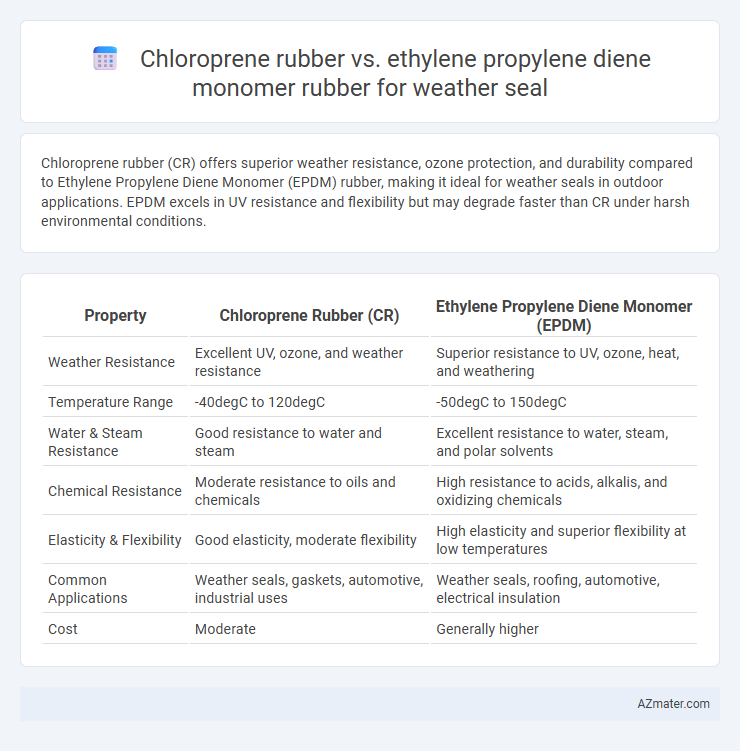
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior weather resistance, ozone protection, and durability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for weather seals in outdoor applications. EPDM excels in UV resistance and flexibility but may degrade faster than CR under harsh environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Weather Resistance | Excellent UV, ozone, and weather resistance | Superior resistance to UV, ozone, heat, and weathering |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 150degC |
| Water & Steam Resistance | Good resistance to water and steam | Excellent resistance to water, steam, and polar solvents |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and chemicals | High resistance to acids, alkalis, and oxidizing chemicals |
| Elasticity & Flexibility | Good elasticity, moderate flexibility | High elasticity and superior flexibility at low temperatures |
| Common Applications | Weather seals, gaskets, automotive, industrial uses | Weather seals, roofing, automotive, electrical insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally higher |
Introduction to Weather Seal Materials
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber are prominent materials used in weather seals due to their excellent resistance to environmental factors. CR offers superior resistance to ozone, oil, and chemicals, making it suitable for applications requiring durability against harsh conditions. EPDM excels in resisting UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and moisture, providing long-lasting weatherproofing for doors, windows, and automotive seals.
Overview of Chloroprene Rubber (CR)
Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its exceptional weather resistance and ozone stability, is widely used in weather seals due to its strong durability and flexibility under extreme temperatures. Its molecular structure provides superior resistance to aging, UV rays, and environmental degradation compared to other elastomers. CR's balanced mechanical properties make it ideal for maintaining airtight and watertight seals in automotive and architectural applications.
Overview of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber (EPDM)
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber (EPDM) offers exceptional weather resistance, making it highly effective for weather seals in automotive and construction applications. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures, ozone, UV radiation, and moisture degradation surpasses that of Chloroprene rubber, ensuring long-term durability and flexibility. EPDM's superior elasticity and chemical resistance contribute to maintaining airtight and watertight seals under diverse environmental conditions.
Weather Resistance: CR vs EPDM
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent weather resistance with strong ozone and UV stability, making it ideal for outdoor weather seal applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM) provides superior resistance to UV rays, ozone, moisture, and extreme temperatures, outperforming many other elastomers in long-term weather durability. EPDM's chemical structure gives it enhanced flexibility and longevity in weather seals, especially in automotive and construction industries where extreme weather resistance is critical.
Ozone and UV Stability Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior ozone and UV stability compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it more resistant to cracking and degradation under prolonged exposure to outdoor elements. EPDM, while highly resilient to heat and oxidation, tends to show less resistance to ozone, causing surface cracks faster than chloroprene in harsh environmental conditions. For weather seal applications requiring long-term exposure to sunlight and ozone-rich atmospheres, chloroprene rubber offers enhanced durability and sustained elasticity.
Temperature Performance: Low and High Extremes
Chloroprene rubber exhibits robust temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and sealing properties in ranges from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate temperature extremes. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber outperforms chloroprene in high-temperature stability, withstanding continuous exposure up to 150degC and transient peaks around 180degC, and excels at low temperatures down to -50degC without losing elasticity. For weather seals requiring superior performance across wide temperature extremes, EPDM offers enhanced durability against heat aging and cold brittleness compared to chloroprene rubber.
Chemical and Oil Resistance Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents compared to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, making it ideal for applications exposed to hydrocarbons. EPDM rubber demonstrates excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV radiation but has limited chemical and oil resistance, leading to potential degradation when exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Thus, CR is preferred for weather seals requiring robust chemical and oil resistance, while EPDM excels in outdoor environments demanding long-term weather durability.
Flexibility and Durability in Sealing Applications
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers excellent flexibility and weather resistance, maintaining elasticity in a broad temperature range, which ensures reliable sealing performance in dynamic environmental conditions. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber excels in durability against ozone, UV radiation, and extreme weather, providing superior long-term sealing integrity under harsh outdoor exposure. For sealing applications requiring both flexibility and extended lifespan, EPDM typically outperforms CR in resisting aging and environmental degradation while CR provides better mechanical resilience in moderately harsh environments.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers competitive pricing but may face supply fluctuations due to raw material dependencies, whereas Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber generally provides more stable availability and cost-effectiveness for large-scale weather seal production. EPDM's superior weather resistance and low maintenance requirements often justify its higher upfront cost compared to CR, which can degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure. Manufacturers prioritizing budget and consistent supply chains tend to favor EPDM for durable weather seals despite a slightly higher initial investment.
Best Applications: Choosing Between CR and EPDM for Weather Seals
Chloroprene rubber (CR) excels in weather seals due to its superior resistance to oil, ozone, and moderate weathering, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber offers outstanding UV, ozone, and extreme temperature resistance, making it the preferred choice for outdoor sealing in roofing, window gaskets, and electrical insulation. For applications demanding chemical resistance and moderate weather exposure, CR is suitable, while EPDM provides enhanced durability under prolonged outdoor conditions and thermal cycling.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber for Weather seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com