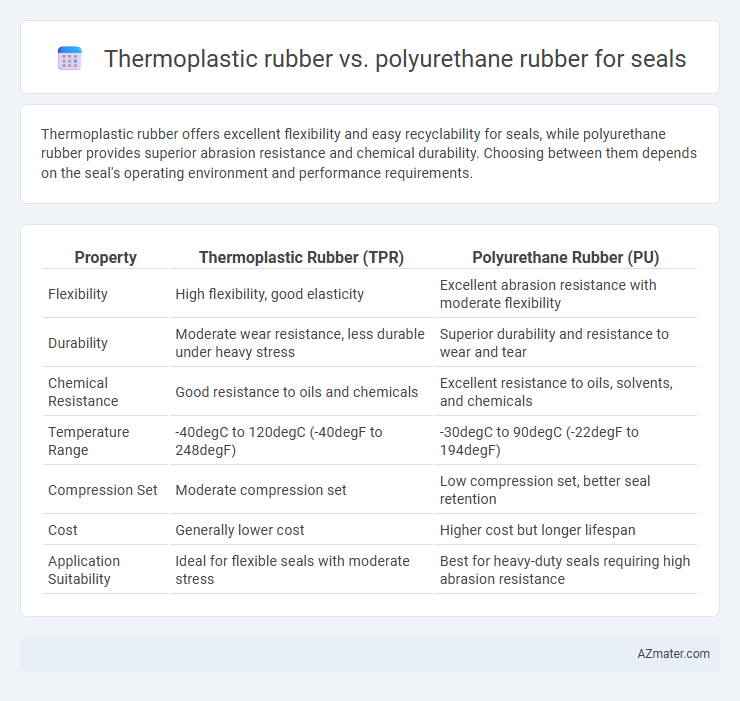
Thermoplastic rubber offers excellent flexibility and easy recyclability for seals, while polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and chemical durability. Choosing between them depends on the seal's operating environment and performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good elasticity | Excellent abrasion resistance with moderate flexibility |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance, less durable under heavy stress | Superior durability and resistance to wear and tear |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -30degC to 90degC (-22degF to 194degF) |
| Compression Set | Moderate compression set | Low compression set, better seal retention |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost but longer lifespan |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for flexible seals with moderate stress | Best for heavy-duty seals requiring high abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Thermoplastic Rubber and Polyurethane Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the elasticity of rubber with the processability of plastics, making it ideal for seals requiring flexibility and ease of molding. Polyurethane rubber (PU) offers superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for seals exposed to harsh environments and heavy wear. Both materials provide excellent sealing capabilities, but TPR excels in flexibility while PU stands out for durability and resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) combines the elasticity of rubber with the recyclability of plastics, featuring a polymer blend of hard thermoplastic grains dispersed within a soft rubber matrix, primarily composed of styrenic block copolymers or olefin-based copolymers. Polyurethane rubber (PUR), on the other hand, is a segmented polymer consisting of alternating hard and soft segments derived from isocyanates and polyols, offering superior chemical resistance and mechanical toughness due to its urethane linkages. The chemical structure of PUR provides enhanced abrasion resistance and elasticity retention under stress, whereas TPR's phase-separated morphology allows for easier processing and thermoforming in seal manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility and good abrasion resistance, whereas polyurethane rubber demonstrates superior tensile strength and enhanced tear resistance, making it more durable under high-stress sealing applications. Polyurethane seals typically exhibit higher hardness and better compression set, ensuring longer lifespan and maintaining effective sealing under heavy mechanical loads. Conversely, thermoplastic rubber seals provide better elasticity and resilience for dynamic or low-load environments, making material selection critical based on specific mechanical performance requirements.
Flexibility and Elasticity for Sealing
Thermoplastic rubber offers superior flexibility with excellent elastic recovery, making it ideal for dynamic sealing applications requiring frequent compression and decompression cycles. Polyurethane rubber provides higher elasticity combined with exceptional abrasion resistance, resulting in seals that maintain tightness under mechanical stress and deformation. Choosing between them depends on the sealing environment: thermoplastic rubber excels in moderate temperature flexibility, while polyurethane rubber performs better under heavy-duty wear and high-stress conditions.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate resistance to chemicals and oils, making it suitable for seals exposed to light hydrocarbons and diluted acids. Polyurethane rubber (PU), however, exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of oils, greases, and solvents, sustaining durability in aggressive chemical environments. Selecting PU seals ensures enhanced longevity and performance in applications requiring robust chemical and oil resistance.
Temperature Tolerance and Stability
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) typically offers temperature tolerance up to around 120degC, making it suitable for moderate thermal environments, while polyurethane rubber excels with stability and performance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 80degC, sometimes extending up to 120degC depending on formulation. Polyurethane exhibits superior abrasion resistance and retains mechanical properties under cyclic temperatures, enhancing seal durability in dynamic applications. Thermoplastic rubber provides easier processing and flexible softness but may degrade faster at elevated temperatures compared to polyurethane's enhanced thermal and chemical stability in seals.
Durability and Lifespan in Sealing Applications
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers moderate durability with good flexibility and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for seals exposed to dynamic stresses and moderate environmental wear. Polyurethane rubber excels in durability and lifespan due to its superior resistance to oil, chemicals, and abrasion, providing long-term sealing performance in harsh conditions and heavy-duty industrial applications. For sealing applications requiring prolonged service life and high wear resistance, polyurethane rubber typically outperforms thermoplastic rubber, reducing maintenance frequency and downtime.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Thermoplastic rubber offers lower production costs and easier processability compared to polyurethane rubber, benefiting high-volume seal manufacturing with faster cycle times and reduced tooling expenses. Polyurethane rubber, while more expensive, provides superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for seals in demanding applications requiring durability and chemical resistance. Manufacturers must balance initial material costs with performance requirements, selecting thermoplastic rubber for cost-effective, high-speed production and polyurethane rubber for enhanced longevity and resilience.
Typical Applications in Sealing Industries
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) is commonly used in seals for automotive weatherstripping, household appliances, and medical devices owing to its flexibility and ease of processing. Polyurethane rubber (PU) excels in heavy-duty sealing applications such as hydraulic cylinder seals, industrial machinery gaskets, and oil seals due to its superior abrasion resistance and high tensile strength. Both materials offer distinct advantages in sealing industries, with TPR favored for lightweight, low-stress environments and PU preferred for demanding, high-performance sealing solutions.
Choosing the Optimal Seal Material: Thermoplastic Rubber vs Polyurethane Rubber
Thermoplastic rubber (TPR) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of processing, making it ideal for seals exposed to moderate abrasion and varied temperatures. Polyurethane rubber excels in high abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and durability under heavy mechanical stress, suitable for demanding sealing applications. Selecting the optimal seal material depends on the specific operating conditions, such as exposure to chemicals, temperature range, and mechanical wear, ensuring enhanced performance and longevity of the seal.
Infographic: Thermoplastic rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com