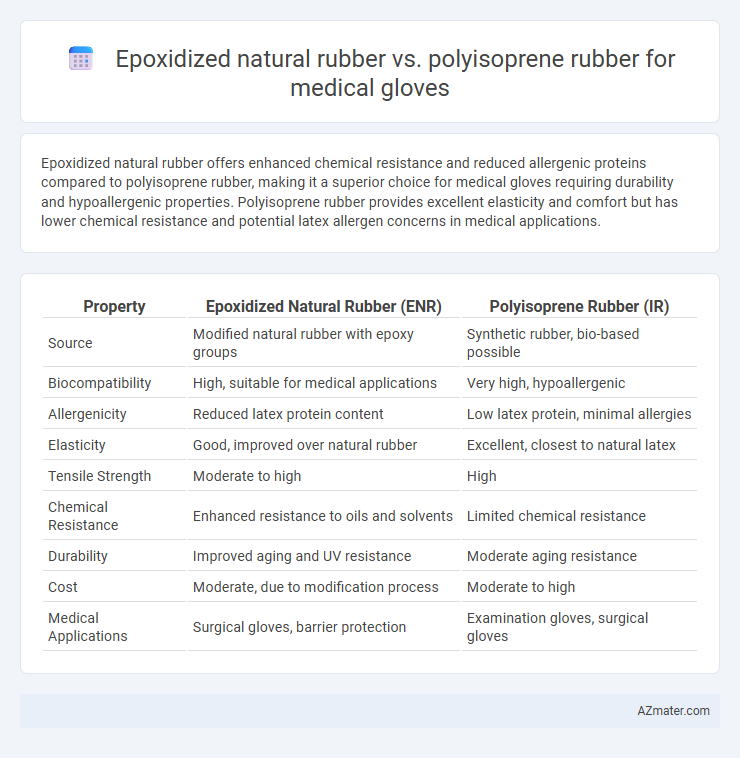
Epoxidized natural rubber offers enhanced chemical resistance and reduced allergenic proteins compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it a superior choice for medical gloves requiring durability and hypoallergenic properties. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent elasticity and comfort but has lower chemical resistance and potential latex allergen concerns in medical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Modified natural rubber with epoxy groups | Synthetic rubber, bio-based possible |
| Biocompatibility | High, suitable for medical applications | Very high, hypoallergenic |
| Allergenicity | Reduced latex protein content | Low latex protein, minimal allergies |
| Elasticity | Good, improved over natural rubber | Excellent, closest to natural latex |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate to high | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Enhanced resistance to oils and solvents | Limited chemical resistance |
| Durability | Improved aging and UV resistance | Moderate aging resistance |
| Cost | Moderate, due to modification process | Moderate to high |
| Medical Applications | Surgical gloves, barrier protection | Examination gloves, surgical gloves |
Introduction to Medical Glove Materials
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and improved elasticity compared to traditional polyisoprene rubber, making it a promising material for medical gloves requiring superior barrier protection. Polyisoprene rubber, valued for its natural latex-like softness and allergen-free properties, provides excellent tactile sensitivity and comfort without compromising durability. Both materials are essential in the medical glove industry, balancing protection, flexibility, and wearer safety.
Overview of Epoxidized Natural Rubber
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) is a chemically modified form of natural rubber that incorporates epoxy groups into the polymer backbone, enhancing its mechanical strength, oil resistance, and biocompatibility compared to standard polyisoprene rubber. This modification improves the thermal stability and reduces the allergenic potential, making ENR a promising alternative for medical gloves where durability and patient safety are critical. ENR's superior barrier properties and resistance to chemical degradation provide enhanced protection in medical environments, positioning it as an effective material for high-performance medical gloves.
Key Properties of Polyisoprene Rubber
Polyisoprene rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior tear resistance, making it ideal for medical gloves requiring durability and dexterity. Its natural latex-like properties provide excellent barrier protection against pathogens and chemicals while maintaining skin sensitivity and comfort. Compared to epoxidized natural rubber, polyisoprene offers reduced allergenic proteins, enhancing suitability for healthcare settings demanding hypoallergenic materials.
Biocompatibility and Allergenicity Comparisons
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits enhanced biocompatibility for medical gloves due to reduced protein content and lower residual latex allergenicity compared to conventional polyisoprene rubber (IR). ENR undergoes chemical modification that disrupts natural latex proteins responsible for Type I hypersensitivity, thereby decreasing allergic reactions among healthcare workers and patients. In contrast, polyisoprene rubber, while hypoallergenic compared to natural latex, still retains some residual proteins and may elicit contact dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) exhibits enhanced mechanical strength and superior durability compared to conventional polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for medical glove applications requiring high tensile strength and abrasion resistance. The introduction of epoxy groups in ENR improves cross-link density and stress distribution, resulting in gloves that resist punctures and tears more effectively. Polyisoprene rubber, while offering excellent elasticity and comfort, generally shows lower mechanical resilience and faster degradation under repetitive stress conditions.
Chemical Resistance in Medical Settings
Epoxidized natural rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it highly suitable for medical gloves exposed to solvents, oils, and disinfectants commonly used in healthcare environments. The epoxide groups in epoxidized natural rubber create a more stable polymer network, enhancing resistance to degradation caused by harsh chemicals. Polyisoprene rubber offers excellent elasticity and comfort but is more susceptible to chemical attack, limiting its lifespan and protective performance in chemically intensive medical settings.
Comfort, Fit, and Sensory Performance
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) enhances comfort and fit in medical gloves by offering increased elasticity and improved barrier properties compared to polyisoprene rubber. Polyisoprene rubber provides superior tactile sensitivity and softness, closely mimicking natural latex, which benefits precise medical tasks requiring high sensory performance. ENR gloves excel in durability and resistance to chemicals, while polyisoprene gloves prioritize comfort and fine touch, making them ideal for extended wear and delicate procedures.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) undergoes chemical modification through epoxidation, introducing epoxy groups that improve oil resistance and compatibility with various additives, making the manufacturing process more complex but allowing customization for specific medical glove properties. Polyisoprene rubber (IR), closely mimicking natural latex with a simpler formulation, offers streamlined processing with established large-scale vulcanization techniques, resulting in consistent elasticity and tactile sensitivity crucial for medical gloves. Scalability favors polyisoprene rubber due to its direct extraction and processing methods, whereas ENR requires additional chemical steps that may limit rapid upscale without advanced production infrastructure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced biodegradability and reduced reliance on synthetic additives compared to conventional polyisoprene rubber, making it a more environmentally sustainable option for medical gloves. ENR's modification process improves resistance to degradation while maintaining natural rubber's renewable carbon footprint, thereby lowering overall ecological impact during production and disposal. Polyisoprene rubber, while also derived from natural sources, typically requires more intensive chemical treatments and energy input, resulting in higher environmental costs and slower biodegradation rates.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and elasticity but comes at a higher production cost compared to traditional polyisoprene rubber, impacting overall glove pricing in the medical sector. Polyisoprene rubber remains the preferred choice due to its widespread availability, lower raw material costs, and superior tactile sensitivity essential for medical gloves. Market availability for polyisoprene is more robust worldwide, ensuring stable supply chains and competitive pricing, whereas ENR gloves are niche, limiting their market penetration despite performance benefits.
Infographic: Epoxidized natural rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Medical glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com