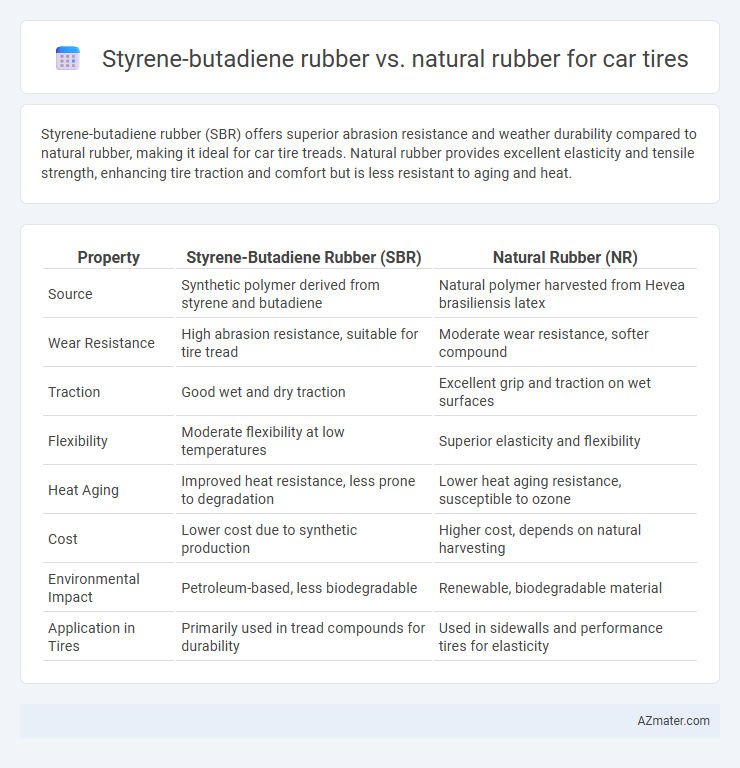
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and weather durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for car tire treads. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and tensile strength, enhancing tire traction and comfort but is less resistant to aging and heat.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Natural Rubber (NR) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic polymer derived from styrene and butadiene | Natural polymer harvested from Hevea brasiliensis latex |
| Wear Resistance | High abrasion resistance, suitable for tire tread | Moderate wear resistance, softer compound |
| Traction | Good wet and dry traction | Excellent grip and traction on wet surfaces |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility at low temperatures | Superior elasticity and flexibility |
| Heat Aging | Improved heat resistance, less prone to degradation | Lower heat aging resistance, susceptible to ozone |
| Cost | Lower cost due to synthetic production | Higher cost, depends on natural harvesting |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-based, less biodegradable | Renewable, biodegradable material |
| Application in Tires | Primarily used in tread compounds for durability | Used in sidewalls and performance tires for elasticity |
Introduction: Styrene-Butadiene Rubber vs Natural Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and natural rubber (NR) are key materials in car tire manufacturing, each offering distinct properties for tire performance. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it suitable for tread compounds exposed to wear and environmental factors. Natural rubber delivers superior elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience, enhancing grip and durability in tires under dynamic driving conditions.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic copolymer composed of styrene and butadiene monomers, featuring a random arrangement that provides enhanced abrasion resistance and aging stability compared to natural rubber. Natural rubber, primarily cis-1,4-polyisoprene, possesses a highly ordered crystalline structure contributing to its superior elasticity and tensile strength but lower resistance to heat and oxidation. The differing chemical compositions influence tire performance, with SBR's styrene content improving durability while natural rubber's molecular structure offers better dynamic properties for car tires.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is synthesized through emulsion or solution polymerization, allowing precise control over molecular weight and composition, which enhances tire durability and performance. Natural rubber is harvested from Hevea brasiliensis latex, followed by purification and mastication to improve processability and elasticity in tire manufacturing. The synthetic nature of SBR offers consistent quality and faster production cycles compared to the seasonally dependent and labor-intensive natural rubber extraction process.
Performance Under Different Weather Conditions
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and heat aging stability compared to natural rubber, making it more durable in hot and dry weather conditions. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and resilience, delivering better traction and performance in wet and cold environments due to its higher tensile strength and flexibility. Car tires combining SBR and natural rubber optimize performance by balancing durability in warm climates with enhanced grip and flexibility in adverse weather.
Tread Wear and Longevity
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and tread wear performance compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for car tire treads subjected to harsh road conditions. SBR's enhanced durability extends tire longevity, providing consistent traction and reduced degradation over time. In contrast, natural rubber excels in flexibility and grip but tends to wear faster under high-stress, high-temperature environments, limiting its lifespan for tire tread applications.
Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits lower rolling resistance compared to natural rubber, enhancing fuel efficiency in car tires by reducing energy loss during tire rotation. The synthetic polymer structure of SBR provides better abrasion resistance and stability at high temperatures, contributing to longer tire life and consistent fuel savings. In contrast, natural rubber offers superior elasticity and grip but results in higher rolling resistance, which can decrease overall fuel economy in automotive applications.
Grip, Traction, and Handling Characteristics
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior grip and traction on wet surfaces compared to natural rubber, making it a common choice for car tires designed for varied weather conditions. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and handling characteristics, delivering better performance in dry conditions and improved ride comfort. Combining SBR with natural rubber in tire compounds enhances grip, traction, and handling by leveraging SBR's abrasion resistance and natural rubber's resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) used in car tires is derived from synthetic polymers produced through petrochemical processes, leading to higher carbon emissions and non-renewable resource dependency compared to natural rubber, which is harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees and is biodegradable. Natural rubber offers superior biodegradability and supports sustainable agriculture when managed properly, reducing environmental footprint through carbon sequestration and lower reliance on fossil fuels. However, SBR tires typically feature enhanced durability and abrasion resistance, potentially extending tire life and mitigating environmental impact through reduced frequency of replacements.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a cost-effective alternative to natural rubber (NR) in car tire manufacturing due to its synthetic production process, resulting in more stable pricing and higher availability throughout the year. Natural rubber, sourced from Hevea brasiliensis trees, is subject to seasonal fluctuations and geopolitical factors, often leading to higher prices and supply inconsistencies. SBR's widespread use in tire treads stems from its lower cost per kilogram and assured market supply, making it a preferred choice for large-scale tire production.
Application Suitability for Modern Car Tires
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers enhanced abrasion resistance and better aging properties compared to natural rubber, making it highly suitable for modern car tire treads subjected to diverse road conditions. Natural rubber excels in providing superior elasticity and tensile strength, crucial for tire sidewalls and components requiring flexibility and fatigue resistance. The combination of SBR's durability and natural rubber's resilience optimizes performance, safety, and longevity in contemporary tire manufacturing.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Natural rubber for Car tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com