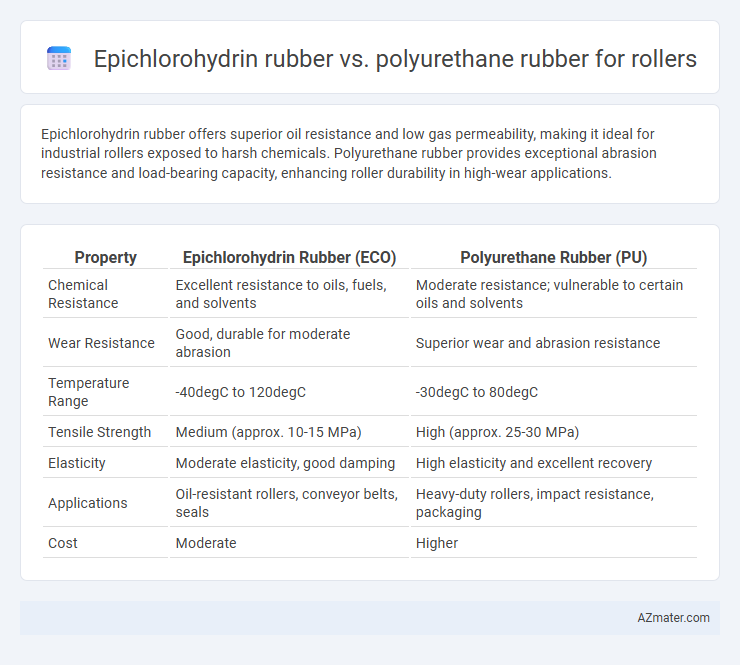
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior oil resistance and low gas permeability, making it ideal for industrial rollers exposed to harsh chemicals. Polyurethane rubber provides exceptional abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, enhancing roller durability in high-wear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epichlorohydrin Rubber (ECO) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Moderate resistance; vulnerable to certain oils and solvents |
| Wear Resistance | Good, durable for moderate abrasion | Superior wear and abrasion resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 80degC |
| Tensile Strength | Medium (approx. 10-15 MPa) | High (approx. 25-30 MPa) |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity, good damping | High elasticity and excellent recovery |
| Applications | Oil-resistant rollers, conveyor belts, seals | Heavy-duty rollers, impact resistance, packaging |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Roller Materials: Epichlorohydrin vs Polyurethane Rubber
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent oil, chemical, and weather resistance, making it ideal for rollers used in harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance, high load-bearing capacity, and outstanding mechanical strength, preferred for applications requiring durability and resilience. Selecting between epichlorohydrin and polyurethane rollers depends on specific operational needs such as exposure to chemicals or mechanical wear.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) features a saturated polymer backbone derived from epichlorohydrin and ethylene oxide, characterized by excellent resistance to ozone, oil, and chemicals due to its polar ether linkages and chloromethyl groups. Polyurethane rubber consists of segmented copolymers formed by the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, exhibiting a microphase-separated structure with hard urethane domains providing high abrasion resistance and mechanical strength. The inherent chemical structure of Epichlorohydrin lends it superior resistance to polar solvents and low gas permeability, while Polyurethane's diverse compositional tunability allows for enhanced elasticity and wear resistance in roller applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, with moderate tensile strength and good flexibility, making it suitable for rollers in harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and high flexibility, ensuring enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity for rollers under heavy mechanical stress. The choice between the two depends on the specific operational demands: Epichlorohydrin excels in chemical resistance, while Polyurethane provides better overall mechanical performance and wear resistance.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to a wide range of oils, fats, and chemicals, making it ideal for environments with exposure to mineral oils and solvents. Polyurethane rubber excels in resisting abrasion and tear but has limited chemical resistance, particularly against strong acids and hydrocarbons. For rollers used in chemical processing or oil handling, Epichlorohydrin rubber provides enhanced durability and longevity under harsh chemical exposure.
Temperature Stability and Environmental Performance
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent temperature stability, maintaining mechanical properties between -40degC and 120degC, making it suitable for applications involving moderate thermal exposure. Polyurethane rubber excels in temperature resistance with a broader range from -50degC to 140degC and superior wear resistance, enhancing roller durability under varying thermal conditions. Environmentally, epichlorohydrin is more resistant to oils and chemicals but has lower biodegradability, while polyurethane is more eco-friendly due to better recyclability and lower environmental impact during production.
Wear, Abrasion, and Fatigue Resistance
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior resistance to wear and abrasion due to its excellent chemical and oil resistance, making it ideal for rollers subjected to harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber outperforms epichlorohydrin in fatigue resistance, offering exceptional durability and resilience under repetitive stress and mechanical strain. Selecting between the two depends on specific roller application requirements, with epichlorohydrin favored for chemical exposure and polyurethane preferred for high-load cyclic conditions.
Adhesion to Metal Cores and Manufacturing Considerations
Epichlorohydrin rubber exhibits superior adhesion to metal cores compared to polyurethane rubber, largely due to its polar chemical structure which promotes strong interfacial bonding. Manufacturing considerations for epichlorohydrin rubber involve controlled vulcanization processes to optimize crosslink density and adhesion durability on metal surfaces. In contrast, polyurethane rubber requires specialized surface treatments and adhesives to achieve comparable bonding, impacting overall production complexity and cost-effectiveness in roller applications.
Cost Analysis: Material and Maintenance Expenses
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers lower initial material costs compared to polyurethane rubber, making it a budget-friendly option for roller applications. Maintenance expenses for Epichlorohydrin tend to be higher due to its susceptibility to wear and chemical degradation, whereas polyurethane rubber provides superior durability and resistance, reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals polyurethane rubber's higher upfront investment can be offset by its extended service life and lower repair frequency.
Application Suitability: Industry-Specific Recommendations
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for applications in the automotive, printing, and packaging industries where oil and fuel exposure is prevalent. Polyurethane rubber excels in abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, which suits heavy-duty rollers in material handling, conveyor systems, and industrial machinery. Selecting Epichlorohydrin rubber is recommended for environments requiring excellent chemical resistance, while Polyurethane rubber is preferable for high-wear and impact-prone roller applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rubber for Roller Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber offers excellent chemical resistance and oil impermeability, making it ideal for rollers exposed to harsh chemicals and oils. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suited for heavy-duty roller applications requiring durability and mechanical strength. Selecting the right rubber depends on the roller's operating environment, with epichlorohydrin preferred for chemical exposure and polyurethane favored for wear resistance and mechanical stress.
Infographic: Epichlorohydrin rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com