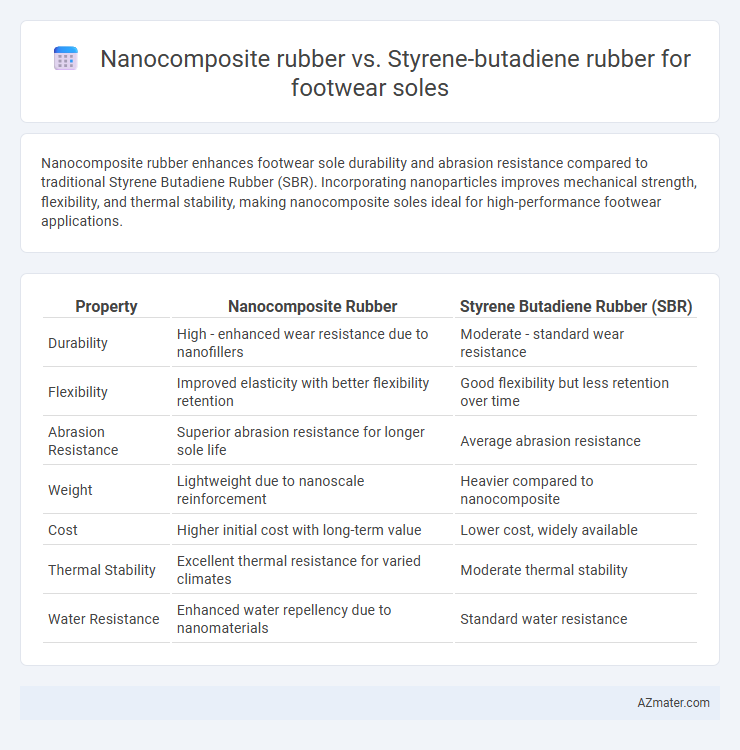
Nanocomposite rubber enhances footwear sole durability and abrasion resistance compared to traditional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). Incorporating nanoparticles improves mechanical strength, flexibility, and thermal stability, making nanocomposite soles ideal for high-performance footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite Rubber | Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High - enhanced wear resistance due to nanofillers | Moderate - standard wear resistance |
| Flexibility | Improved elasticity with better flexibility retention | Good flexibility but less retention over time |
| Abrasion Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance for longer sole life | Average abrasion resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight due to nanoscale reinforcement | Heavier compared to nanocomposite |
| Cost | Higher initial cost with long-term value | Lower cost, widely available |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal resistance for varied climates | Moderate thermal stability |
| Water Resistance | Enhanced water repellency due to nanomaterials | Standard water resistance |
Introduction to Footwear Sole Materials
Footwear sole materials are critical for comfort, durability, and performance, with nanocomposite rubber and styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) playing key roles in modern manufacturing. Nanocomposite rubber incorporates nanoscale fillers such as silica or clay, enhancing mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability compared to traditional SBR. SBR remains popular due to its excellent wear resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, but nanocomposite rubber offers superior longevity and impact absorption, making it ideal for high-performance footwear soles.
Overview of Nanocomposite Rubber
Nanocomposite rubber integrates nanoscale fillers such as silica or carbon nanotubes into a polymer matrix, enhancing mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability compared to conventional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). These nanofillers significantly improve the durability and elasticity of footwear soles, offering superior performance in wear resistance and traction. The advanced dispersion and interaction of nanoparticles within the rubber matrix result in optimized material properties, making nanocomposite rubber a promising alternative to traditional SBR in high-performance footwear applications.
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR): Key Characteristics
Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is widely used in footwear soles due to its excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Its polymer composition enhances durability and provides good aging stability against heat and ozone, critical for long-lasting shoe performance. Compared to nanocomposite rubber, SBR offers predictable mechanical properties and easier processability, making it a preferred choice for mass production in footwear manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) in footwear sole applications due to its enhanced reinforcement from nanoscale fillers like silica or carbon nanotubes. These nanofillers improve tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and tear resistance, resulting in more durable and long-lasting soles. In contrast, SBR offers moderate mechanical properties but lacks the reinforcement efficiency and wear resistance provided by nanocomposite technologies.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Nanocomposite rubber, reinforced with nanoparticles such as silica or clay, significantly enhances wear and abrasion resistance compared to traditional Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) used in footwear soles. The incorporation of nanofillers improves the mechanical properties by increasing hardness and reducing material degradation under repetitive friction. This results in longer-lasting soles with superior performance in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Comfort Analysis
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits superior flexibility and comfort compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in footwear soles due to its enhanced molecular structure and filler dispersion, which improves elasticity and shock absorption. The integration of nanomaterials in nanocomposite rubber increases durability while maintaining softness, leading to better foot cushioning and reduced fatigue during prolonged wear. SBR soles, although cost-effective and abrasion-resistant, typically offer less adaptability to dynamic foot movements, resulting in comparatively lower comfort levels.
Durability and Lifespan in Footwear
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits enhanced durability and a significantly longer lifespan compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in footwear soles due to its superior wear resistance and improved mechanical strength. The incorporation of nanoscale fillers in nanocomposite rubber increases abrasion resistance and reduces degradation under repetitive stress, extending the sole's functional life. In contrast, SBR, while cost-effective and commonly used, tends to exhibit faster wear and lower fatigue resistance, limiting sole durability in high-performance footwear applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite rubber used in footwear soles offers enhanced durability and reduced material consumption compared to conventional Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR), leading to lower carbon emissions throughout the product lifecycle. The incorporation of nanomaterials improves biodegradability and facilitates recycling processes, minimizing landfill waste and environmental pollution. SBR soles, while cost-effective, are derived from petrochemicals with higher energy-intensive manufacturing and slower degradation rates, posing greater sustainability challenges.
Cost Efficiency and Production Considerations
Nanocomposite rubber offers enhanced durability and abrasion resistance for footwear soles, often leading to longer product life and reduced replacement costs compared to Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). While the initial material cost of nanocomposite rubber can be higher, lower wear rates and improved performance in extreme conditions can result in better cost efficiency over the product lifecycle. Production considerations for nanocomposite rubber include the need for specialized mixing and processing equipment to ensure optimal dispersion of nanoparticles, whereas SBR benefits from well-established manufacturing processes and broader availability.
Future Trends in Footwear Sole Materials
Nanocomposite rubber exhibits enhanced durability, abrasion resistance, and flexibility compared to traditional styrene butadiene rubber, making it a promising material for future footwear sole innovations. Advances in nanotechnology enable the incorporation of nanoparticles that improve mechanical strength and thermal stability, aligning with the increasing demand for high-performance, sustainable footwear materials. Emerging trends indicate nanocomposite formulations will drive the development of lighter, more resilient soles with superior traction and environmental benefits over conventional styrene butadiene rubber soles.
Infographic: Nanocomposite rubber vs Styrene butadiene rubber for Footwear sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com