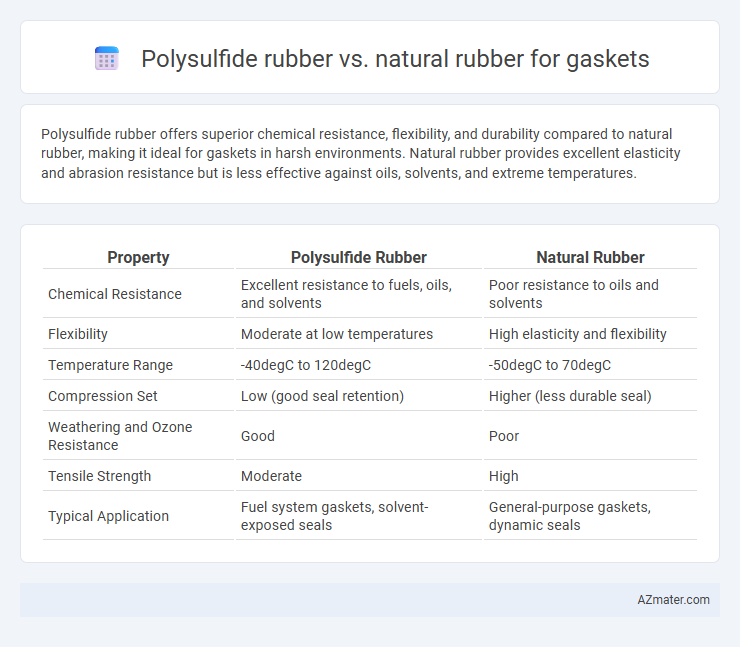
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for gaskets in harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance but is less effective against oils, solvents, and extreme temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents | Poor resistance to oils and solvents |
| Flexibility | Moderate at low temperatures | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 70degC |
| Compression Set | Low (good seal retention) | Higher (less durable seal) |
| Weathering and Ozone Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate | High |
| Typical Application | Fuel system gaskets, solvent-exposed seals | General-purpose gaskets, dynamic seals |
Overview of Polysulfide Rubber and Natural Rubber
Polysulfide rubber is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent chemical resistance, low permeability to gases, and superior flexibility, making it ideal for gasket applications in harsh environments. Natural rubber, derived from latex, offers high tensile strength, good elasticity, and excellent abrasion resistance but lacks the chemical stability of polysulfide rubber. The choice between polysulfide and natural rubber gaskets depends on exposure conditions, with polysulfide preferred for solvents and fuels, while natural rubber suits general sealing needs requiring elasticity and resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polysulfide rubber is characterized by a backbone containing sulfur atoms linked by polysulfide (-Sx-) bridges, imparting excellent chemical resistance and impermeability, while natural rubber consists primarily of cis-1,4-polyisoprene units with a hydrocarbon chain structure offering high elasticity but lower chemical resistance. The presence of sulfur linkages in polysulfide rubber enhances its structural rigidity and resistance to solvents, oils, and fuels, making it suitable for gasket applications in aggressive environments. In contrast, natural rubber's hydrocarbon polymer matrix provides flexibility and tensile strength but is more prone to degradation from oils and chemicals, limiting its effectiveness in harsh chemical environments.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for gaskets requiring strong sealing under dynamic conditions. Natural rubber exhibits high tensile strength and outstanding elasticity, providing exceptional flexibility but limited resistance to oils and solvents. Mechanical properties of polysulfide rubber prioritize durability and elongation under stress, whereas natural rubber delivers high resilience and tear strength suited for less chemically aggressive environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Solvents
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals and solvents, including fuels, oils, and aromatic hydrocarbons, making it ideal for gasket applications in harsh industrial environments. Natural rubber, while flexible and resilient, tends to degrade quickly when exposed to oils, solvents, and many chemicals, limiting its suitability for chemical-resistant gasket uses. The molecular structure of polysulfide rubber provides enhanced durability and chemical stability compared to the protein-based composition of natural rubber.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Polysulfide rubber offers superior temperature performance, maintaining stability and flexibility in extreme conditions ranging from -55degC to 120degC, making it ideal for gasket applications exposed to wide temperature variations. Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity and tensile strength but tends to degrade and harden at temperatures above 70degC, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. The chemical resistance and aging stability of polysulfide rubber significantly enhance gasket durability compared to natural rubber, ensuring longer service life under thermal stress.
Durability and Longevity in Gasket Applications
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, making it highly effective for gaskets exposed to harsh environments and solvents. Its enhanced longevity arises from excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and thermal degradation, which natural rubber typically lacks. Natural rubber gaskets may suffer from faster aging and brittleness under similar conditions, reducing their overall service life in demanding gasket applications.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability for gaskets, often resulting in longer service life and lower replacement frequency compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber is generally more cost-effective upfront due to its widespread availability and lower material costs, but it may degrade faster in harsh environments. For applications requiring resilience against solvents and weathering, polysulfide rubber provides better long-term value despite higher initial expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polysulfide rubber gaskets exhibit superior chemical resistance and durability but involve petrochemical-derived production processes with higher environmental footprints compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber gaskets offer renewable sourcing from rubber trees and enhanced biodegradability, contributing to lower environmental impact and better sustainability profiles. Lifecycle assessments indicate that natural rubber reduces greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion more effectively than synthetic polysulfide alternatives in gasket applications.
Common Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
Polysulfide rubber is widely used in gasket manufacturing for applications requiring excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, such as in aerospace fuel systems and automotive fuel tanks. Natural rubber is preferred in gaskets for general-purpose sealing, especially in oil-resistant and vibration-damping environments like industrial machinery and automotive engines. Both materials offer durability, but polysulfide rubber excels in harsh chemical exposure while natural rubber provides superior mechanical strength and elasticity for dynamic seals.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Gasket Needs
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and long-term durability, making it ideal for gaskets in automotive and industrial applications exposed to fuels and solvents. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience but lacks resistance to oils and chemicals, limiting its use in harsh environments. Choosing the right gasket material depends on factors such as temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, with polysulfide rubber favored for sealing applications requiring robust chemical and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Natural rubber for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com