Styrene-butadiene rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for rollers, while polyurethane rubber provides superior load-bearing capacity and chemical resistance. Choosing between Styrene-butadiene and polyurethane depends on the specific roller application requirements such as durability, flexibility, and exposure conditions.
Table of Comparison
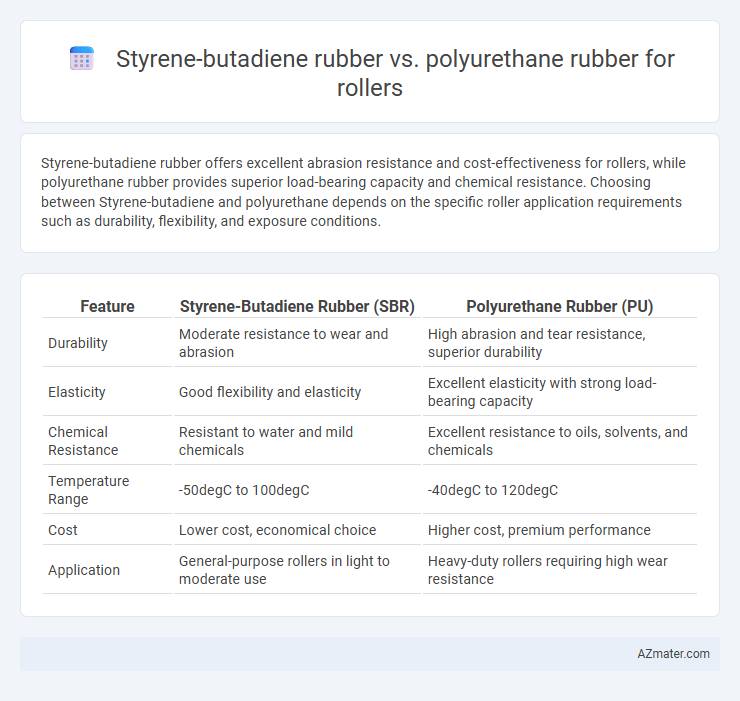
| Feature | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate resistance to wear and abrasion | High abrasion and tear resistance, superior durability |
| Elasticity | Good flexibility and elasticity | Excellent elasticity with strong load-bearing capacity |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to water and mild chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical choice | Higher cost, premium performance |
| Application | General-purpose rollers in light to moderate use | Heavy-duty rollers requiring high wear resistance |
Introduction to Roller Materials
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice for industrial roller applications requiring durability and moderate flexibility. Polyurethane rubber provides superior mechanical strength, higher tear resistance, and enhanced chemical stability, ideal for rollers exposed to aggressive environments and heavy loads. Selection between SBR and polyurethane depends on operational demands such as wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and exposure to oils or solvents.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer widely used for rollers due to its excellent abrasion resistance, good aging stability, and cost-effectiveness compared to natural rubber. SBR exhibits strong resilience and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under dynamic loads and varying temperatures. Its chemical resistance is moderate, making it suitable for general industrial rollers, although less resistant than polyurethane rubber in oil or solvent exposure.
Overview of Polyurethane Rubber (PU)
Polyurethane rubber (PU) offers superior abrasion resistance, excellent load-bearing capacity, and enhanced tear strength compared to styrene-butadiene rubber, making it ideal for heavy-duty roller applications. PU's chemical resistance and elasticity enable longer service life and improved performance under varying operational conditions. These attributes make polyurethane a preferred choice for rollers requiring durability and high mechanical strength in industrial settings.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good resilience, making it suitable for rollers subjected to moderate wear and impact. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior tensile strength, higher load-bearing capacity, and enhanced resistance to oil, chemicals, and elongation, ideal for heavy-duty roller applications requiring durability and flexibility. Key physical properties such as hardness, tear strength, and elongation show polyurethane consistently outperforms SBR in demanding operational environments.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and moderate durability, making it suitable for rollers subjected to medium-impact environments and general wear. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior wear resistance and higher load-bearing capacity, delivering enhanced durability in heavy-duty roller applications with frequent stress and friction. For rollers requiring prolonged lifespan and resistance to cuts, tears, and chemical exposure, polyurethane rubber outperforms Styrene-butadiene rubber significantly.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate chemical resistance, performing well against oils, mild acids, and alkalis, but degrades when exposed to strong solvents and ozone, making it less ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance, especially against oils, solvents, and abrasion, and maintains its properties in diverse environmental conditions, including exposure to UV radiation and extreme temperatures. For roller applications requiring robust chemical resistance and environmental durability, polyurethane rubber provides enhanced longevity and performance compared to SBR.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for roller applications. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior abrasion resistance and longer service life, potentially reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that polyurethane's durability can lead to cost savings over time despite the higher initial investment.
Application Performance in Industrial Rollers
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it suitable for industrial rollers exposed to moderate mechanical stress and heat. Polyurethane rubber outperforms SBR with superior load-bearing capacity, enhanced chemical resistance, and higher tear strength, ideal for heavy-duty rollers in harsh industrial environments involving oils, solvents, and dynamic stress. Industrial applications requiring durability under intense wear and exposure to aggressive chemicals benefit significantly from polyurethane rollers, while SBR remains cost-effective for moderate performance needs.
Maintenance and Lifespan Factors
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) rollers exhibit excellent resistance to abrasion and moderate chemical exposure, resulting in lower maintenance frequency and predictable wear patterns. Polyurethane rubber rollers provide superior resistance to oils, solvents, and mechanical stress, extending lifespan significantly under harsh operational conditions while requiring less frequent replacements. Maintenance intervals for polyurethane rollers tend to be longer due to their enhanced durability, whereas SBR rollers may need more regular inspections and repairs to prevent premature failure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Rollers
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for rollers in heavy-duty industrial applications. Polyurethane rubber surpasses SBR in tear strength, elasticity, and chemical resistance, providing superior durability for high-performance roller demands. Selecting the right rubber depends on application-specific factors such as load, exposure conditions, and longevity requirements, with polyurethane preferred for demanding environments and SBR suited for budget-conscious uses.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com