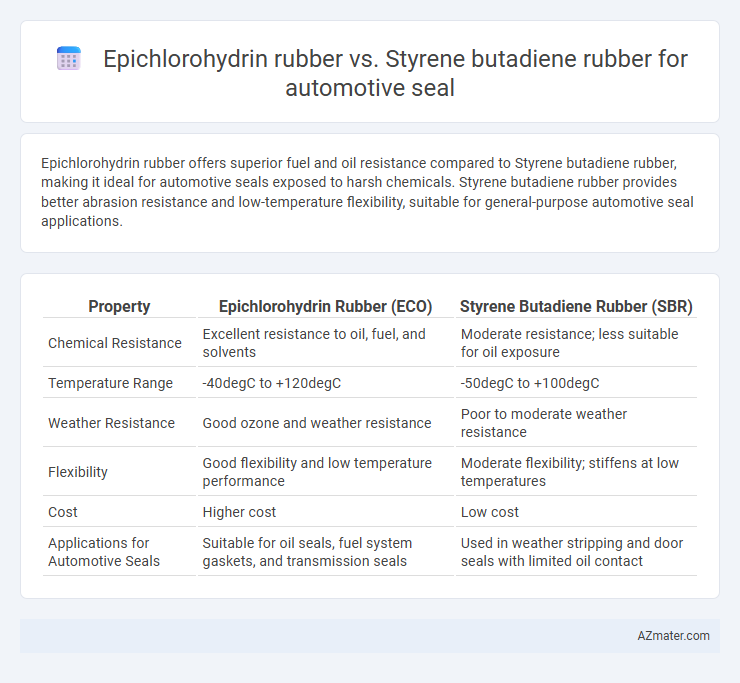
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior fuel and oil resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh chemicals. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, suitable for general-purpose automotive seal applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and solvents | Moderate resistance; less suitable for oil exposure |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to +120degC | -50degC to +100degC |
| Weather Resistance | Good ozone and weather resistance | Poor to moderate weather resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and low temperature performance | Moderate flexibility; stiffens at low temperatures |
| Cost | Higher cost | Low cost |
| Applications for Automotive Seals | Suitable for oil seals, fuel system gaskets, and transmission seals | Used in weather stripping and door seals with limited oil contact |
Introduction to Automotive Seal Materials
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) demonstrates superior resistance to oil, heat, and weathering, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the chemical resistance necessary for prolonged contact with automotive fluids. Selection between ECO and SBR depends on specific performance requirements such as temperature range, exposure to oils, and durability demands in automotive seal applications.
Overview of Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO)
Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, making it highly suitable for automotive seals exposed to harsh chemical environments. ECO offers superior low-temperature flexibility and good compression set resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), which lacks oil resistance and performs poorly in exposure to petroleum-based fluids. The unique chemical structure of epichlorohydrin imparts enhanced durability and dimensional stability, crucial for maintaining seal integrity in automotive engine bays and fuel systems.
Overview of Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used in automotive seals due to its excellent abrasion resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and good aging stability. Compared to Epichlorohydrin rubber, SBR offers superior resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications exposed to friction and mechanical stress. Its balanced properties ensure reliable performance in environments with varying temperatures and moderate exposure to oils and chemicals.
Chemical Resistance: ECO vs SBR
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), particularly against oils, fuels, and ozone, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environments. ECO's unique molecular structure provides enhanced resistance to polar solvents and acids, while SBR is more susceptible to swelling and degradation when in contact with hydrocarbons and oxygenated compounds. For automotive sealing applications demanding prolonged chemical stability, ECO offers greater durability and reliability than SBR.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining flexibility and sealing integrity between -40degC and 120degC, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to extreme environments. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) typically performs well within a narrower temperature range of -50degC to 100degC but tends to harden and lose elasticity faster under prolonged heat exposure. The enhanced thermal stability of epichlorohydrin rubber ensures better durability and leakage prevention in automotive seals operating in higher temperature conditions.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) exhibits superior ozone, oil, and chemical resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments. ECO delivers excellent mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, elongation, and compression set resistance, ensuring enhanced durability and long-term sealing performance under thermal and oxidative stress. SBR, while cost-effective with good abrasion resistance, generally lacks the chemical and heat resistance required for critical automotive sealing applications, leading to faster degradation in aggressive conditions.
Ozone and Weather Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior ozone and weather resistance compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides excellent resistance to ozone cracking, UV radiation, and oxidation, ensuring longer seal life and durability. In contrast, Styrene butadiene rubber tends to degrade faster when exposed to ozone and weathering, limiting its effectiveness in long-term outdoor applications.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil, fuel, and ozone resistance, making it highly durable for automotive seals but typically comes at a higher cost compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which is more economical and widely used due to its good abrasion resistance and ease of processing. Manufacturing with Epichlorohydrin requires specialized curing agents and precise control over vulcanization, potentially increasing production complexity and costs, whereas SBR benefits from well-established, cost-effective manufacturing processes with faster cycle times. Balancing material performance with production economics, SBR remains preferred for volume manufacturing, while Epichlorohydrin is selected for high-performance sealing applications where longevity justifies the investment.
Typical Automotive Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in automotive seals requiring superior resistance to oil, fuel, and weathering, commonly used in engine compartment gaskets, fuel system seals, and transmission components. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is preferred for applications needing good abrasion resistance and cost efficiency, such as door seals, window channel seals, and general-purpose weatherstripping. Both materials provide essential sealing performance, but ECO's chemical resistance makes it ideal for under-the-hood environments exposed to harsh fluids.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Automotive Seals
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil, ozone, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive seals exposed to harsh engine environments and fuel systems. Styrene butadiene rubber provides excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility at low temperatures, suitable for seals in less chemically aggressive, colder areas of the vehicle. Selecting the right rubber depends on factors such as exposure to oils, temperature ranges, and required durability to ensure optimal performance and longevity of automotive seals.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Automotive seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com