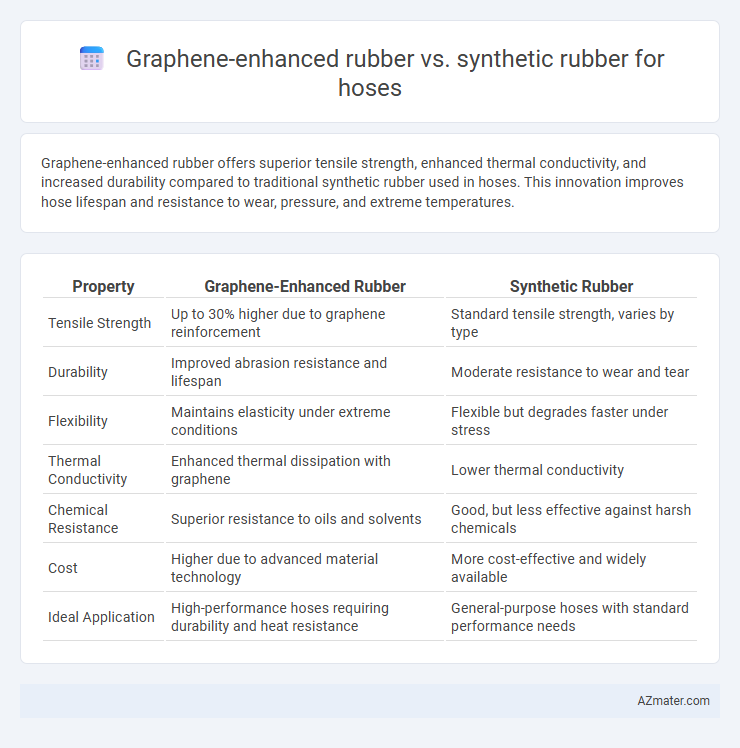
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior tensile strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and increased durability compared to traditional synthetic rubber used in hoses. This innovation improves hose lifespan and resistance to wear, pressure, and extreme temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 30% higher due to graphene reinforcement | Standard tensile strength, varies by type |
| Durability | Improved abrasion resistance and lifespan | Moderate resistance to wear and tear |
| Flexibility | Maintains elasticity under extreme conditions | Flexible but degrades faster under stress |
| Thermal Conductivity | Enhanced thermal dissipation with graphene | Lower thermal conductivity |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to oils and solvents | Good, but less effective against harsh chemicals |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced material technology | More cost-effective and widely available |
| Ideal Application | High-performance hoses requiring durability and heat resistance | General-purpose hoses with standard performance needs |
Introduction to Rubber Types Used in Hoses
Graphene-enhanced rubber incorporates graphene nanoparticles to significantly improve mechanical strength, flexibility, and durability compared to traditional synthetic rubber, which is primarily composed of polymers like nitrile or neoprene. Synthetic rubber used in hoses offers good resistance to oils, chemicals, and abrasion but often lacks the enhanced thermal stability and tensile strength provided by graphene composites. Integrating graphene into rubber matrices optimizes hose performance in demanding industrial applications by boosting lifespan, reducing wear, and improving resistance to extreme temperatures.
What is Graphene-Enhanced Rubber?
Graphene-enhanced rubber integrates graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, into the rubber matrix, significantly improving tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and abrasion resistance compared to conventional synthetic rubber. This advanced composite material offers enhanced durability and flexibility, making hoses more resistant to wear, deformation, and extreme temperatures. Its superior mechanical properties extend hose lifespan and performance in demanding industrial applications where synthetic rubber typically falls short.
Overview of Synthetic Rubber in Hose Manufacturing
Synthetic rubber in hose manufacturing offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. It is primarily composed of polymers like nitrile, neoprene, and EPDM, which provide specific properties such as oil resistance, weather resistance, and temperature tolerance. Compared to graphene-enhanced rubber, synthetic rubber maintains cost-effectiveness while delivering consistent performance under demanding conditions.
Mechanical Strength: Graphene-Enhanced vs Synthetic Rubber
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to traditional synthetic rubber used in hoses, owing to the exceptional tensile strength and elasticity of graphene nanoparticles integrated into the polymer matrix. This enhancement results in improved abrasion resistance, greater puncture tolerance, and extended lifespan under high-pressure conditions. Consequently, hoses made with graphene-enhanced rubber deliver superior durability and reliability in demanding industrial applications where mechanical robustness is critical.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance Comparison
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits significantly superior chemical resistance compared to synthetic rubber, effectively withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and oils without degradation. Its exceptional thermal stability allows it to maintain mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 300degC, whereas typical synthetic rubbers degrade above 150degC. The integration of graphene nanoplatelets enhances cross-link density and barrier properties, resulting in hoses that deliver prolonged lifespan and reliability in harsh chemical and high-temperature environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity compared to synthetic rubber, due to graphene's exceptional tensile strength and ability to distribute stress evenly. This enhancement results in hoses that maintain their shape and performance under repeated bending and stretching, reducing fatigue and cracking. Synthetic rubber, while flexible, typically lacks the same resilience, leading to quicker wear and decreased elasticity over time in demanding hose applications.
Lifespan and Durability of Hose Materials
Graphene-enhanced rubber significantly outperforms synthetic rubber in hose applications due to its exceptional tensile strength and resistance to wear, extending the lifespan of hoses by up to 50% compared to traditional synthetic alternatives. The integration of graphene improves durability by enhancing resistance to abrasion, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures, resulting in hoses that maintain integrity under harsh industrial conditions. These material properties reduce maintenance frequency and downtime, making graphene-enhanced rubber an optimal choice for high-performance hoses requiring long-term reliability.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers improved durability and tensile strength compared to traditional synthetic rubber, potentially extending hose lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. Despite higher initial material costs, graphene integration can streamline manufacturing through faster curing times and enhanced thermal conductivity. However, widespread adoption faces challenges from graphene's current price volatility and the need for specialized processing equipment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene-enhanced rubber significantly reduces environmental impact by improving durability and extending hose lifespan, which decreases waste and resource consumption compared to traditional synthetic rubber. Its superior mechanical properties enable lower material usage during manufacturing, contributing to reduced carbon footprint and energy consumption. The incorporation of graphene also enhances recyclability potential, supporting circular economy practices in hose production.
Which Rubber is Best for Hose Applications?
Graphene-enhanced rubber surpasses synthetic rubber for hose applications due to its superior tensile strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and improved abrasion resistance, ensuring longer hose lifespan and better performance under extreme conditions. Synthetic rubber remains widely used for its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and chemical stability, but it often lacks the durability and wear resistance that graphene enhancement provides. For demanding hose applications requiring high durability and resilience, graphene-enhanced rubber offers the best combination of mechanical properties and operational efficiency.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Hose
 azmater.com
azmater.com