvents |
| Elasticity | High tensile strength, moderate flexibility | Superior elasticity and natural feel |
| Allergenicity | Low allergenic risk; synthetic material | Potential latex allergens present |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and wear resistance | Good durability but less than HNBR |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | -55degC to 70degC |
| Application | Best for chemical exposure and long-term use | Preferred for comfort and tactile sensitivity |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to traditional polyisoprene rubber, making it a preferred choice in medical glove applications where high-performance barrier protection is critical. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex, which is essential for delicate medical procedures requiring precision. Both materials address distinct clinical needs, with HNBR excelling in environments exposed to oils and chemicals, while polyisoprene supports hypoallergenic use and patient comfort.
Overview of Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR)
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber (HNBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, abrasion durability, and temperature stability, making it highly suitable for medical gloves exposed to harsh environments. Its hydrogenation process reduces unsaturation in the polymer chain, enhancing ozone, heat, and oxidative resistance compared to standard nitrile rubber, which is crucial for medical applications requiring long-lasting glove performance. HNBR gloves provide superior protection against oils, solvents, and chemicals, offering a reliable alternative to natural rubber polyisoprene gloves in clinical settings where allergen concerns and chemical exposure are prevalent.
Overview of Polyisoprene Rubber (IR)
Polyisoprene rubber (IR) is a synthetic elastomer that closely mimics natural rubber latex in elasticity, tensile strength, and comfort, making it ideal for medical gloves. It offers excellent tensile properties, superior flexibility, and reduced allergy risks compared to natural rubber latex due to the absence of proteins that cause hypersensitivity. Polyisoprene medical gloves provide reliable barrier protection, chemical resistance, and enhanced tactile sensitivity critical for precise medical procedures.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyisoprene rubber, with higher tensile strength and enhanced abrasion resistance that are critical for durable medical gloves. HNBR provides better resistance to tearing and puncture due to its saturated polymer backbone, ensuring prolonged glove lifespan in demanding medical environments. Polyisoprene rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and softness, typically shows lower tensile strength and mechanical robustness, making it less ideal for applications requiring extended mechanical durability.
Chemical Resistance: HNBR vs Polyisoprene
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, particularly against oils, fuels, and various solvents commonly encountered in medical settings. Polyisoprene, while offering excellent elasticity and comfort, is more susceptible to degradation from hydrocarbons and certain chemicals, limiting its protective capabilities. HNBR's enhanced resistance to oxidation, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals makes it a preferred choice for medical gloves requiring durable barrier protection.
Allergenicity and Skin Compatibility
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits significantly lower allergenicity compared to Polyisoprene rubber due to the absence of natural latex proteins, making it a safer alternative for individuals with latex allergies. Polyisoprene rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and comfort similar to natural rubber latex, poses a higher risk of triggering allergic reactions in sensitive users. Skin compatibility tests demonstrate that HNBR gloves provide superior hypoallergenic properties and reduced irritation potential, making them preferable in medical settings requiring strict biocompatibility standards.
Barrier Properties and Infection Control
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) exhibits superior barrier properties compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it highly effective against viruses, bacteria, and chemical permeation in medical gloves. The enhanced chemical resistance and lower permeability of HNBR contribute to improved infection control, reducing the risk of cross-contamination in clinical settings. Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and tactile sensitivity but is more susceptible to degradation by oils and solvents, potentially compromising barrier integrity.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it cost-efficient for high-demand medical glove applications with extended usage. Polyisoprene gloves, while providing excellent elasticity and comfort akin to natural latex, generally incur higher raw material costs and more complex manufacturing processes due to sensitivity in curing and molding stages. Manufacturing HNBR gloves benefits from improved resistance to heat degradation, allowing faster production cycles and lower overall waste, enhancing cost-efficiency in large-scale glove manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, leading to longer glove life and reduced waste in medical settings. Polyisoprene rubber, derived from natural latex, is biodegradable and comes from renewable sources, making it more environmentally sustainable despite its shorter lifespan. Selecting gloves involves balancing HNBR's enhanced performance with polyisoprene's lower environmental footprint to optimize sustainability in healthcare.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Glove Material
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) offers superior chemical resistance, durability, and excellent puncture resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical gloves used in high-risk environments. Polyisoprene rubber provides exceptional elasticity and comfort with latex-like sensitivity, preferred for patients with latex allergies but limited chemical protection. Selecting the ideal glove material depends on balancing chemical resistance requirements and sensitivity needs, with HNBR suited for intensive use and polyisoprene for allergen-sensitive applications.
Infographic: Hydrogenated nitrile rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com