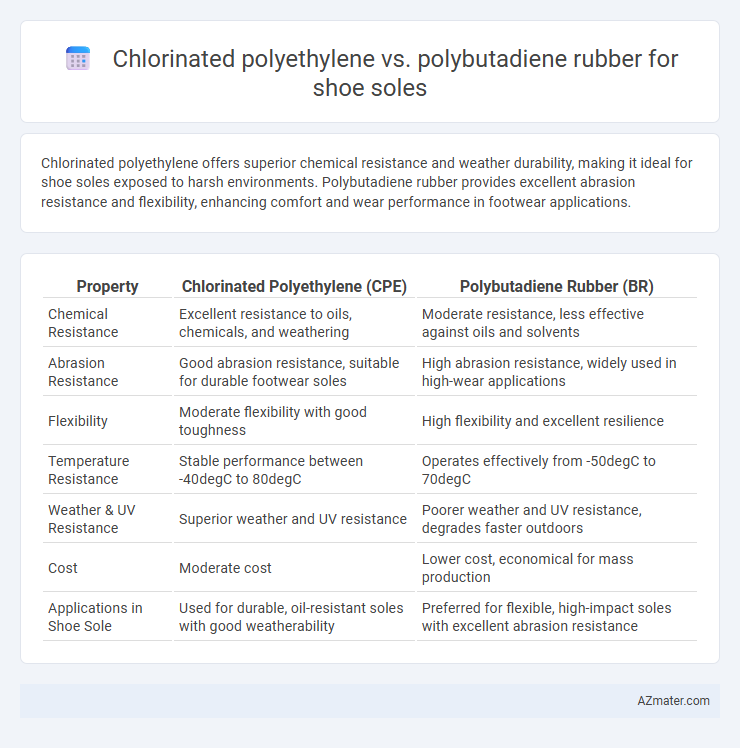
Chlorinated polyethylene offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh environments. Polybutadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, enhancing comfort and wear performance in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) | Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering | Moderate resistance, less effective against oils and solvents |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance, suitable for durable footwear soles | High abrasion resistance, widely used in high-wear applications |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility with good toughness | High flexibility and excellent resilience |
| Temperature Resistance | Stable performance between -40degC to 80degC | Operates effectively from -50degC to 70degC |
| Weather & UV Resistance | Superior weather and UV resistance | Poorer weather and UV resistance, degrades faster outdoors |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost, economical for mass production |
| Applications in Shoe Sole | Used for durable, oil-resistant soles with good weatherability | Preferred for flexible, high-impact soles with excellent abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) and polybutadiene rubber (BR) are prominent materials used in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct advantages. CPE is valued for its excellent chemical resistance, weather durability, and flexibility, making it suitable for outdoor and heavy-duty footwear. Polybutadiene rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, high resilience, and impact strength, ideal for athletic and casual shoes requiring enhanced comfort and durability.
Overview of Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE)
Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) offers superior chemical resistance, weather durability, and excellent flexibility, making it highly suitable for shoe soles exposed to harsh environments. Compared to Polybutadiene rubber, CPE provides enhanced UV stability and resistance to oils and acids, ensuring longer-lasting performance and reduced degradation. This material's balance of toughness and elasticity supports shock absorption and resilience, critical for comfortable, durable footwear applications.
Overview of Polybutadiene Rubber (BR)
Polybutadiene rubber (BR) is a synthetic elastomer renowned for its high wear resistance, excellent flexibility, and low-temperature performance, making it a preferred material for shoe soles that require durability and comfort. Its high resilience and good abrasion resistance contribute to longer-lasting footwear, especially in athletic and casual shoes. Compared to chlorinated polyethylene, BR offers superior traction and impact absorption, enhancing overall shoe sole performance.
Mechanical Properties: CPE vs BR
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) exhibits superior abrasion resistance and weatherability compared to polybutadiene rubber (BR), making it more durable for shoe soles exposed to harsh conditions. Polybutadiene rubber offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, contributing to enhanced cushioning and comfort during wear. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation at break are generally higher in BR, whereas CPE provides better resistance to oils and chemicals, improving sole longevity in industrial environments.
Abrasion Resistance Comparison
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) offers superior abrasion resistance compared to polybutadiene rubber, making it more durable for shoe sole applications subject to frequent wear. CPE exhibits enhanced chemical stability and toughness, which contribute to prolonged sole life under abrasive conditions. Polybutadiene rubber, while flexible and impact-resistant, tends to wear down faster when exposed to rough surfaces, limiting its lifespan in high-abrasion environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Footwear
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, but its flexibility is generally lower than that of polybutadiene rubber (BR), which provides superior elasticity and cushioning. Polybutadiene rubber's high resilience enhances shock absorption, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring enhanced comfort during extended wear. Selecting BR over CPE can significantly improve foot flexibility and reduce fatigue, especially in athletic and casual footwear.
Weather and Chemical Resistance
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) offers superior weather resistance for shoe soles, enduring UV exposure, ozone, and temperature fluctuations without cracking or degrading. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) provides excellent chemical resistance, particularly against oils and solvents, making it durable in harsh chemical environments. CPE is preferable for outdoor footwear due to its enhanced environmental resilience, while BR excels in applications requiring prolonged contact with industrial chemicals.
Cost and Manufacturing Process
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) offers a cost-effective alternative to polybutadiene rubber (BR) for shoe sole manufacturing due to its lower raw material price and simpler processing requirements. The manufacturing process for CPE involves straightforward extrusion and molding, reducing energy consumption and cycle times compared to the more complex vulcanization and curing steps necessary for BR. Cost advantages of CPE arise from its compatibility with existing thermoplastic equipment and reduced reliance on specialized catalysts and additives common in polybutadiene rubber production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability but poses environmental concerns due to chlorine content, which can release harmful dioxins during incineration, impacting sustainability negatively. Polybutadiene rubber (BR), derived from petroleum, exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity, yet its production involves non-renewable resources and generates volatile organic compounds (VOCs), presenting challenges for eco-friendly manufacturing. Choosing between CPE and BR for shoe soles requires careful consideration of life cycle assessments, potential recycling options, and regulatory compliance to minimize environmental footprint.
Best Applications for CPE and BR in Shoe Soles
Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) excels in shoe soles requiring superior chemical resistance, weather durability, and flexibility, making it ideal for outdoor and work footwear exposed to harsh environments. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) offers outstanding abrasion resistance, high resilience, and excellent impact absorption, which suits athletic and casual shoes demanding enhanced comfort and longevity. For shoe soles, CPE's resistance to oils, acids, and UV light complements heavy-duty applications, while BR's low-temperature flexibility and wear resistance make it the preferred choice for performance and sports footwear.
Infographic: Chlorinated polyethylene vs Polybutadiene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com