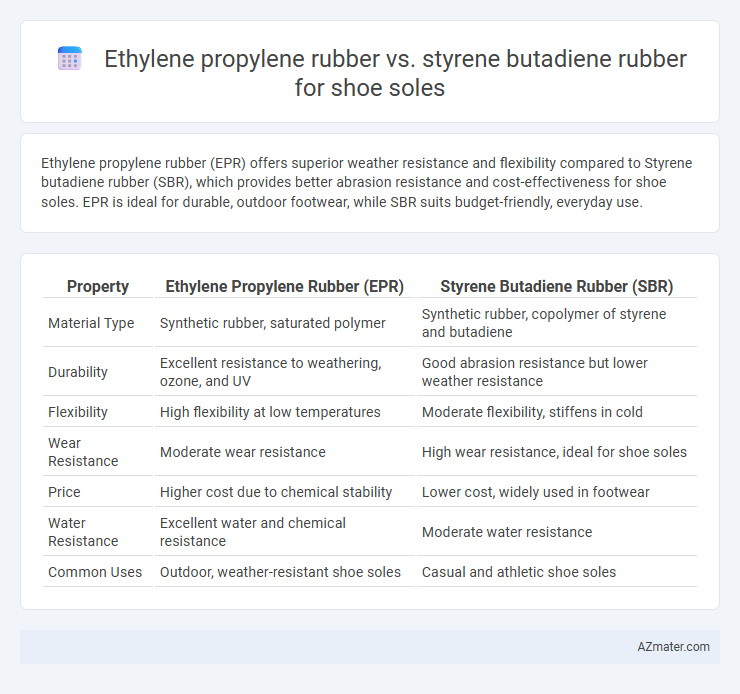
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior weather resistance and flexibility compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), which provides better abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness for shoe soles. EPR is ideal for durable, outdoor footwear, while SBR suits budget-friendly, everyday use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic rubber, saturated polymer | Synthetic rubber, copolymer of styrene and butadiene |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV | Good abrasion resistance but lower weather resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility at low temperatures | Moderate flexibility, stiffens in cold |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | High wear resistance, ideal for shoe soles |
| Price | Higher cost due to chemical stability | Lower cost, widely used in footwear |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water and chemical resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Common Uses | Outdoor, weather-resistant shoe soles | Casual and athletic shoe soles |
Introduction to Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR) is a synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for durable shoe soles that require flexibility and long-term performance. Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and good aging stability, commonly used in shoe soles that demand high wear resistance and cost-effectiveness. Both EPR and SBR provide distinct advantages in shoe manufacturing, with EPR excelling in environmental resistance and SBR in durability against physical wear.
Key Properties of EPR for Shoe Soles
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to heat, oxidation, and weathering, making it highly durable for shoe sole applications. Its superior flexibility and resistance to abrasion enhance comfort and longevity under various environmental conditions. EPR's low-temperature performance and chemical stability provide advantages over styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), especially in extreme climates and harsh usage scenarios.
Key Properties of SBR for Shoe Soles
Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is favored for shoe soles due to its excellent abrasion resistance, cushioning, and water resistance, making it ideal for durable and comfortable footwear. Its high tensile strength and good aging properties under UV light and oxygen exposure ensure long-lasting performance. Compared to ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), SBR offers superior grip and resilience, which are critical for safety and wear in various walking conditions.
Durability Comparison: EPR vs SBR
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure compared to Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), making EPR soles more durable in outdoor conditions. SBR tends to have better abrasion resistance and traction, but its wear life degrades faster under prolonged environmental stress. In terms of overall durability for shoe soles, EPR is preferred for applications requiring long-term resilience, while SBR is suitable for cost-effective, moderate-use footwear.
Flexibility and Comfort in Shoe Applications
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior flexibility and excellent resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for shoe soles that require durability and prolonged comfort. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides moderate flexibility but excels in abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in athletic and casual footwear. For optimal shoe sole performance, EPR enhances cushioning and flexibility, whereas SBR emphasizes toughness and wear resistance, influencing comfort during extended use.
Resistance to Abrasion and Wear
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers excellent resistance to abrasion and wear, making it a durable choice for shoe soles subjected to rough surfaces and continuous friction. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) also provides good abrasion resistance but typically exhibits faster wear under heavy mechanical stress compared to EPR. The superior aging stability and weather resistance of EPR contribute to longer-lasting soles, especially in demanding outdoor conditions.
Weather and Chemical Resistance Differences
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior weather resistance, with excellent stability against ozone, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh environmental conditions. In contrast, Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) exhibits moderate resistance to weathering but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV and ozone exposure, limiting its durability in outdoor use. Chemically, EPR resists a broader range of acids, alkalis, and polar solvents, while SBR is more susceptible to swelling and breakdown when in contact with oils and certain chemicals.
Cost Analysis: EPR vs SBR Shoe Soles
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) typically incurs higher raw material costs compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), influencing overall production expenses for shoe soles. While EPR offers superior weather resistance and flexibility, SBR remains the more cost-effective option due to its lower price and adequate abrasion resistance for common footwear applications. Manufacturers often balance the increased durability and performance benefits of EPR against the budget-friendly nature of SBR when selecting materials for shoe sole production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) is favored for shoe soles due to its superior ozone and weather resistance, enabling longer product life and reducing waste. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), derived from petroleum, has higher landfill impact and lower biodegradability, contributing to greater environmental pollution. EPR's stability and potential for recycling enhance its sustainability profile over SBR in footwear applications.
Selecting the Optimal Rubber for Shoe Soles
Ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) offers superior weather resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to harsh environmental conditions and prolonged wear. Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, benefiting applications where high durability and budget constraints are priorities. Selecting the optimal rubber for shoe soles requires balancing EPR's resilience and flexibility with SBR's toughness and affordability to meet specific performance requirements.
Infographic: Ethylene propylene rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com