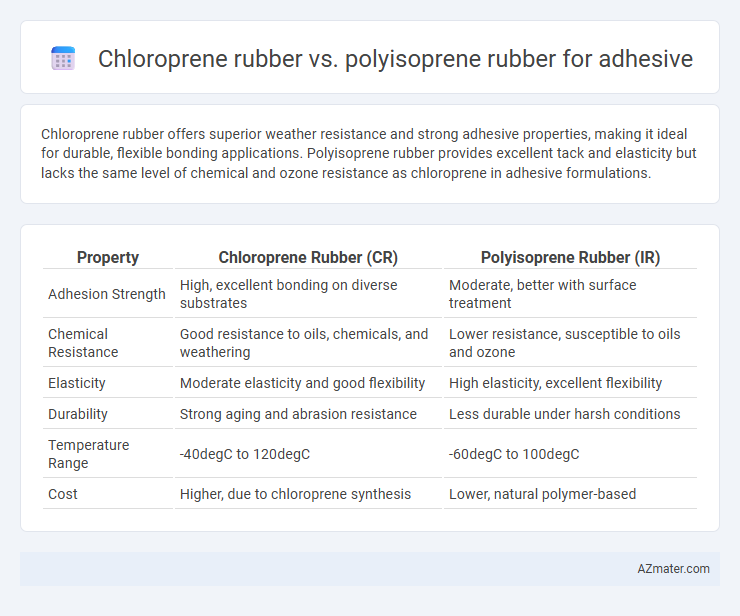
Chloroprene rubber offers superior weather resistance and strong adhesive properties, making it ideal for durable, flexible bonding applications. Polyisoprene rubber provides excellent tack and elasticity but lacks the same level of chemical and ozone resistance as chloroprene in adhesive formulations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Polyisoprene Rubber (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion Strength | High, excellent bonding on diverse substrates | Moderate, better with surface treatment |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering | Lower resistance, susceptible to oils and ozone |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity and good flexibility | High elasticity, excellent flexibility |
| Durability | Strong aging and abrasion resistance | Less durable under harsh conditions |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -60degC to 100degC |
| Cost | Higher, due to chloroprene synthesis | Lower, natural polymer-based |
Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber and Polyisoprene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and polyisoprene rubber (IR) are synthetic elastomers widely used in adhesive formulations due to their distinct chemical structures and properties. Chloroprene rubber offers excellent weathering resistance, chemical stability, and adhesion to various substrates, making it ideal for durable adhesive applications. Polyisoprene rubber, closely resembling natural rubber, provides superior elasticity and tackiness, enhancing adhesive performance in flexible bonding scenarios.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) consists of polychloroprene with chlorine atoms attached to the polymer backbone, providing excellent chemical resistance and weatherability, while polyisoprene rubber (IR) is a natural or synthetic polymer with a repeating isoprene unit and lacks chlorine, resulting in higher elasticity and better tensile strength. The presence of chlorine in chloroprene rubber enhances its resistance to oils, solvents, and oxidation, making it advantageous for adhesive applications requiring durability. Polyisoprene's unsaturated hydrocarbon structure offers superior flexibility but lower chemical resistance compared to the chlorinated structure in chloroprene rubber adhesives.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber (IR), making it ideal for durable adhesive applications. CR exhibits higher tensile strength (up to 25 MPa) and better abrasion resistance, whereas IR provides greater elasticity and superior tack due to its natural rubber origin. CR's moderate hardness (Shore A 55-70) contrasts with IR's softer texture (Shore A 40-60), influencing adhesive flexibility and bonding performance across different substrates.
Adhesive Performance Characteristics
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior adhesive performance due to its excellent balance of adhesion strength, chemical resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for bonding metals, fabrics, and elastomers. Polyisoprene rubber (IR) offers good initial tack and flexibility but generally shows lower resistance to heat, oils, and solvents, resulting in reduced long-term adhesive durability under harsh conditions. CR's enhanced cohesive strength and resistance to environmental degradation contribute to its widespread use in high-performance adhesive applications requiring durability and strong bonding.
Resistance to Heat, Oil, and Chemicals
Chloroprene rubber offers superior resistance to heat, oils, and various chemicals compared to polyisoprene rubber, making it ideal for demanding adhesive applications in automotive and industrial settings. Its enhanced durability against oxidative degradation and solvent exposure ensures long-term performance under harsh conditions. Polyisoprene rubber, while providing excellent elasticity, lacks the same level of chemical and thermal stability, limiting its use in high-exposure adhesive environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity in Adhesive Applications
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity in adhesive applications due to its balanced molecular structure, which enhances resistance to aging, ozone, and weathering. Polyisoprene rubber (IR), primarily composed of natural rubber, offers exceptional elasticity and tensile strength but demonstrates lower resistance to environmental degradation compared to chloroprene. The choice between CR and IR adhesives depends on the required durability and flexibility under dynamic or harsh conditions, with CR favored for long-term elasticity and IR preferred for applications requiring high initial stretch and recovery.
Aging, Weather, and Ozone Resistance
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior aging, weather, and ozone resistance compared to polyisoprene rubber (IR), making it ideal for adhesives exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CR's molecular structure includes chlorine atoms that enhance its oxidative stability and prevent degradation under UV radiation, while IR is prone to ozone cracking and accelerated aging due to its unsaturated hydrocarbon backbone. Consequently, adhesives formulated with chloroprene rubber maintain their mechanical integrity and adhesive properties longer in outdoor applications than those made with polyisoprene rubber.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Chloroprene rubber typically offers a cost advantage over polyisoprene rubber due to more stable supply chains and broader availability in industrial markets, which supports large-scale adhesive production. Polyisoprene rubber, while favored for its natural origin and excellent elasticity, tends to have higher price volatility influenced by natural latex supply fluctuations and limited synthetic alternatives. The cost-effectiveness of chloroprene rubber makes it a preferred choice for adhesive formulations requiring consistent performance and budget control.
Typical Applications in Adhesive Industry
Chloroprene rubber (CR) is widely used in adhesives for its excellent resistance to weathering, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive, marine, and industrial bonding applications. Polyisoprene rubber (IR) offers superior elasticity and tack, commonly used in pressure-sensitive adhesives, medical tapes, and high-performance contact adhesives where flexibility and strong initial grab are crucial. Both elastomers serve distinct roles, with CR favored for durability in harsh environments and IR preferred for applications requiring enhanced adhesion and conformability.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Adhesive Needs
Chloroprene rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for adhesives requiring durability in harsh environments. Polyisoprene rubber provides superior elasticity and tack, suitable for applications needing strong initial adhesion and flexibility. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing performance factors such as chemical resistance, elasticity, and environmental exposure specific to your adhesive requirements.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Polyisoprene rubber for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com