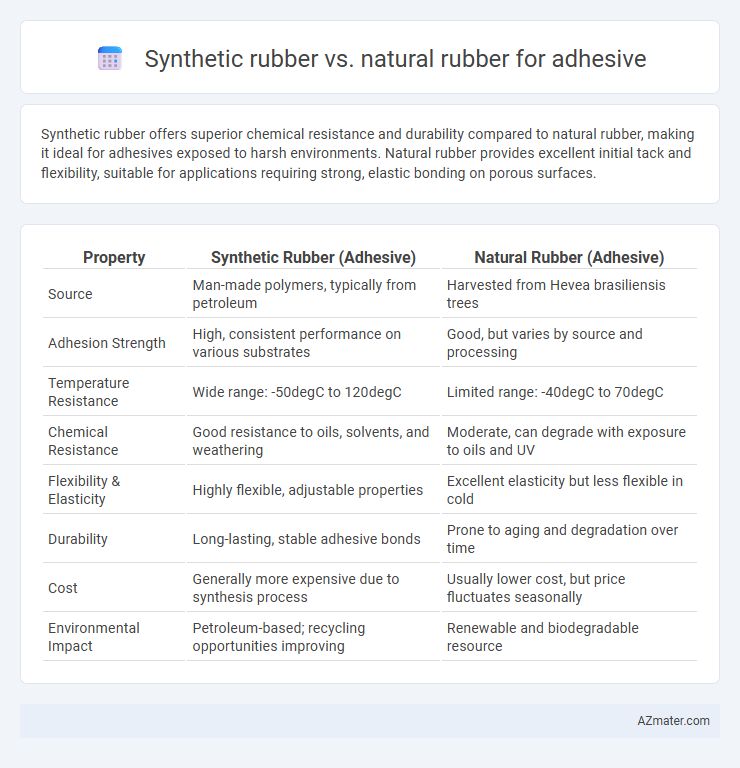
Synthetic rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for adhesives exposed to harsh environments. Natural rubber provides excellent initial tack and flexibility, suitable for applications requiring strong, elastic bonding on porous surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Rubber (Adhesive) | Natural Rubber (Adhesive) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers, typically from petroleum | Harvested from Hevea brasiliensis trees |
| Adhesion Strength | High, consistent performance on various substrates | Good, but varies by source and processing |
| Temperature Resistance | Wide range: -50degC to 120degC | Limited range: -40degC to 70degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering | Moderate, can degrade with exposure to oils and UV |
| Flexibility & Elasticity | Highly flexible, adjustable properties | Excellent elasticity but less flexible in cold |
| Durability | Long-lasting, stable adhesive bonds | Prone to aging and degradation over time |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to synthesis process | Usually lower cost, but price fluctuates seasonally |
| Environmental Impact | Petroleum-based; recycling opportunities improving | Renewable and biodegradable resource |
Introduction to Synthetic and Natural Rubber
Synthetic rubber is a man-made elastomer derived from petroleum-based monomers, offering consistent quality and enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion. Natural rubber, sourced from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, provides excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and adhesive properties due to its high molecular weight polyisoprene content. Both materials serve critical roles in adhesive formulations, with synthetic rubber favored for durability and chemical resistance, while natural rubber excels in flexibility and tackiness.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Synthetic rubber, primarily composed of polymers such as styrene-butadiene (SBR) or polyisoprene, features a more controlled chemical composition and uniform molecular structure, enhancing adhesive properties like resistance to heat and chemicals. Natural rubber, derived from polyisoprene with a cis-1,4 configuration, possesses a highly elastic molecular structure but lacks consistency in composition, which can affect adhesive performance under variable environmental conditions. The vulcanization process in both types introduces cross-linking in their polymer chains, improving their mechanical strength and adhesion characteristics, but synthetic variants often provide superior chemical resistance due to tailored monomer units.
Source and Production Processes
Synthetic rubber is derived from petrochemical sources through polymerization processes, enabling consistent quality and tailored properties ideal for adhesive formulations. Natural rubber is harvested as latex from Hevea brasiliensis trees and undergoes coagulation and drying, offering excellent elasticity but with variability due to seasonal and environmental factors. Production of synthetic rubber involves controlled chemical reactions such as emulsion or solution polymerization, while natural rubber relies on agricultural harvesting methods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic rubber adhesives, primarily derived from petroleum-based polymers, contribute significantly to carbon emissions and are less biodegradable, raising concerns about environmental pollution and long-term waste management. Natural rubber adhesives, sourced from renewable Hevea brasiliensis sap, offer enhanced biodegradability and lower ecological footprint, promoting sustainable harvesting practices and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Advances in bio-based synthetic rubbers aim to bridge performance with eco-friendliness, but natural rubber remains superior in lifecycle sustainability within adhesive applications.
Performance Characteristics in Adhesives
Synthetic rubber in adhesives offers superior resistance to temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and aging compared to natural rubber, enhancing durability and longevity. Natural rubber provides excellent initial tack and elasticity, making it suitable for high-performance pressure-sensitive adhesives requiring strong adhesion and flexibility. Performance optimization in adhesives often involves balancing synthetic rubber's robustness with natural rubber's adhesive properties to meet specific application demands.
Adhesion Strength and Versatility
Synthetic rubber adhesives generally offer higher adhesion strength and greater versatility across diverse surfaces compared to natural rubber adhesives, which have limitations in bonding certain materials. The molecular structure of synthetic rubbers such as styrene-butadiene or nitrile enhances durability, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Natural rubber adhesives, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, often exhibit lower resistance to heat and chemicals, restricting their use in specialized environments.
Cost and Availability
Synthetic rubber generally offers more consistent cost advantages due to large-scale industrial production and stable supply chains, reducing fluctuations common in natural rubber markets influenced by weather and geopolitical factors. Natural rubber, while sometimes cheaper in raw form, faces availability challenges linked to agricultural conditions and harvesting cycles, potentially increasing overall costs for adhesive manufacturers. The reliability and scalability of synthetic rubber make it a preferred choice in adhesive applications where cost predictability and steady supply are critical.
Durability and Lifespan
Synthetic rubber adhesives, such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and nitrile rubber (NBR), offer superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to natural rubber adhesives due to their enhanced resistance to heat, oils, and environmental degradation. Natural rubber adhesives exhibit excellent initial tack and flexibility but tend to deteriorate faster under UV exposure and oxidation, resulting in a shorter service life. The chemically engineered molecular structure of synthetic rubber provides improved mechanical strength and aging resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring extended adhesive performance.
Applications in Various Industries
Synthetic rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance and consistent quality, making it ideal for adhesives in automotive, electronics, and medical industries where durability and precision are crucial. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and tackiness, preferred in packaging, footwear, and construction adhesives for flexible bonding requirements. Both types cater to diverse industry demands, with synthetic variants excelling in harsh environments and natural rubber favored for eco-friendly, high-performance adhesive solutions.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Adhesive Formulation
Selecting the right rubber for adhesive formulation hinges on performance requirements such as elasticity, chemical resistance, and temperature stability. Synthetic rubber variants like SBR and NBR offer superior resistance to oils and solvents, making them ideal for industrial adhesives, while natural rubber provides excellent tack and flexibility suited for general-purpose and pressure-sensitive adhesives. Understanding the specific application environment and bonding needs ensures optimal adhesive durability and effectiveness.
Infographic: Synthetic rubber vs Natural rubber for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com