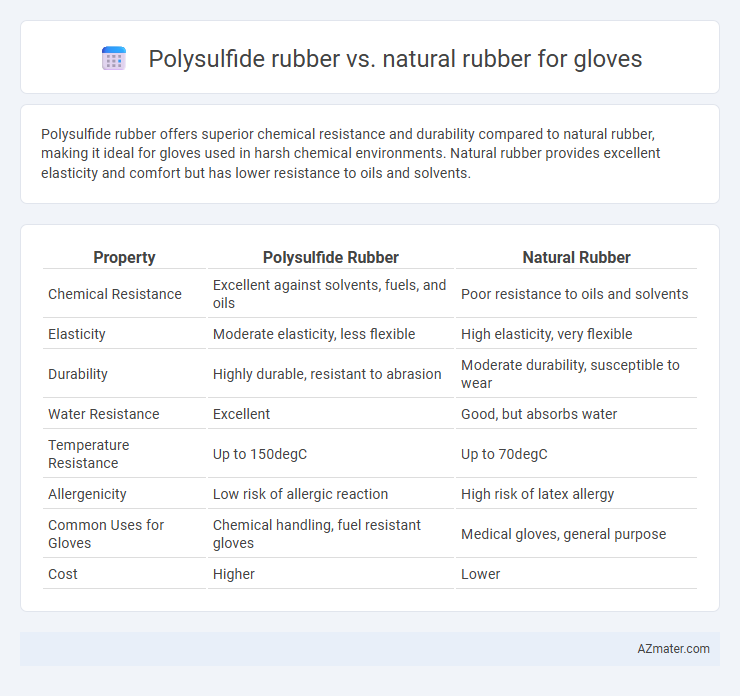
Polysulfide rubber offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to natural rubber, making it ideal for gloves used in harsh chemical environments. Natural rubber provides excellent elasticity and comfort but has lower resistance to oils and solvents.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfide Rubber | Natural Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against solvents, fuels, and oils | Poor resistance to oils and solvents |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, less flexible | High elasticity, very flexible |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to abrasion | Moderate durability, susceptible to wear |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good, but absorbs water |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 70degC |
| Allergenicity | Low risk of allergic reaction | High risk of latex allergy |
| Common Uses for Gloves | Chemical handling, fuel resistant gloves | Medical gloves, general purpose |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Polysulfide and Natural Rubber
Polysulfide rubber, a synthetic elastomer known for its superior chemical resistance and durability, is commonly used in protective gloves designed for harsh chemical environments. Natural rubber, derived from latex of rubber trees, offers excellent elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, making it ideal for general-purpose and medical gloves. The choice between polysulfide and natural rubber gloves depends on specific requirements such as chemical exposure, flexibility, and comfort.
Composition and Chemical Structure
Polysulfide rubber consists of long chains linked by sulfur-sulfur bonds, providing excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for protective gloves used in harsh chemical environments. Natural rubber is primarily composed of cis-1,4-polyisoprene, a hydrocarbon polymer offering superior elasticity and tensile strength but lower resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals compared to polysulfide rubber. The sulfide linkages in polysulfide rubber enhance durability against degradation, whereas natural rubber's unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds are more susceptible to oxidation and chemical attack.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polysulfide rubber gloves undergo a vulcanization process involving sulfur cross-linking, enhancing chemical resistance and flexibility, while natural rubber gloves are produced through latex harvesting followed by coagulation and sulfur vulcanization for elasticity and strength. Polysulfide rubber manufacturing requires precise control of sulfur content and heat application to form durable polysulfide bonds, contrasting with the more straightforward latex processing and curing used for natural rubber. These process differences result in polysulfide rubber gloves offering superior resistance to solvents and oils compared to natural rubber gloves, which excel in elasticity and tactile sensitivity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfide rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to natural rubber, making it an ideal choice for gloves used in harsh industrial environments. Its chemical resistance and resistance to wear and tear extend glove lifespan, especially under exposure to oils, solvents, and extreme temperatures. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and comfort but tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress and chemical exposure, reducing its long-term durability.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polysulfide rubber gloves exhibit superior chemical resistance against solvents, oils, and acids due to their sulfur-based crosslinking, making them ideal for industrial and chemical handling applications. In contrast, natural rubber gloves offer excellent elasticity and comfort but have limited resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and strong oxidizing agents. This makes polysulfide rubber the preferred choice for environments requiring enhanced protection from aggressive chemicals.
Comfort and Flexibility in Gloves
Polysulfide rubber offers enhanced chemical resistance but generally exhibits lower flexibility and comfort compared to natural rubber gloves, which provide superior elasticity and softness, promoting prolonged wear without discomfort. Natural rubber gloves conform better to hand contours, allowing for greater dexterity and breathability, essential for tasks requiring fine motor skills. Comfort in gloves is significantly influenced by the material's stretchability and tactile sensitivity, areas where natural rubber consistently outperforms polysulfide rubber.
Allergenicity and Skin Reactions
Polysulfide rubber gloves exhibit lower allergenicity compared to natural rubber gloves, as polysulfide materials lack the latex proteins responsible for Type I allergic reactions. Natural rubber gloves often trigger skin sensitization and irritant contact dermatitis due to residual latex proteins and added chemicals like accelerators. Using polysulfide rubber gloves minimizes the risk of Type I latex allergy and reduces the incidence of skin reactions in sensitive individuals.
Cost and Availability
Polysulfide rubber gloves generally offer lower material costs due to synthetic production methods, making them more affordable than natural rubber gloves, which depend on fluctuating latex harvests. Availability of polysulfide rubber is consistent year-round owing to industrial manufacturing, while natural rubber supply can be impacted by seasonal variations and agricultural factors. Cost-efficiency and steady supply make polysulfide rubber gloves a preferred choice in large-scale industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polysulfide rubber used in gloves exhibits higher chemical resistance but suffers from poor biodegradability, leading to long-term environmental persistence and increased landfill burden. Natural rubber gloves, derived from renewable latex sources, offer superior biodegradability and lower ecological footprint due to their organic, plant-based origins. The environmental impact of natural rubber gloves is significantly reduced by sustainable harvesting practices and their ability to decompose faster in natural settings compared to synthetic polysulfide alternatives.
Best Applications for Each Rubber Type
Polysulfide rubber excels in chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for gloves used in harsh industrial environments and handling solvents or acids. Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and comfort, preferred for medical gloves, surgical applications, and tasks requiring high tactile sensitivity. Choosing between polysulfide and natural rubber depends on the balance of chemical protection versus flexibility and comfort needed for specific glove applications.
Infographic: Polysulfide rubber vs Natural rubber for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com