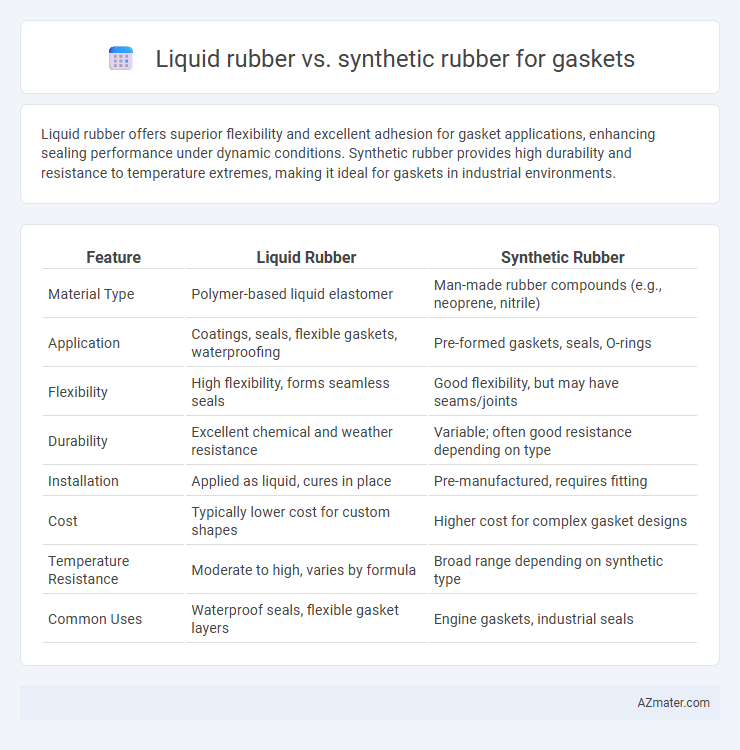
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent adhesion for gasket applications, enhancing sealing performance under dynamic conditions. Synthetic rubber provides high durability and resistance to temperature extremes, making it ideal for gaskets in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Rubber | Synthetic Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer-based liquid elastomer | Man-made rubber compounds (e.g., neoprene, nitrile) |
| Application | Coatings, seals, flexible gaskets, waterproofing | Pre-formed gaskets, seals, O-rings |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, forms seamless seals | Good flexibility, but may have seams/joints |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and weather resistance | Variable; often good resistance depending on type |
| Installation | Applied as liquid, cures in place | Pre-manufactured, requires fitting |
| Cost | Typically lower cost for custom shapes | Higher cost for complex gasket designs |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate to high, varies by formula | Broad range depending on synthetic type |
| Common Uses | Waterproof seals, flexible gasket layers | Engine gaskets, industrial seals |
Introduction to Rubber Gaskets
Rubber gaskets are essential sealing components used in various industrial applications to prevent leaks between mating surfaces. Liquid rubber, known for its flexibility and easy application, forms a seamless, durable seal that adapts well to irregular shapes. Synthetic rubber, such as nitrile or EPDM, offers enhanced chemical resistance and temperature stability, making it suitable for demanding environments needing reliable gasket performance.
What is Liquid Rubber?
Liquid rubber is a versatile elastomeric coating applied as a liquid that cures to form a flexible, impermeable membrane, making it ideal for gasket applications requiring excellent sealing and resistance to water, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Unlike synthetic rubber, which is typically pre-formed into solid sheets or shapes, liquid rubber can be sprayed or brushed directly onto complex surfaces to create seamless gaskets that conform precisely to irregular geometries. Its enhanced adhesion properties and ability to form airtight seals improve gasket durability and performance in automotive, industrial, and construction sectors.
Understanding Synthetic Rubber Types
Synthetic rubber types such as Nitrile (NBR), Neoprene (CR), and EPDM each offer distinct properties valuable for gasket applications; Nitrile excels in oil resistance, Neoprene provides excellent weather and ozone resistance, while EPDM withstands heat and steam. Liquid rubber, often based on synthetic elastomers like polyurethane or silicone, provides seamless application and superior flexibility, but may lack the chemical resistance or hardness specific synthetic rubbers offer. Selecting the appropriate synthetic rubber type for gaskets depends on operational environment factors such as temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Key Properties Comparison: Liquid vs Synthetic Rubber
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless application, providing excellent adhesion and resistance to water, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it ideal for complex gasket shapes. Synthetic rubber gaskets, such as those made from EPDM or neoprene, provide robust durability, high tensile strength, and excellent resistance to heat, oil, and abrasion, delivering long-lasting performance in demanding environments. While liquid rubber ensures a perfect seal and ease of repair, synthetic rubber excels in mechanical stability and resistance to extreme temperatures.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and chemicals, making it highly durable for gasket applications. Synthetic rubber, such as neoprene or EPDM, provides consistent mechanical strength and resilience but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh environmental factors. Overall, liquid rubber gaskets tend to have longer service life and better aging performance compared to synthetic rubber counterparts.
Chemical Resistance Performance
Liquid rubber gaskets exhibit superior chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and acids compared to many synthetic rubber types, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments. Synthetic rubbers such as EPDM, NBR, and Viton offer varied chemical resistance profiles; Viton excels with fuels and high-temperature chemicals, while EPDM resists weathering and polar solvents but poorly withstands hydrocarbons. Selecting liquid rubber often ensures enhanced durability and extended gasket life in harsh chemical applications where synthetic rubbers may degrade faster.
Temperature Tolerance: Which Is Better?
Liquid rubber offers superior temperature tolerance for gaskets, withstanding ranges from -40degF to 400degF, making it ideal for high-heat applications. Synthetic rubber, such as neoprene or nitrile, typically operates effectively between -30degF and 250degF. For extreme temperature conditions, liquid rubber provides enhanced durability and stability, ensuring reliable gasket performance.
Installation and Application Differences
Liquid rubber offers superior adaptability for gasket installation, effortlessly filling irregular surfaces and complex shapes due to its flowing consistency, whereas synthetic rubber typically requires precise pre-cutting or molding before application. Liquid rubber gaskets cure in place, allowing for faster, more customized sealing in diverse environments, while synthetic rubber gaskets are often limited to standard shapes and may need more extensive installation time and equipment. The application of liquid rubber is preferred in scenarios demanding quick turnaround and on-site adjustments, while synthetic rubber remains common for mass-produced, uniform gasket requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness: Liquid vs Synthetic Rubber
Liquid rubber offers a cost-effective solution for gaskets due to its easy application, minimal waste, and lower tooling expenses compared to synthetic rubber. Synthetic rubber gaskets typically require higher upfront costs for material processing and mold fabrication but provide consistent performance in high-stress environments. Choosing liquid rubber can reduce initial investment and maintenance costs, while synthetic rubber ensures durability under extreme temperatures and chemical exposure.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless application for custom gasket shapes, making it ideal for complex or irregular surfaces. Synthetic rubber, including nitrile and EPDM variants, provides excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and weathering, suitable for industrial or automotive gasket applications. Selecting the right rubber depends on factors such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress specific to your gasket requirements.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Synthetic rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com