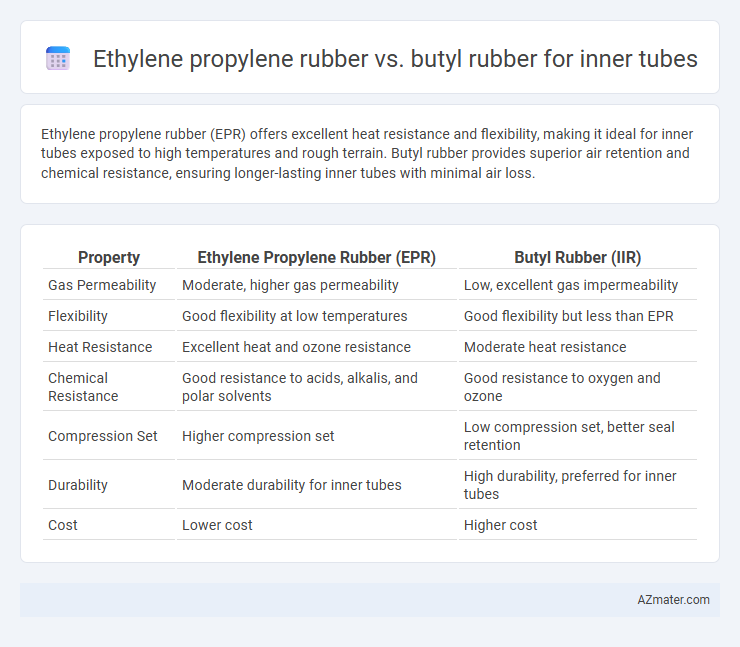
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent heat resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to high temperatures and rough terrain. Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and chemical resistance, ensuring longer-lasting inner tubes with minimal air loss.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Permeability | Moderate, higher gas permeability | Low, excellent gas impermeability |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility but less than EPR |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent heat and ozone resistance | Moderate heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and polar solvents | Good resistance to oxygen and ozone |
| Compression Set | Higher compression set | Low compression set, better seal retention |
| Durability | Moderate durability for inner tubes | High durability, preferred for inner tubes |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Inner Tube Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and butyl rubber are key materials used in inner tube manufacturing, known for their unique properties in enhancing tire durability and air retention. EPR offers excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it suitable for inner tubes subjected to harsh environmental conditions. Butyl rubber excels in impermeability and flexibility, providing superior air retention and impact resistance, critical for maintaining tire pressure and ride comfort.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it highly suitable for inner tube applications in various vehicle types. EPR offers superior flexibility and durability compared to Butyl rubber, with enhanced impermeability to gases, ensuring longer air retention and improved performance under varying temperature conditions. The polymer's resistance to aging and low compression set makes it a preferred choice in demanding environments where butyl rubber might degrade faster.
Overview of Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent air impermeability, making it highly suitable for inner tubes that require long-lasting inflation. Its chemical structure provides superior resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering compared to ethylene propylene rubber, enhancing durability in harsh conditions. These properties make butyl rubber a preferred choice for inner tubes in automotive and bicycle tires, ensuring improved performance and reliability.
Key Properties Comparison: EPR vs Butyl Rubber
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent heat resistance, flexibility, and ozone resistance, making it suitable for inner tubes exposed to high temperatures and dynamic stresses. Butyl rubber excels in low gas permeability and superior air retention, ensuring longer inflation intervals and better durability for inner tubes under varying pressure conditions. Both materials provide good resilience, but the choice depends on balancing thermal stability (favoring EPR) versus air retention performance (favoring butyl rubber).
Air Retention Capabilities
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent air retention due to its low permeability to gases, making it a preferred choice for inner tubes requiring long-lasting inflation. Butyl rubber exceeds EPR in air retention properties because of its superior impermeability to air and moisture, contributing to enhanced durability and reduced maintenance. Inner tubes made from butyl rubber maintain pressure longer under varying temperatures and mechanical stress, ensuring better performance in automotive and bicycle applications.
Resistance to Heat and Ozone
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) demonstrates superior resistance to heat and ozone compared to butyl rubber, maintaining flexibility and structural integrity at elevated temperatures up to 150degC. Butyl rubber offers excellent impermeability and good overall durability but degrades faster when exposed to prolonged ozone and UV radiation due to its chemical composition. For inner tubes requiring enhanced heat aging and ozone resistance, EPR provides a more reliable performance, especially in high-temperature environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior flexibility compared to butyl rubber, allowing inner tubes made from EPR to better absorb road vibrations and maintain shape under stress. Butyl rubber excels in elasticity, providing excellent air retention and resistance to gas permeability, which enhances the durability of inner tubes over time. While EPR prioritizes flexible performance for smoother rides, butyl rubber's elastic properties ensure longer-lasting air pressure maintenance and puncture resistance in inner tubes.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers lower raw material costs and easier processing compared to butyl rubber, making it more cost-effective for inner tube manufacturing. Butyl rubber provides superior air impermeability and chemical resistance, but its higher production complexity and material cost increase overall expenses. Manufacturers often balance EPR's affordability and ease of handling against butyl's performance benefits when selecting materials for inner tubes.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) excels in inner tube applications requiring excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive and industrial tires exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability and flexibility at low temperatures, which is essential for high-performance bicycle and motorcycle inner tubes demanding long air retention and puncture resistance. Selecting EPR or butyl rubber depends on the balance between environmental exposure durability and air retention needs for specific inner tube uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Inner Tubes
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent flexibility, weather resistance, and ozone stability, making it ideal for inner tubes exposed to varying environmental conditions. Butyl rubber provides superior air retention and low gas permeability, ensuring longer-lasting inflation and durability under pressure. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing the need for elasticity and environmental resilience (favoring EPR) against the requirement for airtightness and longevity (favoring butyl rubber).
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Butyl rubber for Inner tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com