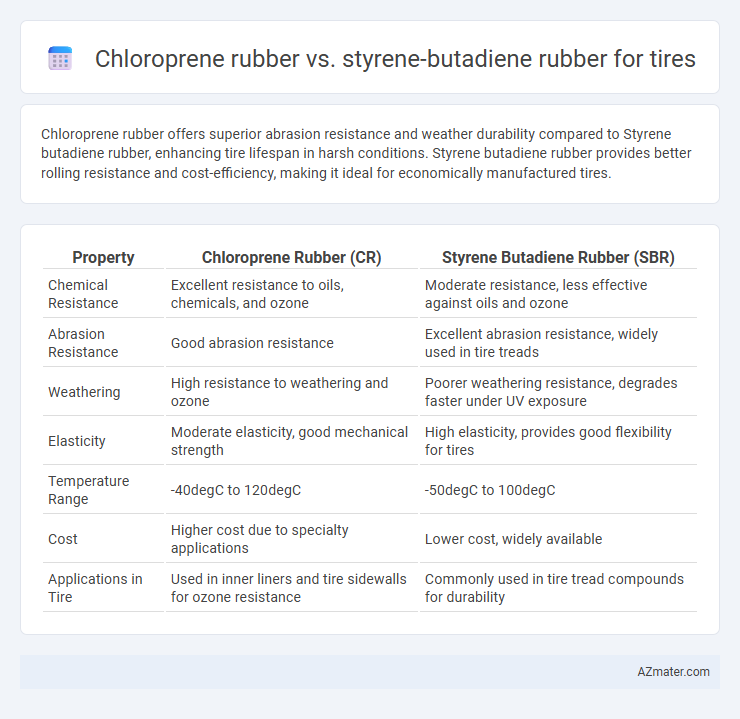
Chloroprene rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and weather durability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber, enhancing tire lifespan in harsh conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber provides better rolling resistance and cost-efficiency, making it ideal for economically manufactured tires.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chloroprene Rubber (CR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and ozone | Moderate resistance, less effective against oils and ozone |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance, widely used in tire treads |
| Weathering | High resistance to weathering and ozone | Poorer weathering resistance, degrades faster under UV exposure |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, good mechanical strength | High elasticity, provides good flexibility for tires |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -50degC to 100degC |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialty applications | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications in Tire | Used in inner liners and tire sidewalls for ozone resistance | Commonly used in tire tread compounds for durability |
Introduction to Chloroprene Rubber and Styrene Butadiene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber (CR), known for its excellent oil, chemical, and weather resistance, is widely used in tire manufacturing to enhance durability and performance under harsh conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it a cost-effective choice for tire tread compounds that require good wear and traction. Both rubbers play crucial roles in tire applications, with CR providing enhanced resilience and SBR contributing to improved overall tire longevity.
Chemical Structure Differences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) features repeating units of chloroprene with a chlorine atom enhancing its chemical stability and resistance to oils and weathering, while Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) consists of styrene and butadiene monomers, offering a balance of abrasion resistance and flexibility due to its aromatic and diene components. The presence of chlorinated sites in CR's molecular chain provides superior resistance to ozone and heat compared to the non-chlorinated hydrocarbon backbone of SBR. These chemical structure differences directly impact their performance in tire applications, with CR excelling in durability and weather resistance, whereas SBR is favored for cost-efficiency and tread wear.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior ozone resistance and weathering stability compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it more durable for tire applications exposed to harsh environments. CR offers higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, enhancing the tire's longevity and performance under stress, while SBR provides greater flexibility and lower rolling resistance, contributing to improved fuel efficiency. The elasticity of SBR allows for better grip on wet surfaces, but CR's enhanced mechanical robustness is preferred for heavy-duty tires requiring enhanced toughness and durability.
Performance in Tire Applications
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior oil and ozone resistance along with excellent weatherability, enhancing tire durability in harsh environmental conditions. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides improved abrasion resistance and better wet traction, making it a cost-effective choice for tire treads. Tires incorporating CR often exhibit longer service life and stability, while SBR-based tires deliver enhanced grip and wear performance on varied road surfaces.
Durability and Longevity in Tires
Chloroprene rubber (CR) offers superior ozone, weather, and oil resistance compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), enhancing tire durability under harsh environmental conditions. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and good aging properties but generally exhibits lower resistance to heat and ozone, potentially reducing tire longevity. Tires formulated with Chloroprene rubber tend to maintain structural integrity longer, making them preferable for long-lasting, high-performance applications.
Resistance to Weathering and Ozone
Chloroprene rubber (CR) exhibits superior resistance to weathering and ozone compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making it an ideal choice for tire applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions. CR's molecular structure provides enhanced protection against oxidative degradation, maintaining flexibility and durability over prolonged outdoor exposure. In contrast, SBR is more susceptible to cracking and loss of mechanical properties when subjected to ozone and UV radiation.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) generally has higher production costs due to its complex synthesis and superior chemical resistance, making it less cost-efficient than styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) for tire manufacturing. SBR dominates the tire industry with widespread availability and lower raw material costs, providing an economically favorable option for large-scale tire production. Supply chain stability and extensive production infrastructure further enhance SBR's cost efficiency and accessibility compared to chloroprene rubber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with SBR generally offering improved eco-friendliness due to better recyclability and lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. CR, derived from polychloroprene, involves chlorine-based chemistry that can release harmful substances and generate more toxic byproducts compared to SBR, whose synthesis relies on non-chlorinated monomers. Sustainable tire manufacturing increasingly favors SBR for its compatibility with bio-based feedstocks and lower ecological footprint, supporting carbon reduction goals in the automotive industry.
Industry Standards and Manufacturer Preferences
Chloroprene rubber (CR) and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) are both widely used in tire manufacturing, with CR known for its superior oil resistance and weather durability, meeting ASTM D2000 standards for automotive applications. SBR, favored for its cost-effectiveness and abrasion resistance, adheres to industry benchmarks such as ISO 1629 and is preferred in passenger car and truck tire treads. Manufacturers often choose CR for premium tires requiring enhanced chemical stability, while SBR dominates mass-market tires due to balanced performance and economy.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Tires
Chloroprene rubber offers superior oil resistance and weather durability, making it ideal for tires exposed to harsh environmental conditions or chemical exposure. Styrene butadiene rubber excels in abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, providing strong performance in standard passenger car tires. Selecting the right rubber depends on the specific tire application, with chloroprene preferred for specialized demands and styrene butadiene favored for general use due to its balance of performance and value.
Infographic: Chloroprene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com