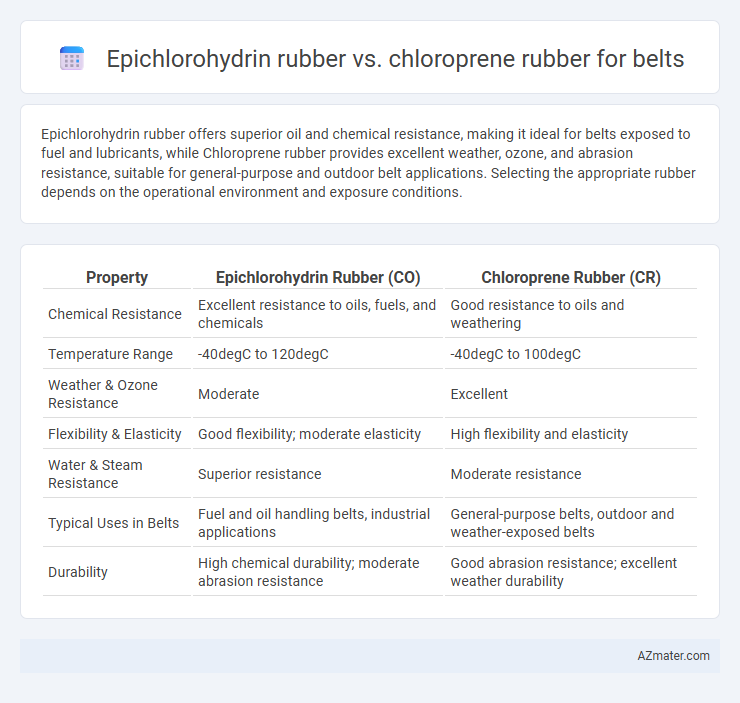
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for belts exposed to fuel and lubricants, while Chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather, ozone, and abrasion resistance, suitable for general-purpose and outdoor belt applications. Selecting the appropriate rubber depends on the operational environment and exposure conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (CO) | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance to oils and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | Good flexibility; moderate elasticity | High flexibility and elasticity |
| Water & Steam Resistance | Superior resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Typical Uses in Belts | Fuel and oil handling belts, industrial applications | General-purpose belts, outdoor and weather-exposed belts |
| Durability | High chemical durability; moderate abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance; excellent weather durability |
Overview of Epichlorohydrin and Chloroprene Rubbers
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) offers excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and ozone, making it ideal for belts exposed to harsh chemical environments and moderate heat. Chloroprene rubber (neoprene) provides balanced properties with good weathering, ozone, and flame resistance, delivering durability and flexibility for general-purpose belt applications. Both rubbers exhibit strong mechanical strength, but epichlorohydrin's superior oil resistance makes it preferred in industrial belts requiring chemical stability.
Key Chemical and Physical Properties
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and ozone, with a tensile strength typically around 15-25 MPa and elongation at break of 300-400%, making it ideal for belts in harsh chemical environments. Chloroprene rubber, known for its superior weather, ozone, and flame resistance, offers tensile strength in the range of 10-22 MPa and elongation up to 400%, providing durability for belts exposed to outdoor conditions. Both rubbers possess good abrasion resistance, but epichlorohydrin rubber generally outperforms chloroprene in low permeability and chemical stability, critical for industrial belt applications requiring high chemical endurance.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and wear properties compared to chloroprene rubber, making it highly suitable for belts exposed to harsh conditions and continuous friction. Chloroprene rubber provides good resistance to weathering and moderate abrasion but generally wears faster under heavy mechanical stress. The enhanced chemical structure of epichlorohydrin rubber results in better durability and longer service life in industrial belt applications where abrasion and wear resistance are critical.
Temperature Stability and Heat Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior temperature stability and heat resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, maintaining performance in continuous service temperatures up to 120degC and short-term exposure around 150degC. Chloroprene rubber typically withstands temperatures up to 100degC continuously and has moderate heat resistance but degrades faster under prolonged high-temperature conditions. Epichlorohydrin's enhanced thermal properties make it ideal for belts used in environments requiring consistent operation under elevated temperatures and exposure to oils and chemicals.
Oil, Fuel, and Chemical Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, fuels, and a wide range of chemicals compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for belts exposed to aggressive chemical environments. Chloroprene rubber provides good balanced resistance but tends to degrade faster when in continuous contact with hydrocarbons and certain solvents. For industrial belts requiring extended durability in harsh oil and fuel conditions, epichlorohydrin rubber ensures enhanced longevity and performance.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior flexibility with excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for belts requiring performance in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber provides enhanced elasticity and good tensile strength, ensuring belts maintain shape and resist deformation under dynamic loads. The choice between these rubbers balances Epichlorohydrin's flexibility and chemical resistance against Chloroprene's elasticity and mechanical durability for specific belt applications.
Ozone and Weathering Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior ozone and weathering resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it highly suitable for belts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its unique molecular structure provides excellent resistance to cracking and degradation caused by prolonged ozone exposure and UV radiation. Chloroprene rubber, while durable, tends to show accelerated surface oxidation and loss of mechanical properties under continuous ozone and weathering stress, reducing belt longevity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance, providing longer belt life in harsh industrial environments, which enhances cost-effectiveness despite its typically higher initial price. Chloroprene rubber, also known as neoprene, is more widely available and generally less expensive, making it a budget-friendly option for standard belt applications with moderate chemical exposure. Choosing between Epichlorohydrin and Chloroprene rubber depends on balancing upfront material costs against durability needs and supply chain accessibility.
Common Applications in Belt Manufacturing
Epichlorohydrin rubber is commonly used in belts requiring excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial conveyor belt applications exposed to harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber, also known as neoprene, offers superior flexibility, weather resistance, and durability, often employed in timing belts and power transmission belts subjected to dynamic stress and outdoor conditions. Both materials provide strong abrasion resistance, but epichlorohydrin excels in oil-heavy environments while chloroprene is favored for general-purpose belts with moderate chemical exposure.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Belt Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oil, chemicals, and ozone, making it ideal for belts exposed to harsh industrial environments, while chloroprene rubber provides excellent weather resistance, flexibility, and moderate chemical resistance, suitable for general-purpose conveyor belts. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific operational conditions such as temperature range, exposure to oils, and mechanical stress; epichlorohydrin is preferred for applications requiring enhanced durability against petroleum products, whereas chloroprene is favored for outdoor or moderate chemical exposure. Evaluating factors like tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elongation at break ensures optimal belt performance and longevity in the chosen rubber compound.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Chloroprene rubber for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com