Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and water, making it ideal for gasket applications in harsh outdoor environments. Neoprene provides excellent oil, chemical, and heat resistance, suitable for industrial gaskets exposed to fuels and lubricants.
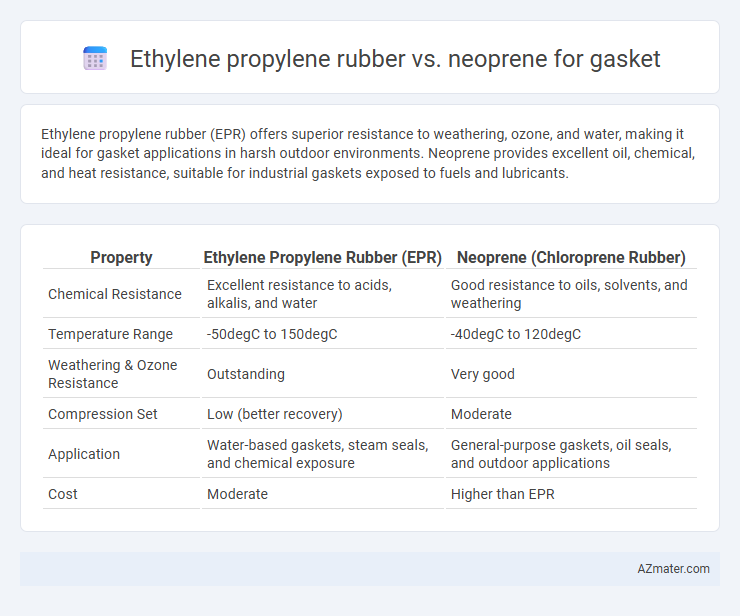
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Neoprene (Chloroprene Rubber) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and water | Good resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Weathering & Ozone Resistance | Outstanding | Very good |
| Compression Set | Low (better recovery) | Moderate |
| Application | Water-based gaskets, steam seals, and chemical exposure | General-purpose gaskets, oil seals, and outdoor applications |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than EPR |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and neoprene are popular gasket materials known for their unique properties suited to various industrial applications. EPR offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for outdoor and high-temperature uses, while neoprene provides superior oil, chemical, and solvent resistance. Selection between Ethylene propylene rubber and neoprene gaskets depends on environmental exposure, chemical compatibility, and mechanical stress requirements.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR/EPDM) is a synthetic elastomer widely used for gaskets due to its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, oxidation, and a broad range of chemicals. Its superior flexibility and durability in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 120degC make it ideal for automotive, roofing, and industrial sealing applications. EPR gaskets outperform neoprene in acid and alkali environments, while maintaining strong resilience against compression set and aging.
Overview of Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber, a synthetic polymer known for its excellent chemical stability and flexibility over a wide temperature range, is widely used in gasket applications. Its superior resistance to oils, solvents, weathering, and ozone makes it ideal for sealing in harsh industrial environments. Compared to ethylene propylene rubber, neoprene offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance, ensuring reliable gasket performance in automotive, HVAC, and marine industries.
Key Properties Comparison: EPDM vs Neoprene
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber offers superior resistance to heat, ozone, weathering, and steam, making it ideal for outdoor and automotive gasket applications. Neoprene exhibits excellent chemical resistance, especially to oils, solvents, and refrigerants, alongside good mechanical strength, which suits industrial environments requiring exposure to hydrocarbon-based substances. EPDM provides better flexibility over a broad temperature range (-40degC to 130degC), while Neoprene performs well between -40degC and 120degC but excels in environments with moderate chemical exposure.
Chemical Resistance: EPDM vs Neoprene
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and water-based chemicals compared to Neoprene, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh chemical environments. Neoprene demonstrates better resistance to oils, fuels, and aliphatic hydrocarbons but can degrade when exposed to strong acids or alkalis. Selecting between EPDM and Neoprene gaskets depends on the specific chemical exposure, with EPDM preferred for water and chemical resistance and Neoprene favored for oil and fuel contact.
Weathering and UV Resistance
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior weathering and UV resistance compared to neoprene, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to harsh outdoor conditions. EPR maintains flexibility and resists cracking or hardening after prolonged sunlight exposure, while neoprene tends to degrade faster under UV radiation. This durability extends the service life of EPR gaskets in applications requiring reliable sealing against environmental factors such as ozone, sunlight, and temperature fluctuations.
Temperature Performance Capabilities
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent temperature resistance, typically performing well in a range from -50degC to 150degC, making it suitable for applications involving high heat exposure. Neoprene gaskets, on the other hand, typically withstand temperatures from -40degC to 120degC, providing moderate heat resistance with added durability against oils and weathering. For gasket applications requiring superior thermal endurance, EPR is often preferred due to its extended temperature performance and stability under thermal cycling.
Common Applications for Each Material
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is commonly used for gaskets in the automotive, roofing, and electrical insulation industries due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. Neoprene gaskets are preferred in chemical processing, refrigeration, and marine applications because of their superior oil, chemical, and ozone resistance. Both materials offer durable sealing solutions, with EPR favored for high-temperature environments and Neoprene chosen for environments exposed to oils and chemicals.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) typically offers lower material and manufacturing costs compared to neoprene, making it a budget-friendly option for gasket applications. EPR is widely available due to its extensive use in automotive and industrial markets, ensuring steady supply and reduced lead times. Neoprene, while slightly more expensive, provides moderate availability but may incur higher expenses related to sourcing specialized grades for specific chemical resistance requirements.
Choosing the Right Gasket Material: EPDM or Neoprene
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPDM) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and water, making it ideal for outdoor and water-based gasket applications. Neoprene provides excellent oil, chemical, and heat resistance, suitable for automotive and industrial environments where exposure to oils and solvents is common. Selecting between EPDM and neoprene depends on the specific environmental conditions and chemical exposures the gasket will encounter.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Neoprene for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com