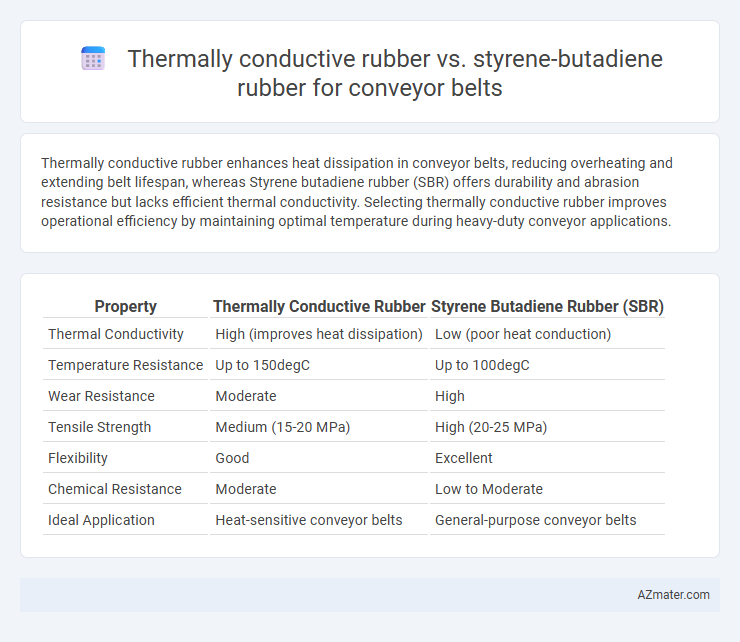
Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation in conveyor belts, reducing overheating and extending belt lifespan, whereas Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers durability and abrasion resistance but lacks efficient thermal conductivity. Selecting thermally conductive rubber improves operational efficiency by maintaining optimal temperature during heavy-duty conveyor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermally Conductive Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (improves heat dissipation) | Low (poor heat conduction) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 100degC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Tensile Strength | Medium (15-20 MPa) | High (20-25 MPa) |
| Flexibility | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Ideal Application | Heat-sensitive conveyor belts | General-purpose conveyor belts |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation in conveyor belts, crucial for high-temperature industrial applications, while styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness in general-purpose belts. Conveyor belt materials must balance thermal management and mechanical durability to ensure operational efficiency and longevity under varying environmental conditions. Selecting between thermally conductive rubber and SBR depends on the specific thermal load, wear resistance, and application requirements of the conveyor system.
Overview of Thermally Conductive Rubber
Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation in conveyor belts, preventing overheating and extending belt lifespan, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. It contains specialized fillers such as graphite or boron nitride, which significantly improve thermal conductivity compared to standard Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). These properties enable efficient temperature regulation, reduce downtime, and maintain mechanical integrity under thermal stress, unlike SBR, which primarily offers abrasion resistance and elasticity but lacks effective heat transfer capabilities.
Properties of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it a reliable choice for conveyor belt applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. Its high tensile strength and moderate heat resistance ensure consistent performance, while its cost-effectiveness enhances economic efficiency for industrial uses. Compared to thermally conductive rubber, SBR provides superior wear resistance but lacks enhanced thermal dissipation properties essential for high-temperature environments.
Thermal Conductivity: Key Differences
Thermally conductive rubber exhibits significantly higher thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1 to 5 W/m*K, compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which usually has thermal conductivity around 0.15 to 0.2 W/m*K. This enhanced thermal property in thermally conductive rubber allows for better heat dissipation in conveyor belts, reducing heat buildup and improving operational efficiency in high-temperature environments. SBR, while offering good abrasion resistance and flexibility, is less effective in managing heat, making it less suitable for applications requiring efficient thermal management.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Thermally conductive rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) when used in conveyor belts, offering enhanced resistance to wear, tear, and deformation under heavy loads. The increased thermal conductivity in these specialized rubbers improves heat dissipation, reducing the risk of material breakdown caused by friction and operational heat. While SBR provides good elasticity and abrasion resistance, thermally conductive rubber ensures longer service life and reliability in high-temperature and high-stress conveyor belt applications.
Heat Dissipation and Performance
Thermally conductive rubber enhances heat dissipation effectively, reducing overheating and extending the conveyor belt's operational life, whereas Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate heat resistance but lacks efficient thermal conductivity. Improved thermal management in thermally conductive rubber minimizes the risk of belt deformation and material degradation during high-temperature applications. Consequently, conveyor belts with thermally conductive rubber exhibit superior performance in industries requiring continuous heat exposure, such as mining and manufacturing.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Thermally conductive rubber outperforms Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in conveyor belt applications by offering superior durability and enhanced wear resistance, essential for high-friction and high-temperature environments. Its improved thermal management reduces heat buildup, minimizing material degradation and extending belt lifespan compared to SBR, which is more prone to cracking and abrasion under similar conditions. Consequently, thermally conductive rubber provides a resilient, long-lasting solution for demanding conveyor systems.
Suitability for Industrial Applications
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation, making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in high-temperature industrial environments where thermal management is critical. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), while economically favorable and resistant to abrasion, lacks adequate thermal conductivity, limiting its performance under intense heat conditions. For industrial conveyor belts requiring durability and efficient heat transfer, thermally conductive rubber ensures enhanced operational reliability and extended service life.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Thermally conductive rubber offers enhanced heat dissipation for conveyor belts, reducing operational downtime and maintenance costs, but it generally comes with a higher initial price compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). SBR remains economically favorable due to its lower raw material and production expenses, making it suitable for standard conveyor applications with moderate thermal requirements. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing upfront investment against long-term savings from improved thermal management.
Choosing the Right Material for Conveyor Belts
Thermally conductive rubber offers superior heat dissipation compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for conveyor belts operating in high-temperature environments or requiring rapid heat transfer to prevent material degradation. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the thermal conductivity needed for heat-sensitive applications. Selecting the right conveyor belt material depends on balancing thermal management needs, mechanical durability, and budget constraints, with thermally conductive rubber preferred for heat-intensive processes.
Infographic: Thermally conductive rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com