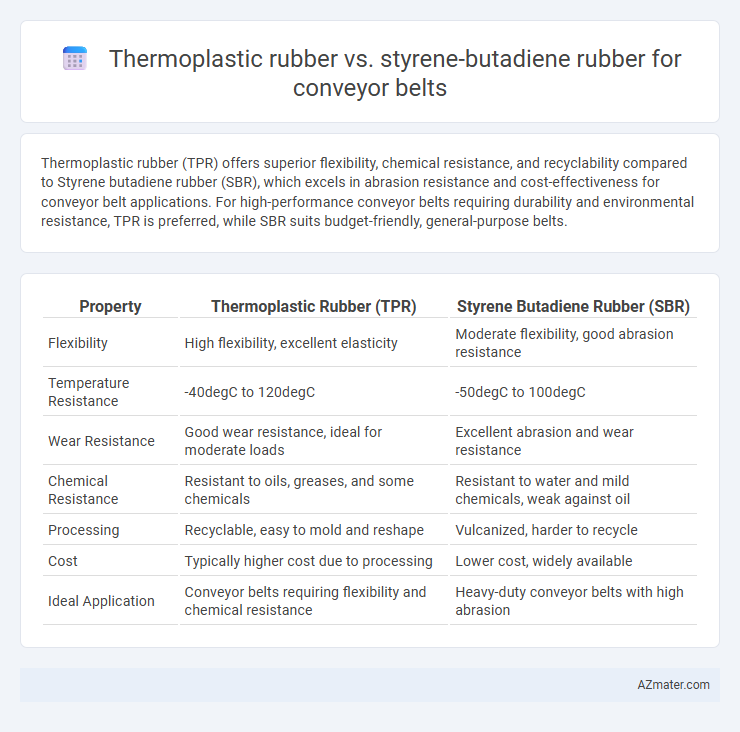
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which excels in abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for conveyor belt applications. For high-performance conveyor belts requiring durability and environmental resistance, TPR is preferred, while SBR suits budget-friendly, general-purpose belts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent elasticity | Moderate flexibility, good abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance, ideal for moderate loads | Excellent abrasion and wear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, greases, and some chemicals | Resistant to water and mild chemicals, weak against oil |
| Processing | Recyclable, easy to mold and reshape | Vulcanized, harder to recycle |
| Cost | Typically higher cost due to processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Ideal Application | Conveyor belts requiring flexibility and chemical resistance | Heavy-duty conveyor belts with high abrasion |
Introduction to Conveyor Belt Materials
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) are prominent materials used in conveyor belts due to their distinct properties suited for various industrial applications. TPR offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability in environments requiring frequent bending and exposure to oils, while SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for general-purpose conveyor belts. Selecting the appropriate material depends on factors such as temperature ranges, mechanical stress, surface friction, and operational environment specific to the conveyor system.
Overview of Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR)
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the elasticity of rubber with the recyclability and processing ease of plastics, making it a versatile material for conveyor belts. TPR offers excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility over a wide temperature range, and good chemical stability, which enhances conveyor belt durability in harsh industrial environments. Compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), TPR provides easier fabrication and faster production cycles, reducing manufacturing costs while maintaining comparable mechanical performance.
Understanding Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used in conveyor belt applications due to its excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability. Compared to Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR), SBR offers superior grip, durability, and resilience under various environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides enhanced tensile strength and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor systems.
Mechanical Properties: TPR vs. SBR
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) exhibits higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it more durable for conveyor belt applications under heavy mechanical loads. SBR offers better elasticity and resilience, which allows for greater flexibility and shock absorption but may wear out faster under continuous friction. In terms of hardness, TPR generally provides a wider range of customizable Shore hardness values, enhancing its suitability for varying conveyor belt requirements.
Flexibility and Wear Resistance Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior flexibility compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it ideal for conveyor belts that require frequent bending and twisting without cracking. SBR, however, excels in wear resistance due to its strong abrasion durability and resistance to heat and aging, which extends belt life in abrasive environments. Choosing between TPR and SBR depends on the conveyor belt's operational demands, with TPR favored for flexibility and SBR preferred for enhanced wear resistance in heavy-duty applications.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) maintains flexibility and resilience in extreme temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for conveyor belts exposed to fluctuating climates. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) typically performs well between -30degC and 70degC but can become brittle in colder environments and degrade under prolonged heat exposure. For conveyor belts operating in harsh temperature conditions, TPR offers superior thermal stability and consistent performance compared to SBR.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Differences
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making TPR more effective against acids, alkalis, and various solvents encountered in conveyor belt applications. SBR tends to degrade more rapidly when exposed to oils and petroleum-based substances, whereas TPR maintains its integrity and flexibility under prolonged oil exposure. These differences in chemical and oil resistance directly impact the durability and maintenance frequency of conveyor belts in industrial environments.
Cost Efficiency and Longevity
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers higher cost efficiency for conveyor belts due to its recyclability and lower processing costs compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR provides superior longevity with better resistance to abrasion and heat, making it ideal for heavy-duty conveyor applications. Selecting between TPR and SBR depends on balancing upfront cost savings with the need for long-term durability in specific industrial environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior recyclability and lower environmental impact compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which relies on petroleum-based raw materials and generates more waste in disposal. TPR's ability to be melted and reprocessed reduces landfill contributions and energy consumption, supporting sustainable conveyor belt production. Conversely, SBR's manufacturing and degradation release more pollutants, making TPR a more eco-friendly choice for conveyor belt applications focused on sustainability.
Best Applications: When to Choose TPR or SBR for Conveyor Belts
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and ease of processing, making it ideal for conveyor belts in applications requiring frequent bending or moderate chemical exposure. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) delivers excellent wear resistance and heat stability, suited for heavy-duty conveyor belts in harsh environments with high mechanical stress and lower chemical exposure. Selecting TPR benefits light to medium load conveyors with intricate designs, while SBR is preferred for high-impact, high-temperature industrial conveyor systems.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Conveyor belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com