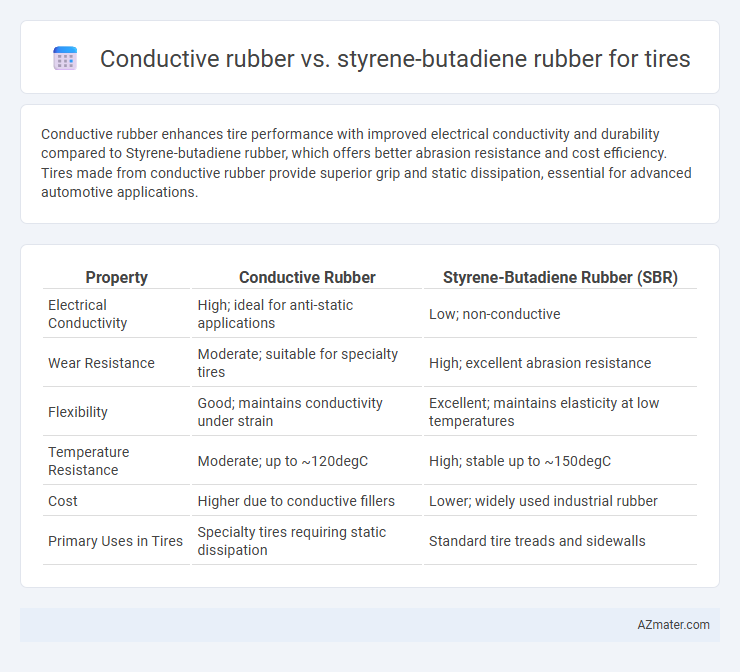
Conductive rubber enhances tire performance with improved electrical conductivity and durability compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber, which offers better abrasion resistance and cost efficiency. Tires made from conductive rubber provide superior grip and static dissipation, essential for advanced automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Rubber | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High; ideal for anti-static applications | Low; non-conductive |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate; suitable for specialty tires | High; excellent abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Good; maintains conductivity under strain | Excellent; maintains elasticity at low temperatures |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate; up to ~120degC | High; stable up to ~150degC |
| Cost | Higher due to conductive fillers | Lower; widely used industrial rubber |
| Primary Uses in Tires | Specialty tires requiring static dissipation | Standard tire treads and sidewalls |
Introduction to Rubber Types in Tire Manufacturing
Conductive rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) serve distinct roles in tire manufacturing due to their unique properties. Conductive rubber is primarily used for its ability to dissipate static electricity, enhancing safety and performance in tires for electric vehicles. SBR offers exceptional abrasion resistance and durability, making it the most common choice for passenger car tire treads and sidewalls.
What is Conductive Rubber?
Conductive rubber is a type of elastomer infused with conductive fillers such as carbon black, metal particles, or graphene to enhance electrical conductivity while maintaining flexibility. Compared to Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which is primarily valued for its abrasion resistance and durability in tire manufacturing, conductive rubber provides improved static dissipation and electromagnetic interference shielding properties. This makes conductive rubber especially suitable for applications requiring antistatic performance and electrical grounding in tires.
Overview of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a synthetic rubber widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, making it ideal for achieving durable tire treads. Compared to conductive rubber, SBR offers superior mechanical strength and heat resistance, essential for high-performance tires subjected to continuous friction and load. The polymer's copolymer structure of styrene and butadiene provides a balance of elasticity and toughness, enhancing tire lifespan and traction on both dry and wet surfaces.
Electrical Conductivity: Why It Matters in Tires
Conductive rubber significantly improves electrical conductivity in tires, enhancing static electricity dissipation and reducing the risk of sparks during vehicle operation. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), with its low inherent conductivity, relies on fillers like carbon black to achieve necessary conductive properties but often falls short in maintaining consistent electrical performance. Effective electrical conductivity in tires is crucial for safety in dry and wet conditions, ensuring better traction control and preventing electrical buildup that could damage vehicle sensors or trigger fire hazards.
Performance Characteristics: Conductive Rubber vs. SBR
Conductive rubber offers superior electrical conductivity and enhanced abrasion resistance compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), making it ideal for tires requiring anti-static or electromagnetic interference dissipation. SBR exhibits excellent wear resistance, aging stability, and good performance in wet conditions, contributing to longer tread life and reliable traction. While conductive rubber improves safety in electronic-sensitive environments, SBR remains the preferred choice for general tire durability and cost-effectiveness.
Durability & Wear Resistance Comparison
Conductive rubber exhibits superior wear resistance due to its unique composition, enhancing tire durability under high-stress conditions. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers good abrasion resistance and flexibility but typically wears faster in harsh environments compared to conductive rubber. Tires utilizing conductive rubber maintain longer tread life and improved performance in demanding applications due to enhanced durability characteristics.
Cost Efficiency & Manufacturing Considerations
Conductive rubber offers enhanced electrical properties but generally incurs higher material and processing costs compared to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), which remains the industry standard for tire manufacturing due to its cost efficiency and proven performance. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability at a lower price point, enabling large-scale production with established processing techniques. Manufacturing considerations favor SBR for its compatibility with current mixing, extrusion, and curing methods, while conductive rubber often requires specialized handling and may increase production complexity and expenses.
Environmental Impact of Conductive Rubber and SBR
Conductive rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) differ significantly in their environmental impact, with conductive rubber often incorporating conductive fillers that may complicate recycling and increase ecological footprint due to resource-intensive production processes. SBR, widely used in tire manufacturing, offers better recyclability and lower environmental toxicity but involves the use of petrochemical derivatives contributing to non-renewable resource depletion. Evaluating the life cycle assessment reveals that SBR tires generally have a reduced global warming potential compared to conductive rubber variants, making them more environmentally favorable in sustainable tire applications.
Application Suitability in Modern Tires
Conductive rubber, often formulated with carbon black or metal fillers, excels in antistatic properties, making it suitable for tires requiring improved electrical conductivity and reduced static buildup. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers superior abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it the preferred choice for the tread and sidewall of modern passenger car tires due to enhanced durability and traction. Combining conductive rubber layers with SBR components in tire construction enhances overall performance by balancing electrical conductivity with mechanical strength for applications like electric vehicles and high-performance tires.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Tire Performance
Selecting between conductive rubber and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) for tire manufacturing hinges on specific performance requirements. Conductive rubber excels in dissipating static electricity and improving traction in wet or icy conditions due to its enhanced electrical conductivity. Styrene-butadiene rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and durability, making it ideal for general-purpose tires that demand extended tread life and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Conductive rubber vs Styrene-butadiene rubber for Tire
 azmater.com
azmater.com