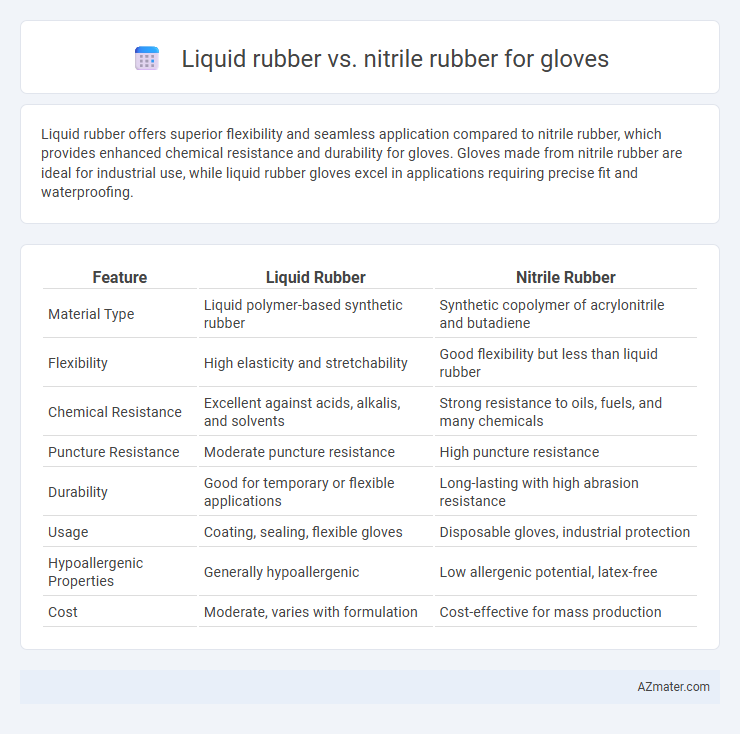
Liquid rubber offers superior flexibility and seamless application compared to nitrile rubber, which provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability for gloves. Gloves made from nitrile rubber are ideal for industrial use, while liquid rubber gloves excel in applications requiring precise fit and waterproofing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Rubber | Nitrile Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Liquid polymer-based synthetic rubber | Synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Flexibility | High elasticity and stretchability | Good flexibility but less than liquid rubber |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, alkalis, and solvents | Strong resistance to oils, fuels, and many chemicals |
| Puncture Resistance | Moderate puncture resistance | High puncture resistance |
| Durability | Good for temporary or flexible applications | Long-lasting with high abrasion resistance |
| Usage | Coating, sealing, flexible gloves | Disposable gloves, industrial protection |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Generally hypoallergenic | Low allergenic potential, latex-free |
| Cost | Moderate, varies with formulation | Cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction to Liquid Rubber and Nitrile Rubber
Liquid rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its excellent flexibility, waterproofing, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for protective coatings and adhesives in glove manufacturing. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, offers superior puncture resistance and protection against oils, fuels, and many chemicals, making it a preferred material for disposable gloves. Both materials provide durable barrier properties, but nitrile rubber excels in industrial and medical applications due to its enhanced chemical resistance and durability.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Liquid rubber for gloves typically consists of polymerized liquid elastomers like styrene-butadiene or polyurethane, offering flexible and seamless coatings with adjustable thickness. Nitrile rubber, a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, provides strong resistance to oils, chemicals, and punctures due to its tightly cross-linked molecular structure. The chemical composition of nitrile rubber results in superior durability and chemical resistance compared to liquid rubber's more customizable but less chemically resistant formulations.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Liquid rubber gloves are produced through a dipping process where formers are submerged in liquid rubber compounds, allowing precise control over thickness and seamless designs, ideal for custom fitting and reducing waste. Nitrile rubber gloves use a similar dipping method but require higher vulcanization temperatures and longer curing times to enhance chemical resistance and durability. The manufacturing process of nitrile gloves involves more complex compound formulation, ensuring enhanced puncture resistance, while liquid rubber provides more flexibility in creating thinner, highly elastic gloves suitable for specialized applications.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Liquid rubber gloves exhibit superior durability due to their excellent resistance to abrasion, punctures, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Nitrile rubber gloves provide outstanding tensile strength and puncture resistance compared to natural rubber, with enhanced protection against oils, fats, and certain chemicals. When analyzing strength and durability, nitrile gloves offer a balance of flexibility and resilience, while liquid rubber coatings enhance durability in repeated use and harsh environments.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Liquid rubber gloves offer superior chemical resistance against a wide range of acids, alkalis, and solvents due to their seamless and flexible barrier properties. Nitrile rubber gloves provide excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and many solvents, making them a preferred choice in industrial and medical environments. Both materials excel in protection, but liquid rubber is often favored for harsher chemical exposures, while nitrile balances durability with resistance to punctures and abrasions.
Comfort and Fit for Users
Liquid rubber gloves offer superior flexibility and conform closely to the hand's contours, enhancing comfort and providing a snug fit ideal for precision tasks. Nitrile rubber gloves, known for their durability and chemical resistance, deliver a comfortable fit but may feel less flexible compared to liquid rubber variants. Choosing liquid rubber improves tactile sensitivity and reduces hand fatigue, making them preferable for extended wear.
Allergen Considerations
Liquid rubber gloves typically use synthetic materials that reduce the risk of latex allergen exposure, making them suitable for individuals with latex allergies. Nitrile rubber gloves, composed of a synthetic copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene, are widely recognized for their hypoallergenic properties and lower likelihood of causing allergic reactions compared to natural latex. Selecting nitrile rubber gloves ensures reduced allergen concerns while maintaining durability and chemical resistance in various applications.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Liquid rubber gloves, often made from natural latex, exhibit superior biodegradability compared to nitrile rubber gloves derived from synthetic polymers. Nitrile rubber, while offering excellent chemical resistance, involves petroleum-based production processes that result in a higher environmental footprint and slower degradation rates. Selecting liquid rubber gloves aligns better with sustainability goals due to their faster decomposition and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources.
Cost and Market Availability
Liquid rubber gloves generally offer a lower cost due to simpler manufacturing processes and reduced material usage compared to nitrile rubber gloves, which require more complex polymerization techniques. Nitrile rubber gloves dominate the market availability, favored in medical and industrial sectors for their superior chemical resistance and durability, leading to widespread global supply chains. The cost advantage of liquid rubber gloves makes them appealing for bulk applications, while the higher-priced nitrile gloves maintain strong demand in specialized markets.
Best Use Cases and Industry Recommendations
Liquid rubber provides superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for coatings and sealants in industrial and automotive applications, where durability under harsh conditions is critical. Nitrile rubber gloves excel in medical, laboratory, and food handling environments due to their excellent puncture resistance, oil resistance, and hypoallergenic properties, offering robust protection against oils, fats, and solvents. Industry recommendations often favor nitrile gloves for healthcare and food industries, while liquid rubber coatings are preferred for industrial wear and protective layering requiring high abrasion and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Liquid rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com