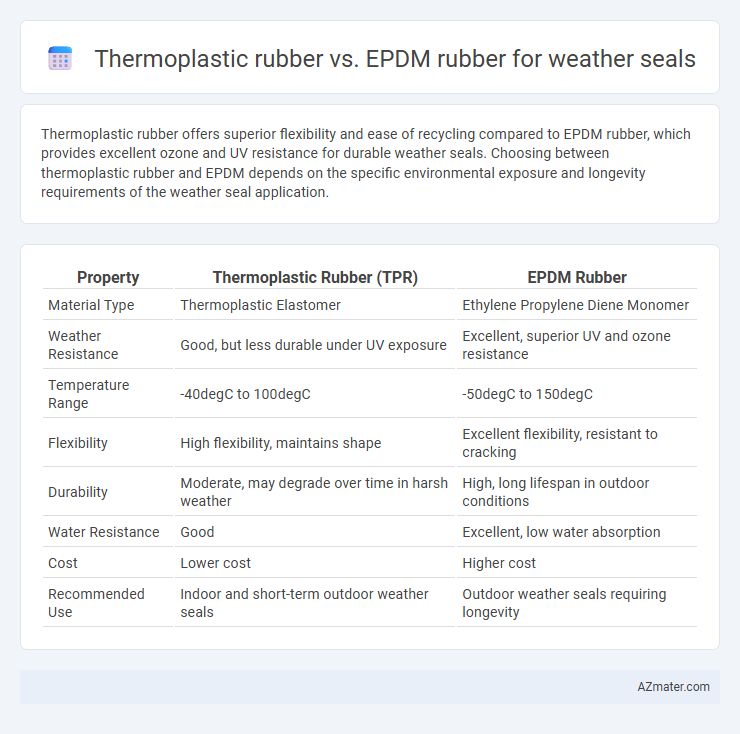
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility and ease of recycling compared to EPDM rubber, which provides excellent ozone and UV resistance for durable weather seals. Choosing between thermoplastic rubber and EPDM depends on the specific environmental exposure and longevity requirements of the weather seal application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer |
| Weather Resistance | Good, but less durable under UV exposure | Excellent, superior UV and ozone resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, maintains shape | Excellent flexibility, resistant to cracking |
| Durability | Moderate, may degrade over time in harsh weather | High, long lifespan in outdoor conditions |
| Water Resistance | Good | Excellent, low water absorption |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Recommended Use | Indoor and short-term outdoor weather seals | Outdoor weather seals requiring longevity |
Introduction to Weather Seal Materials
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) and EPDM rubber are commonly used materials for weather seals, offering excellent protection against environmental elements. TPR combines the flexibility of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics, providing durability and ease of installation in automotive and door/window seals. EPDM rubber is highly resistant to UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting weatherproofing in outdoor applications.
Overview of Thermoplastic Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the elastic properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics, making it ideal for weather seal applications requiring flexibility and durability. Its ability to be melted and reshaped without losing material properties ensures efficient manufacturing and consistent performance in sealing against moisture, dust, and temperature variations. TPR offers excellent resistance to abrasion, UV rays, and chemicals, providing long-lasting weatherproofing compared to traditional EPDM rubber seals.
Understanding EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber excels as a weather seal material due to its superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, maintaining flexibility in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 125degC. Unlike thermoplastic rubber (TPR), EPDM offers exceptional durability against oxidation and aging, making it ideal for outdoor sealing applications. Its chemical composition allows it to repel water and withstand prolonged exposure to environmental stressors, ensuring long-term performance in automotive and construction seals.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for weather seals requiring frequent movement, while EPDM rubber excels in UV resistance, ozone tolerance, and temperature stability from -40degC to 150degC, ideal for outdoor sealing applications. EPDM's superior elasticity and compressive set resistance ensure long-lasting sealing performance under harsh environmental conditions. TPR typically provides better processability and recyclability, but EPDM outperforms in durability and resistance to weathering agents critical for effective weather seals.
Weather Resistance: Thermoplastic Rubber vs EPDM
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate weather resistance with good flexibility and UV stability, making it suitable for various outdoor applications. EPDM rubber surpasses TPR in weather resistance due to its superior resistance to ozone, UV radiation, heat, and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-lasting performance as a weather seal. EPDM's exceptional durability in harsh environmental conditions makes it the preferred choice for sealing applications exposed to prolonged weather exposure.
Durability and Longevity
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility and resistance to ozone, UV, and varying temperatures, making it suitable for weather seals requiring moderate durability. EPDM rubber demonstrates superior longevity due to its outstanding resistance to heat, oxidation, and weathering, maintaining elasticity in extreme environments over extended periods. EPDM's resilience against harsh conditions makes it the preferred choice for long-lasting weather seals in automotive and construction applications.
Flexibility and Compression Set
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers superior flexibility due to its elastic polymer chains, enabling it to maintain performance in dynamic weather seal applications. EPDM rubber exhibits excellent compression set resistance, retaining its shape and sealing effectiveness after prolonged exposure to temperature extremes and weathering. TPR's ability to stretch without permanent deformation contrasts with EPDM's resilience against permanent compression, making each ideal for specific sealing requirements based on flexibility or long-term durability.
Installation and Maintenance
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers easier installation for weather seals due to its flexibility and ability to be heat-formed, allowing precise fitting on irregular surfaces. EPDM rubber requires more careful preparation and curing, making installation more labor-intensive but provides superior resistance to UV, ozone, and extreme temperatures. Maintenance for TPR seals involves regular cleaning to prevent buildup, while EPDM seals benefit from minimal upkeep due to their long-lasting durability and resistance to weathering.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) generally offers lower manufacturing costs compared to EPDM rubber due to its easier processability and shorter cycle times, making it economically favorable for large-scale production of weather seals. EPDM rubber provides superior weather resistance and durability but comes with higher raw material and processing expenses, impacting overall cost-effectiveness in long-term applications. Evaluating the initial investment against lifecycle performance is crucial when choosing between TPR and EPDM for weather sealing solutions.
Best Applications for Each Material
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) excels in weather seal applications requiring flexibility, abrasion resistance, and ease of installation, making it ideal for automotive door seals and window gaskets exposed to varying temperatures. EPDM rubber offers superior resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, making it the preferred choice for roofing seals, outdoor window frames, and industrial weather stripping. Both materials ensure durable sealing performance, but TPR is best suited for dynamic, flexible applications while EPDM is optimal for harsh environmental exposure.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs EPDM rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com