Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil and chemical resistance compared to Butyl rubber, making it ideal for sealants exposed to harsh environments. Butyl rubber provides excellent air and moisture impermeability, ensuring durable and flexible sealing performance in moderate chemical conditions.
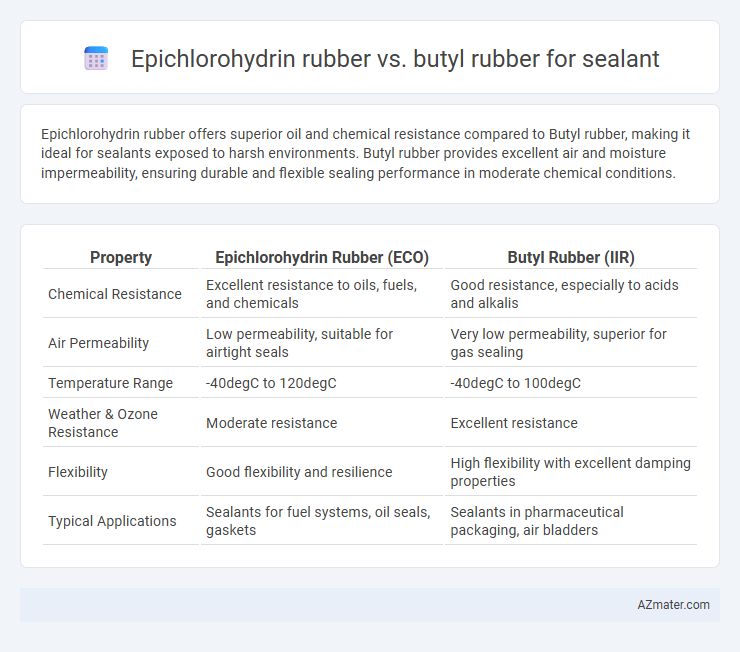
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Butyl Rubber (IIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Good resistance, especially to acids and alkalis |
| Air Permeability | Low permeability, suitable for airtight seals | Very low permeability, superior for gas sealing |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | Moderate resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and resilience | High flexibility with excellent damping properties |
| Typical Applications | Sealants for fuel systems, oil seals, gaskets | Sealants in pharmaceutical packaging, air bladders |
Introduction to Epichlorohydrin Rubber and Butyl Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent ozone, oil, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for demanding sealant applications in automotive and industrial sectors. Butyl rubber, derived from isobutylene and isoprene, offers superior impermeability to gases and weather resistance, commonly used in inner tubes and sealants requiring air retention and durability. Both rubbers provide unique sealing properties, with Epichlorohydrin excelling in chemical exposure and Butyl in airtightness and weatherproofing.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a chlorinated epoxy backbone that provides excellent oil and chemical resistance due to its polar epichlorohydrin groups, whereas butyl rubber (IIR) is a copolymer of isobutylene with a small amount of isoprene, creating a saturated hydrocarbon backbone responsible for superior air and gas impermeability. The chemical structure of ECO imparts higher resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat compared to butyl rubber, which excels in elasticity and damping properties but has lower chemical resistance. Compositionally, ECO's chlorine atoms increase its polarity and chemical robustness, while butyl rubber's saturated hydrocarbon chain limits reactivity, making each suitable for specific sealing applications based on environmental and chemical exposure.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) excels in oil resistance, low gas permeability, and moderate tensile strength, making it suitable for sealants exposed to fuels and chemicals. Butyl rubber offers superior air impermeability, excellent elasticity, and exceptional resistance to ozone and weathering, resulting in durable sealants for automotive and construction applications. Tensile strength of ECO ranges from 8 to 15 MPa, while butyl rubber typically demonstrates tensile strength between 3 to 7 MPa with higher elongation at break, emphasizing its flexibility and resilience in dynamic sealing environments.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent thermal stability with continuous use temperatures up to 100degC and superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and a wide range of chemicals including fuels, oils, and solvents. Butyl rubber provides exceptional chemical resistance to acids, alkalis, polar solvents, and excellent impermeability to gases, with thermal tolerance typically up to 120degC in continuous service. For applications requiring robust thermal endurance and resistance to aggressive chemicals, butyl rubber's higher temperature limit and broader chemical compatibility often make it the preferred choice over epichlorohydrin rubber in sealant formulations.
Weathering and Ozone Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent weathering resistance due to its high polarity and chemical stability, making it highly effective against ozone exposure and oxidative aging. Butyl rubber demonstrates superior ozone resistance thanks to its saturated polymer backbone, which prevents ozone cracking and prolongs sealant lifespan in harsh environmental conditions. Both elastomers offer robust performance for sealants, with Epichlorohydrin favored for chemical resistance and Butyl preferred for extreme ozone and weather durability.
Adhesion Qualities for Sealant Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior adhesion qualities for sealant applications due to its excellent resistance to oil, chemicals, and weathering, ensuring strong and durable bonds on diverse substrates. Butyl rubber offers good flexibility and excellent impermeability but typically demonstrates weaker adhesion to non-porous surfaces compared to epichlorohydrin rubber, often requiring primers for effective bonding. In sealing applications demanding robust adhesion and chemical resistance, epichlorohydrin rubber is often preferred for its consistent performance under harsh environmental conditions.
Processing and Curing Characteristics
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone, with relatively straightforward processing due to its good extrusion and molding properties, while curing typically requires sulfur or peroxide vulcanization to achieve flexible and durable seals. Butyl rubber offers superior impermeability and chemical resistance, with more complex curing behavior that often involves halogenation or curing with sulfur compounds, resulting in exceptional air and gas barrier performance essential for high-quality sealants. Both materials require careful temperature and catalyst control during curing to optimize cross-link density, mechanical strength, and elongation properties critical for effective sealing applications.
Typical Sealant Application Scenarios
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for sealants in automotive gaskets, fuel system components, and industrial machinery exposed to harsh chemicals. Butyl rubber provides superior air and moisture impermeability, excelling in applications such as glazing sealants, roofing membranes, and medical tubing where airtight and watertight seals are critical. Both materials are selected based on environmental exposure and chemical compatibility, with Epichlorohydrin favored for oil resistance and Butyl for impermeability in typical sealant scenarios.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility at a moderate cost, making it suitable for specialized sealant applications requiring durability in harsh environments. Butyl rubber is generally more cost-effective and exhibits excellent air impermeability and weather resistance, contributing to its popularity in sustainable sealing solutions with a longer lifecycle and reduced environmental impact. For eco-friendly projects, butyl rubber's lower carbon footprint and recyclability often outweigh the higher raw material expenses associated with epichlorohydrin rubber.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Sealant Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to ozone, oil, and weathering, making it ideal for sealants in harsh industrial environments requiring chemical and weather durability. Butyl rubber provides excellent impermeability to gases and outstanding flexibility at low temperatures, making it suitable for applications demanding airtight seals and vibration resistance. Selecting the right rubber depends on balancing epichlorohydrin's chemical resilience with butyl's gas impermeability to optimize sealant performance for specific environmental conditions.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Butyl rubber for Sealant
 azmater.com
azmater.com