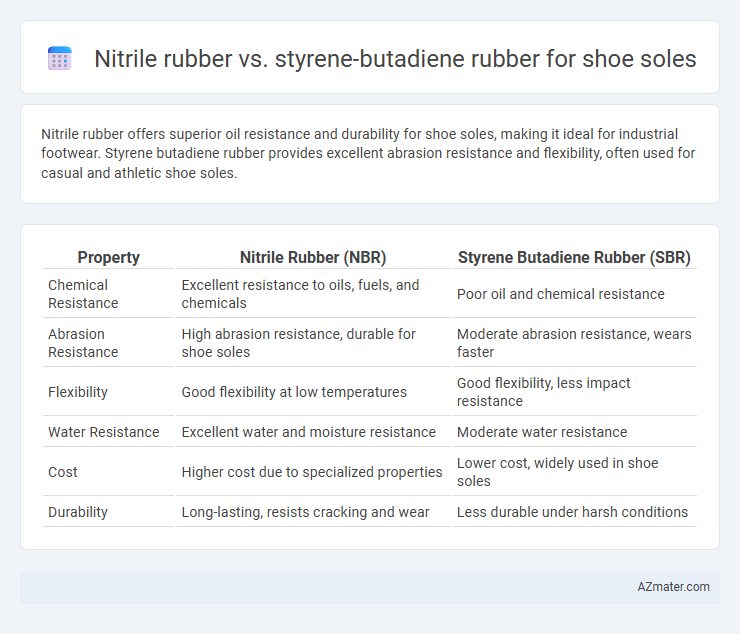
Nitrile rubber offers superior oil resistance and durability for shoe soles, making it ideal for industrial footwear. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, often used for casual and athletic shoe soles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Poor oil and chemical resistance |
| Abrasion Resistance | High abrasion resistance, durable for shoe soles | Moderate abrasion resistance, wears faster |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility at low temperatures | Good flexibility, less impact resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water and moisture resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties | Lower cost, widely used in shoe soles |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists cracking and wear | Less durable under harsh conditions |
Introduction to Nitrile Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers strong abrasion resistance and good aging stability, commonly used in footwear for its cost-effectiveness and flexibility. Both materials provide significant advantages, with NBR favored for chemical resistance and SBR preferred for general wear and impact absorption in shoe soles.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, characterized by its high resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals due to the polar nitrile groups. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of styrene and butadiene monomers, offering good abrasion resistance and aging properties but lower chemical resistance compared to NBR. The chemical structure of NBR features a higher polarity from acrylonitrile units, enhancing solvent resistance, while SBR's nonpolar styrene and butadiene units provide better flexibility and wear resistance for shoe sole applications.
Key Physical Properties for Shoe Soles
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to oily and greasy environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent aging stability and good abrasion resistance, often preferred for general-purpose footwear with moderate durability needs. Both materials exhibit strong elasticity, but NBR's enhanced compression set resistance ensures longer-lasting sole shape retention under heavy use.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) exhibits superior oil resistance and abrasion durability compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it an excellent choice for shoe soles exposed to harsh environments and frequent wear. SBR offers good abrasion resistance but typically falls short in chemical and oil resistance, leading to faster degradation under strenuous conditions. The enhanced durability and wear resistance of NBR significantly extend the lifespan of shoe soles used in industrial or outdoor settings.
Flexibility and Comfort Performance
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent oil resistance, making it durable for shoe soles, but it tends to be less flexible than styrene butadiene rubber (SBR). Styrene butadiene rubber provides enhanced flexibility and cushioning, contributing to improved comfort and shock absorption in footwear applications. For shoe soles prioritizing flexibility and comfort, SBR delivers better performance due to its higher elasticity and softer feel underfoot.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Differences
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to hydrocarbons and solvents. While SBR is prone to swelling and degradation when in contact with oils and certain chemicals, NBR maintains its structural integrity and durability under these conditions. This makes nitrile rubber the preferred choice for footwear requiring enhanced resistance to oils, greases, and chemicals in industrial or automotive environments.
Temperature and Weather Tolerance
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to extreme temperatures, maintaining flexibility in cold conditions down to -40degC and heat tolerance up to 120degC, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to varying climates. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) performs well in moderate temperatures but tends to harden and crack below -20degC and degrades faster under prolonged UV exposure and ozone. Nitrile's enhanced weather tolerance and resistance to oil and chemicals provide greater durability and longevity for outdoor footwear applications.
Slip Resistance on Various Surfaces
Nitrile rubber outperforms styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in slip resistance due to its superior abrasion resistance and excellent grip on wet and oily surfaces commonly encountered in shoe soles. The molecular structure of nitrile rubber provides enhanced durability and traction on smooth, slippery floors, reducing the risk of slips and falls. SBR, while cost-effective, tends to have lower slip resistance and degrades faster under harsh environmental conditions, making nitrile rubber the preferred choice for high-performance slip-resistant shoe soles.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers higher oil and abrasion resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), making it slightly more expensive but cost-effective for durable shoe soles in industrial applications. SBR, widely available and less costly due to abundant production, remains the preferred material for general-purpose shoe soles, balancing performance with budget constraints. Market availability of SBR is extensive globally, whereas NBR availability is more limited and concentrated in regions with strong automotive and industrial rubber sectors.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior resistance to oils and chemicals, contributing to longer shoe sole durability and reduced waste compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). SBR, primarily derived from petroleum, has a higher environmental footprint due to its energy-intensive production and lower biodegradability, while NBR's enhanced lifespan supports sustainability through extended product use. However, both materials present challenges in end-of-life disposal, emphasizing the need for improved recycling technologies to mitigate environmental impacts.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com